Location
2D/3D• Location[point] returns the global coordinates, {x, y} or {x, y, z}, of the specified point.
• Location[axis] returns the global coordinates of the origin of the specified axis.
• Location[bnum, lpnt] is interpreted as Location[Point[bnum, lpnt]].
• Location[bnum] returns the location and angular orientation coordinates of body bnum in a flat list.
• The bnum argument can take any of the forms accepted by Loads to obtain the location coordinates of multiple bodies.
• Location is also a setting for the Solution option for several Mech functions.
• Solution->Location causes such functions to seek a solution for only the location of the current model. • Location[All] returns the entire vector of dependent variables.
• To use Location[bnum], bnum must be the number of a body in the current model.
• In Modeler2D, the behavior of Location[bnum] varies depending on whether the current solution method is Angular or Euler. With the Euler solution method, Location[2] returns {X2, Y2, Ei2, Ej2}, while with the Angular solution method, Location[2] returns {X2, Y2, 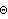 2}. 2}.
• Modeler3D always represents angular orientation with four Euler parameters.
• The alternatives to the Location setting for the Solution option are Velocity, Acceleration, Static, Kinematic, and Dynamic.
• See also: Rotation, SolveMech, SetCouple. Further Examples Load the Modeler2D package and define a simple model. Here is an expression representing the location vector of a point at {3, 5} on the crank.
Out[2]= | 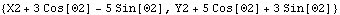 |
Here are the variables used to represent the location and angular orientation of the crank and link bodies.
Out[3]= | 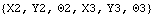 |
Here is a solution to the current model with only the location terms included.
Out[4]= | 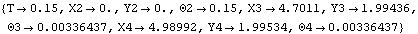 |
Here is the numerical value of the location of a point at {3, 0} on the crank.
Out[5]= | 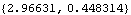 |
See HelpModel2D.
|