BarnesG[z]
gives the Barnes G-function ![]() .
.


BarnesG
BarnesG[z]
gives the Barnes G-function ![]() .
.
Details

- BarnesG is also known as the double gamma function.
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numeric manipulation.
- The Barnes G-function is defined as
![TemplateBox[{n}, BarnesG]=product_(k=1)^(n-1)TemplateBox[{k}, Gamma] TemplateBox[{n}, BarnesG]=product_(k=1)^(n-1)TemplateBox[{k}, Gamma]](Files/BarnesG.en/2.png) for positive integers
for positive integers 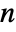 and is otherwise defined as
and is otherwise defined as ![TemplateBox[{z}, BarnesG]=(2 pi)^(z/2) exp((z-1) (TemplateBox[{z}, LogGamma]-z/2)-TemplateBox[{{-, 2}, z}, PolyGamma2]) TemplateBox[{z}, BarnesG]=(2 pi)^(z/2) exp((z-1) (TemplateBox[{z}, LogGamma]-z/2)-TemplateBox[{{-, 2}, z}, PolyGamma2])](Files/BarnesG.en/4.png) .
. - The Barnes G-function satisfies the functional equation
![TemplateBox[{{z, +, 1}}, BarnesG]=TemplateBox[{z}, BarnesG] TemplateBox[{z}, Gamma] TemplateBox[{{z, +, 1}}, BarnesG]=TemplateBox[{z}, BarnesG] TemplateBox[{z}, Gamma]](Files/BarnesG.en/5.png) .
. - BarnesG[z] is an entire function of z with no branch cut discontinuities.
- For certain special arguments, BarnesG automatically evaluates to exact values.
- BarnesG can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- BarnesG automatically threads over lists.
- BarnesG can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Plot over a subset of the reals:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Series expansion at the origin:
Series expansion at Infinity:
Scope (27)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix BarnesG function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (4)
Visualization (2)
Function Properties (10)
BarnesG is defined for all real and complex values:
Approximate function range of BarnesG:
BarnesG is an analytic function of x:
BarnesG is neither non-increasing nor non-decreasing:
BarnesG is not injective:
BarnesG is surjective:
BarnesG is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
BarnesG has no singularities or discontinuities:
BarnesG is neither convex nor concave:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Differentiation (2)
Applications (5)
Integer values of BarnesG are related to the superfactorial:
BarnesG may be generated by symbolic solvers:
Compute the number of bits needed to store a large integer:
For ![]() an odd prime, a generalization of Wilson's theorem states that
an odd prime, a generalization of Wilson's theorem states that ![]() . Verify for the first few odd primes:
. Verify for the first few odd primes:
Define a Cauchy matrix constructed from the first ![]() positive integers and an integer shift
positive integers and an integer shift ![]() :
:
Show the Cauchy matrix for arbitrary ![]() :
:
The determinant of this Cauchy matrix can be expressed in terms of BarnesG. Verify with a specific value of ![]() for the first few cases:
for the first few cases:
Properties & Relations (2)
Related Guides
Related Links
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), BarnesG, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BarnesG.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "BarnesG." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BarnesG.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). BarnesG. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BarnesG.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_barnesg, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BarnesG}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BarnesG.html}", note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_barnesg, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BarnesG}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BarnesG.html}, note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}