HjorthDistribution[m,s,f]
represents the Hjorth distribution with location parameter m, scale parameter s, and shape parameter f.


HjorthDistribution
HjorthDistribution[m,s,f]
represents the Hjorth distribution with location parameter m, scale parameter s, and shape parameter f.
Details
- HjorthDistribution is a distribution that has been applied in reliability analysis for modeling different classes of failure behavior.
- The survival function for value
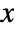 in a Hjorth distribution is given by
in a Hjorth distribution is given by 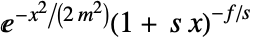 for
for 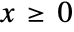 and
and 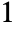 otherwise.
otherwise. - HjorthDistribution[m,s,f] allows m and s to be any real positive numbers and f to be any non-negative real number.
- HjorthDistribution[m,s,f] allows m, s and f to be any quantities such that m*s and m*f are dimensionless. »
- HjorthDistribution can be used with such functions as Mean, CDF, and RandomVariate.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (6)
Generate a sample of pseudorandom numbers from a Hjorth distribution:
Compare its histogram to the PDF:
Distribution parameters estimation:
Estimate the distribution parameters from sample data:
Compare the density histogram of the sample with the PDF of the estimated distribution:
Different moments with closed forms as functions of parameters:
Closed form for symbolic order:
Consistent use of Quantity in parameters yields QuantityDistribution:
Applications (5)
The lifetime of a device follows HjorthDistribution. Find the reliability of the device:
Plot the possible shapes of the hazard rate:
The failure behavior of a component is described by HjorthDistribution with parameters ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() . Find the probability that the component fails within its first year:
. Find the probability that the component fails within its first year:
Plot the density function of the time of failure:
Find the time at which the component is most likely to fail:
Find the mean time to failure:
Find how long a component can survive with a safety of 90%:
Find the probability that the component survives for at least one more year after having survived two years:
Simulate the failure times for 30 independent components like this:
A piece of electronic equipment has initially high failure rate due to the randomness in the quality variations during its production. Its lifetime can be modeled by HjorthDistribution with parameters ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() . Plot the hazard function:
. Plot the hazard function:
Probability of failure within the first year (warranty period):
To avoid early failures, the equipment is operated at stress level during a "burn-in" period. Find the length of the burn-in period after which the failure probability within the first year is reduced by half:
Find the expected lifetime of the equipment after having survived the burn-in period:
Find the time at which the equipment is most reliable:
Simulate the failure times for 50 independent pieces of equipment like this:
A rather simple mechanical system is composed of three independent components: two of type A and one of type B. The measured failure times, in days, are:
Find the estimated distribution for both components, assuming HjorthDistribution:
Compare the distribution of the time to failure of each component with the data:
The system works as long as one component of each type is working. Find the reliability of the system:
Find the mean time to failure:
Find the probability that the system fails after three days:
A simple mechanical system is composed of three independent components: two of type A and one of type B. The system works as long as one component of each type is working. The failure times of each component type follow the distributions:
Find the probability that both components A fail before B does:
Each time that a component A fails, it is immediately replaced. Find the average number of components of type A used by the system before B fails:
The expected lifetime of the system when adding more components of type A:
Properties & Relations (5)
Hjorth distribution is closed under scaling by a positive factor:
Relationships to other distributions:
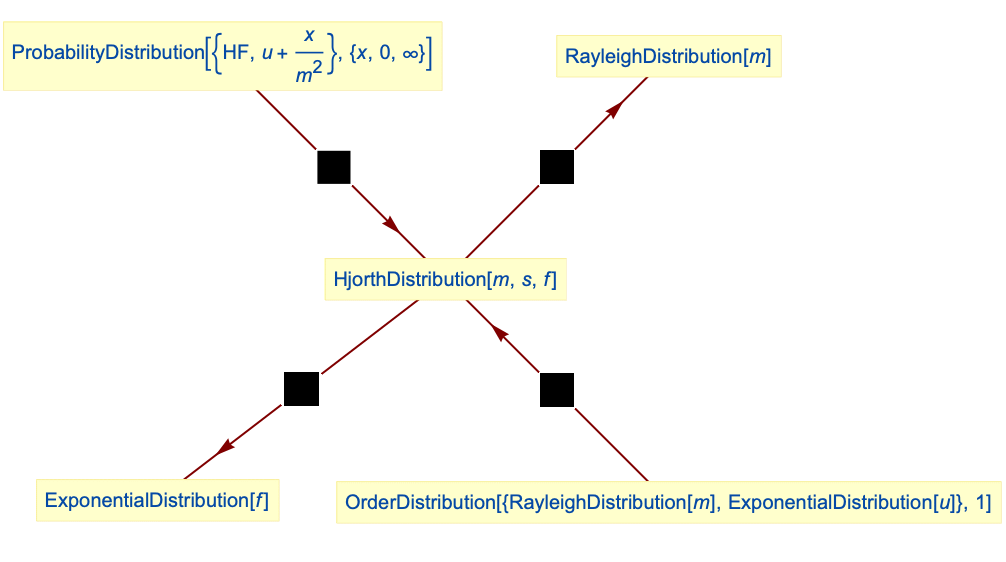
Hjorth distribution simplifies to RayleighDistribution:
Hjorth distribution can be obtained as ParameterMixtureDistribution of a linear hazard rate distribution with initial failure rate following GammaDistribution:
The linear hazard rate distribution could be obtained as OrderDistribution of ExponentialDistribution and RayleighDistribution:
ExponentialDistribution is a limiting case of Hjorth distribution:
Possible Issues (5)
HjorthDistribution is not defined when m or s is not a positive real number:
HjorthDistribution is not defined when f is a non-negative real number:
Substitution of invalid parameters into symbolic outputs gives results that are not meaningful:
The characteristic function of the Hjorth distribution does not have a closed‐form representation:
The function values can be obtained for numeric inputs:
The closed form of the moments of Hjorth distribution could lead to some numerical instabilities for some parameters:
Find numerical approximation for the moment using inexact parameters:
Alternatively, evaluate the closed expression at higher precision:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), HjorthDistribution, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HjorthDistribution.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "HjorthDistribution." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HjorthDistribution.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). HjorthDistribution. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HjorthDistribution.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_hjorthdistribution, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HjorthDistribution}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HjorthDistribution.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_hjorthdistribution, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HjorthDistribution}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HjorthDistribution.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}