FindMaximum[f,x]
searches for a local maximum in f, starting from an automatically selected point.
FindMaximum[f,{x,x0}]
searches for a local maximum in f, starting from the point x=x0.
FindMaximum[f,{{x,x0},{y,y0},…}]
searches for a local maximum in a function of several variables.
FindMaximum[{f,cons},{{x,x0},{y,y0},…}]
searches for a local maximum subject to the constraints cons.
FindMaximum[{f,cons},{x,y,…}]
starts from a point within the region defined by the constraints.


FindMaximum
FindMaximum[f,x]
searches for a local maximum in f, starting from an automatically selected point.
FindMaximum[f,{x,x0}]
searches for a local maximum in f, starting from the point x=x0.
FindMaximum[f,{{x,x0},{y,y0},…}]
searches for a local maximum in a function of several variables.
FindMaximum[{f,cons},{{x,x0},{y,y0},…}]
searches for a local maximum subject to the constraints cons.
FindMaximum[{f,cons},{x,y,…}]
starts from a point within the region defined by the constraints.
Details and Options


- FindMaximum returns a list of the form {fmax,{x->xmax}}, where fmax is the maximum value of f found, and xmax is the value of x for which it is found.
- If the starting point for a variable is given as a list, the values of the variable are taken to be lists with the same dimensions.
- The constraints cons can contain equations, inequalities or logical combinations of these.
- The constraints cons can be any logical combination of:
-
lhs==rhs equations lhs>rhs or lhs>=rhs inequalities {x,y,…}∈reg region specification - FindMaximum first localizes the values of all variables, then evaluates f with the variables being symbolic, and then repeatedly evaluates the result numerically.
- FindMaximum has attribute HoldAll, and effectively uses Block to localize variables.
- FindMaximum[f,{x,x0,x1}] searches for a local maximum in f using x0 and x1 as the first two values of x, avoiding the use of derivatives.
- FindMaximum[f,{x,x0,xmin,xmax}] searches for a local maximum, stopping the search if x ever gets outside the range xmin to xmax.
- Except when f and cons are both linear, the results found by FindMaximum may correspond only to local, but not global, maxima.
- By default, all variables are assumed to be real.
- For linear f and cons, x∈Integers can be used to specify that a variable can take on only integer values.
- The following options can be given:
-
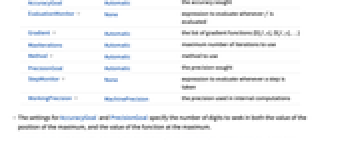
AccuracyGoal Automatic the accuracy sought EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate whenever f is evaluated Gradient Automatic the list of gradient functions {D[f,x],D[f,y],…} MaxIterations Automatic maximum number of iterations to use Method Automatic method to use PrecisionGoal Automatic the precision sought StepMonitor None expression to evaluate whenever a step is taken WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations - The settings for AccuracyGoal and PrecisionGoal specify the number of digits to seek in both the value of the position of the maximum, and the value of the function at the maximum.
- FindMaximum continues until either of the goals specified by AccuracyGoal or PrecisionGoal is achieved.
- Possible settings for Method include "ConjugateGradient", "PrincipalAxis", "LevenbergMarquardt", "Newton", and "QuasiNewton", with the default being Automatic.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (12)
With different starting points, get different local maxima:
Local maximum of a two-variable function starting from ![]() ,
, ![]() :
:
Local maximum constrained within a disk:
Starting point does not have to be provided:
For linear objective and constraints, integer constraints can be imposed:
Or constraints can be specified:
Find the maximum distance between points in two regions:
Find the maximum ![]() such that the rectangle and ellipse still intersect:
such that the rectangle and ellipse still intersect:
Find the maximum ![]() for which
for which ![]() contains the given three points:
contains the given three points:
Use ![]() to specify that
to specify that ![]() is a vector in
is a vector in ![]() :
:
Options (7)
AccuracyGoal & PrecisionGoal (2)
This enforces convergence criteria ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
This enforces convergence criteria ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Setting a high WorkingPrecision makes the process convergent:
Gradient (1)
Method (1)
In this case the default derivative-based methods have difficulties:
Direct search methods which do not require derivatives can be helpful in these cases:
NMaximize also uses a range of direct search methods:
StepMonitor (1)
Steps taken by FindMaximum in finding the maximum of a function:
WorkingPrecision (1)
Set the working precision to ![]() ; by default AccuracyGoal and PrecisionGoal are set to
; by default AccuracyGoal and PrecisionGoal are set to ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (2)
FindMaximum tries to find a local maximum; NMaximize attempts to find a global maximum:
Maximize finds a global maximum and can work in infinite precision:
FindMaximum gives both the value of the maximum and the maximizer point:
FindArgMax gives the location of the maximum:
FindMaxValue gives the value at the maximum:
Possible Issues (6)
With machine-precision arithmetic, even functions with smooth maxima may seem bumpy:
Going beyond machine precision often avoids such problems:
If the constraint region is empty, the algorithm will not converge:
If the maximum value is not finite, the algorithm will not converge:
Integer linear programming algorithm is only available for machine-number problems:
Sometimes providing a suitable starting point can help the algorithm to converge:
It can be time-consuming to compute functions symbolically:
Restricting the function definition prevents symbolic evaluation:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2003 (5.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2003), FindMaximum, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindMaximum.html (updated 2014).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2003. "FindMaximum." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2014. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindMaximum.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2003). FindMaximum. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindMaximum.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_findmaximum, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FindMaximum}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindMaximum.html}", note=[Accessed: 05-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_findmaximum, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FindMaximum}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindMaximum.html}, note=[Accessed: 05-February-2026]}