BioMoleculeAlign[ref,biomol]
returns a copy of biomol that has been aligned with reference biomolecule ref.
BioMoleculeAlign[ref,biomol,mapping]
uses the supplied mapping to determine which chains to include in the alignment.
BioMoleculeAlign[ref,biomol,mapping,prop]
aligns the biomolecules and returns the property prop of the alignment.


BioMoleculeAlign
BioMoleculeAlign[ref,biomol]
returns a copy of biomol that has been aligned with reference biomolecule ref.
BioMoleculeAlign[ref,biomol,mapping]
uses the supplied mapping to determine which chains to include in the alignment.
BioMoleculeAlign[ref,biomol,mapping,prop]
aligns the biomolecules and returns the property prop of the alignment.
Details

- BioMoleculeAlign is used to structurally align two peptide or nucleic acid molecules in space.
- BioMoleculeAlign uses a structure-based sequence-independent algorithm to align 3D structures by optimizing the template-modeling score objective function, or TM-score. It is often used when comparing a predicted structure to an experimentally determined structure.
- The TM-score for a given alignment is defined by
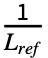 ∑i
∑i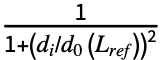 , where Lref is the length of the reference structure, di is the distance between backbone atoms for the ith aligned residue, and d0(Lref)=1.24
, where Lref is the length of the reference structure, di is the distance between backbone atoms for the ith aligned residue, and d0(Lref)=1.24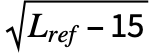 -1.8 is a distance scale to normalize the result. The alignment that maximizes the TM-score is returned.
-1.8 is a distance scale to normalize the result. The alignment that maximizes the TM-score is returned. - The TM-score lies between 0 and 1, where 1 indicates a perfect match. A TM-score below 0.2 is considered to be from random chance, while a score over 0.5 indicates a roughly the same folding.
- mapping should be either Automatic or a rule between chain labels in ref and biomol, e.g. {"A","B"}{"C","D"}. When a rule is given, only the specified chains will be considered in the alignment.
- prop can be one of the following:
-
"BioMolecule" the aligned biomolecule "Transformation" the transformation function used "RMSError" the alignment root mean squared error "TMScore" the template-modeling score for the alignment "AlignedResidueCount" the number of residues aligned "SequenceIdentity" fraction of aligned residues that are identitical "SequenceCharacterAlignment" a visual representation of the aligned sequences "TMScore" template-modeling score for the alignment All an Association with all properties
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Create a biomolecule based on an experimental crystal structure:
Now take the peptide sequence from that biomolecule and fold it:
The predicted structure's 3D coordinates are unrelated to the experimental structure:
Now align the predicted structure with the experimental structure and show them in 3D:
Find the RMSD error in the alignment:
Align a smaller peptide to a specific chain in a larger peptide:
Align the smaller peptide to a different chain:
BioMoleculeAlign can align peptides with dissimilar sequences but similar 3D structures:
The structures are aligned very well as shown by the low RMSD error and high TM-score:
Nearly all the amino acid residues participate in the alignment:
Scope (2)
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), BioMoleculeAlign, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BioMoleculeAlign.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "BioMoleculeAlign." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BioMoleculeAlign.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). BioMoleculeAlign. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BioMoleculeAlign.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_biomoleculealign, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BioMoleculeAlign}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BioMoleculeAlign.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_biomoleculealign, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BioMoleculeAlign}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BioMoleculeAlign.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-February-2026]}