ColorBalance[image]
adjusts the colors in image to achieve a balance that simulates the effect of neutral lighting.
ColorBalance[image,ref]
adjusts colors in image so that the reference color specified by ref is mapped to white.
ColorBalance[image,reftarget]
maps the reference color ref to target.


ColorBalance
ColorBalance[image]
adjusts the colors in image to achieve a balance that simulates the effect of neutral lighting.
ColorBalance[image,ref]
adjusts colors in image so that the reference color specified by ref is mapped to white.
ColorBalance[image,reftarget]
maps the reference color ref to target.
Details and Options

- ColorBalance is typically used for white or gray balancing, removing unrealistic color casts from images. This usually results in representing objects with neutral colors as gray.
- ColorBalance works with images with explicit color spaces. Images with ColorSpace->Automatic are converted to "RGB" or "Grayscale" before being adjusted.
- Either of the ref or target can be any of the following:
-
color explicit color whitepoint named white point as used as a setting for WhitePoint temperature color specified by a temperature {temperature,tint} color specified by a temperature and a tint {pos1,pos2,…} mean color at positions posi in the original image markerimage mean color sampled according to a marker image - The mean color above is computed in the Lab color space.
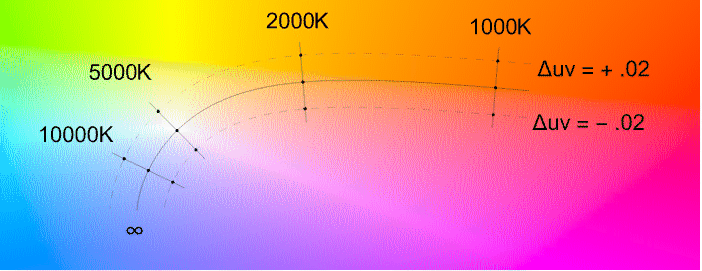
- The temperature can be specified as a value in Kelvin, typically in the range 2000 K and 20,000 K. The tint can be given in units of
 , typically in the range
, typically in the range  and
and  .
. - Temperature and tint can be visualized in the MacAdam chromaticity diagram below, where the curve corresponds to a radiating blackbody and tint adjustments are moves on isothermal lines, orthogonal to the temperature curve.
- ColorBalance takes a Method option. Possible settings include:
-
"GrayScaling" scaling the mean of the image "RGBScaling" scaling in the RGB space "LMSScaling" scaling in the LMS space "ChromaticityScaling" scaling of the chromaticities in the LMS space - With the method "LMSScaling", the scaling is performed using the Bradford transformation matrix to convert between XYZ and LMS.
- With a given {temperature,tint} pair, Method"ChromaticityScaling" is always used; otherwise, Method->"LMSScaling" is used. »

Examples
open all close allScope (8)
Specify the white reference using a specific color:
Specify the white region using a list of pixel positions:
Specify the white region using a marker image:
Specify the reference white temperature:
Specify the reference white temperature and tint:
Specify reference and target colors:
Perform a chromatic adaptation by specifying the reference and target WhitePoint:
Perform a chromatic adaptation by specifying the reference color and the target WhitePoint:
Options (6)
Method (6)
Use Method->"RGBScaling" to rescale the image in the RGB space:
When a strong color cast is present, scaling the pixels in the RGB space may not fix the color cast:
Use Method->"LMSScaling" to scale the pixels in the LMS space:
Use Method->"ChromaticityScaling" to make the average color neutral (a shade of gray):
Use "RGBScaling" with no reference or target colors:
This corresponds to transforming the max color value to 1 for each channel:
"ChromaticityScaling" typically creates a more balanced image:
Notice that it is computationally more expensive:
If the color is specified using temperature and tint, Method->"ChromaticityScaling" is used:
With no reference or target colors, available methods make assumptions about the image scene:
"RGBScaling" and "LMSScaling" assume that the image contains a white object:
"ChromaticityScaling" assumes that the average color is neutral (i.e. gray):
Applications (4)
Underwater images (2)
Correct a strong blue color cast, assuming there should be some white in the picture:
If white pixels are present already, Method"LMSScaling" will have little or no effect:
The default assumption of a neutral average color may yield extreme results:
Manually specify a region where the average color is computed:
Time of day (1)
Properties & Relations (2)
When an image has dark pixels, ImageAdjust yields a result similar to the "RGBscaling" method:
The chromatic mapping performed by ColorBalance is generally not invertible:
Possible Issues (1)
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2015), ColorBalance, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ColorBalance.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2015. "ColorBalance." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ColorBalance.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2015). ColorBalance. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ColorBalance.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_colorbalance, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ColorBalance}", year="2015", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ColorBalance.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_colorbalance, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ColorBalance}, year={2015}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ColorBalance.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}