HistogramTransform
HistogramTransform[image]
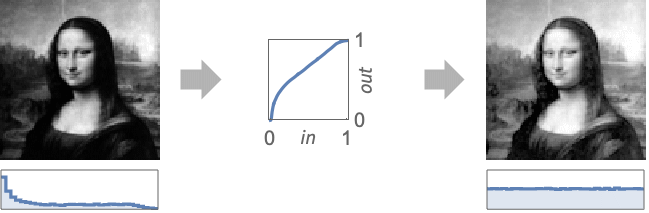
transforms pixel values of image so that its histogram is nearly flat.
HistogramTransform[image,ref]
modifies pixel values of image so that its histogram would have nearly the same distribution as ref.
HistogramTransform[image,ref,n]
uses n equally spaced quantiles.
HistogramTransform[{x1,x2,…},…]
transforms values xi.
Details
- HistogramTransform is a point operation that changes the shape of the image histogram. Histogram transformation is typically used for equalization or matching with a reference distribution.
- HistogramTransform[image] returns an image with an approximately flat histogram, effectively known as histogram equalization.
- HistogramTransform[image,ref] finds an interpolating function between the quantiles of image and ref and applies it to each pixel in image, effectively known as histogram matching.
- HistogramTransform works with 3D as well as 2D images, and also with lists of arbitrary rank datasets.
- HistogramTransform[image,…] returns an image of the same type as the input image.
- With multichannel images, HistogramTransform[image] operates separately on each channel.
- HistogramTransform[{data1,data2,…},…] transforms multiple datasets datai.
- In HistogramTransform[image,ref], ref should be a univariate distribution, an image with either one channel or the same number of channels as image, a list of values, or a list of datasets with length equal to the number of channels in image.
- HistogramTransform[source] is equivalent to HistogramTransform[source,UniformDistribution[{0,1}]].
- HistogramTransform[source,ref,n] finds an interpolating function with n equally spaced quantiles.
- HistogramTransform[image,ref] is equivalent to HistogramTransform[image,ref,256].
- With HistogramTransform[data,ref,Automatic], the number of quantiles is the same as the number of bins used in Histogram[data].
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (6)
Applications (6)
Basic Applications (3)
Color Transformation (2)
Transfer colors between images:
Perform the transfer in the Lab color space instead:
Colorize a grayscale image by searching for neighborhoods with similar luminance in a color image:
Convert images into a color space where luminance and color information are not correlated:
Normalize the luminance images by reshaping the histogram:
Compute luminance neighborhood statistics and construct a function that gives the color associated to the closest luminance neighborhood:
For each pixel of the grayscale image, create a new pixel by preserving the initial luminance and selecting the nearest color in the reference image:
Multidimensional Probability Density Function Transfer (1)
Reshape the histogram of a multidimensional dataset by iteratively reshaping random marginal histograms:
Reshape a bivariate dataset to match binormal samples:
Assess the result by visualizing the joint histograms before and after the transfer:
Test whether the transformed data is distributed according to the reference distribution:
Reshape the joint histogram of the hue and the saturation to a circle:
Visualize the joint histograms before and after the transfer:
Properties & Relations (1)
HistogramTransformInterpolation can be used to get the transformation function used in HistogramTransform:
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), HistogramTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HistogramTransform.html (updated 2014).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "HistogramTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2014. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HistogramTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). HistogramTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HistogramTransform.html