ImagePyramid[image]
creates a Gaussian image pyramid formed from image.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype]
returns a Gaussian or Laplacian pyramid depending of the specified pyrtype.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype,n]
returns up to n levels of the pyramid.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype,{size}]
returns pyramid levels down to image dimensions given by size.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype,n,s]
returns a pyramid with successive levels downsampled by factor s.


ImagePyramid
ImagePyramid[image]
creates a Gaussian image pyramid formed from image.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype]
returns a Gaussian or Laplacian pyramid depending of the specified pyrtype.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype,n]
returns up to n levels of the pyramid.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype,{size}]
returns pyramid levels down to image dimensions given by size.
ImagePyramid[image,pyrtype,n,s]
returns a pyramid with successive levels downsampled by factor s.
Details and Options



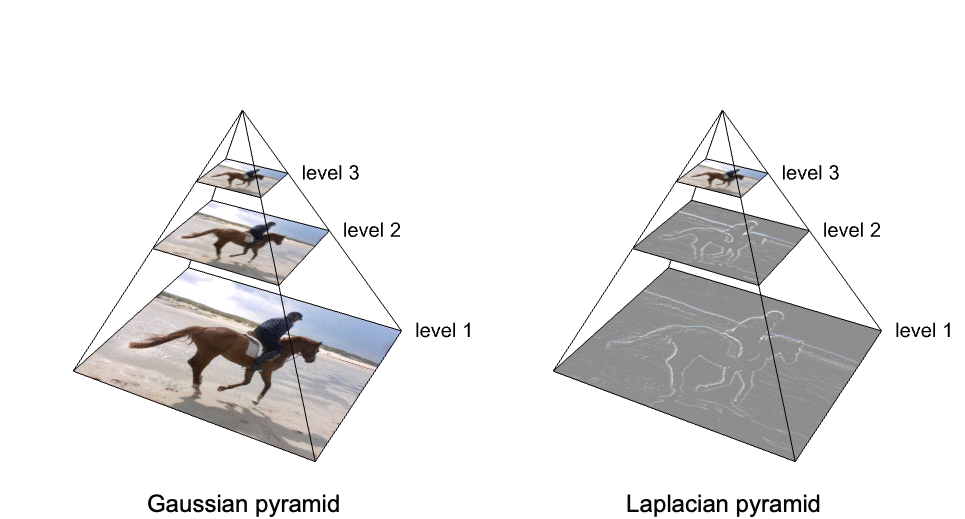
- Image pyramid is a multi-resolution representation of an image to facilitate efficient multiscale processing. Typical applications include noise removal, image blending, texture synthesis and efficient rendering.
- An image pyramid consists of several images with consecutively lower resolutions. Typically, specific levels of the pyramid are processed, and the result is reconstructed using the inverse process.
- ImagePyramid works with arbitrary 2D and 3D images.
- Use InverseImagePyramid to reconstruct the image from an image pyramid.
- The pyramid type pyrtype can be any of the following:
-
"Lowpass" or "Gaussian" iteratively blurs and downsamples "Bandpass" or "Laplacian" difference pyramid by upsampling and subtracting the lower levels from the upper levels {"Lowpass",ker} use ker for downsampling {"Bandpass",ker1,ker2} use ker1 for downsampling and ker2 for upsampling pyr use specifications of a reference pyramid pyr - Kernel specification ker can be given by an array or any valid setting for Resampling.
- By default, ImagePyramid[image] creates a Gaussian pyramid with all possible levels using a scaling factor of 2.
- Using pyr["Properties"], all available properties are returned.
- Using pyr["prop"], properties or content of the constructed image pyramid can be extracted.
- Available properties "prop" are:
-
levels extract images as specific levels "ImageDimensions" dimensions of the original image "LevelCount" the number of levels available "Levels" all images "LowpassKernel" lowpass kernel used when creating the pyramid "HighpassKernel" highpass kernel used when creating the pyramid "Padding" padding scheme used when creating the pyramid "ScalingFactor" the scaling factor used when creating the pyramid "Type" type of the pyramid, "Lowpass" or "Bandpass" - Level specification levels can take any of the following settings:
-
All all levels of the pyramid n the n 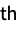 level
level-n counts from the last level {n1,n2,…} a list of level indices m;;n levels m through n m;;n;;s levels m through n with step s - ImagePyramid preserves the image type when creating a lowpass pyramid and returns a pyramid of a real type when creating a bandpass pyramid.
- By default, a "Reversed" padding is used. Use the Padding option to specify other settings.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (7)
Data (3)
Parameters (4)
The default lowpass kernel applied in each level before downsampling is the Gaussian kernel:
Use a binomial kernel instead:
Use a Gaussian kernel with standard deviation σ equal to half the downsampling factor a:
Specify the number of levels to be returned:
Specify an image size that is smaller than or equal to the smallest image in the pyramid:
This pyramid has two levels. The next pyramid level of size 50×38 would have been smaller than 50×50:
The default downsampling factor between successive levels is 2:
Options (1)
Applications (6)
Efficient Image Viewer (1)
Multiscale Feature Detection (3)
Apply a gradient filter at several scales simultaneously:
Reconstruct assuming a Laplacian pyramid to add up features extracted from all levels:
Alter pyramid levels and type to detect mountain ridges at all scales:
Reconstruct assuming a Laplacian pyramid to add up features extracted from all levels:
Perform a multiscale saliency filtering:
Apply ImageSaliencyFilter to an image:
Apply a saliency filter to all levels of the image pyramid to get a multiscale result:
Use Laplacian reconstruction to add up filter responses at all levels:
Possible Issues (1)
Images with constant alpha-channel result in Laplacian image pyramids that appear to be empty:
All pyramid levels except the last one will have an alpha channel equal to 0 and appear invisible:
The image reconstruction works, since the data in the color channel is present and the alpha channel of the fully opaque last level contributes to the correct alpha channel for the reconstructed image:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2019), ImagePyramid, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImagePyramid.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2019. "ImagePyramid." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImagePyramid.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2019). ImagePyramid. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImagePyramid.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_imagepyramid, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ImagePyramid}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImagePyramid.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_imagepyramid, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ImagePyramid}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImagePyramid.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}