is an option for Graphics3D and related functions that specifies what simulated lighting to use in coloring 3D surfaces.


Lighting
is an option for Graphics3D and related functions that specifies what simulated lighting to use in coloring 3D surfaces.
Details

- The following settings can be given:
-
Automatic default lighting schemes None no lighting "light" named lighting {s1,s2,…} light sources s1, s2, … - Possible named lighting settings "light" include:
-
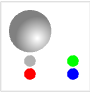
"Standard" colored light sources in default positions 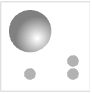
"Neutral" white light sources in default positions 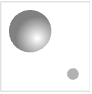
"Accent" a directional white light source in default direction 
"ThreePoint" three directional white light sources in default directions - Each light source si can be of the following forms:
-
AmbientLight uniform ambient light DirectionalLight directional light PointLight spherical point light SpotLight spotlight - Lighting{s1,…} combines the light sources si with any inherited light sources. To prevent combining with inherited light sources, use Lighting{None, s1,…}.
- Lighting->Automatic uses ambient light together with four light sources fixed relative to the final displayed image.
- Lighting can be specified separately for particular objects in Graphics3D by giving a style option Style[obj,Lighting->spec].
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (24)
Lighting Specification (18)
Default lighting on a white surface:
Default lighting when ColorFunction is specified:
No lighting means diffuse or specular colors will not be visible:
Using Glow specifies pure color without interaction with lights:
Ambient light is uniformly applied to all the surfaces in the scene:
Ambient light gives overall lighting on the scene:
Directional light is specified by a color and a vector defined by two points:
Directional lights with different colors:
Directional lights with different directions:
Directional lights on a specular surface:
Specify a spherical point light source by a color and a position:
Point lights with different colors:
Point lights at various positions:
Point lights on specular surfaces:
Specify spotlight by position, target position, and half-angle:
Spotlights with different colors:
Spotlights from different positions:
Lighting Positions (3)
Specify the light source position in the graphics coordinate system by default:
The light source moves with the graphic when the view point changes:
Specify the light position by a fraction of the graphics coordinates using Scaled:
The light source moves with the graphic when the view point changes:
Specify the light position in the view coordinate system using ImageScaled:
The light source position is always fixed relative to the view point:
Lighting Attenuation (3)
By default, point lights are not affected by the distance from an object:
Specify a point light that attenuates with respect to the distance:
Specify a point light that attenuates by the square of the distance:
By default, spotlights fall off sharply outside the cone:
Spotlights with different spot exponent ![]() has intensity
has intensity ![]() :
:
Spotlight without attenuation:
Generalizations & Extensions (8)
The colored lighting is equivalent to the following explicit setting:
The accent lighting is equivalent to the following explicit setting:
The neutral lighting is equivalent to the following explicit setting:
Predefined three-point lighting:
The three-point lighting is equivalent to the following explicit setting:
Specify lighting for each object:
Specify lighting within the graphics:
If not specified, the target direction is given toward the center of the objects:
Specify diffuse and specular colors separately for both objects and lights:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (8)
Surface color and lighting interact with each other:
Diffuse object and lighting colors can be exchanged and produce the same effect:
Specular object and lighting colors can be exchanged and produce the same effect:
Specularity gives mirror-like reflection:
The final color is a linear combination of all the surface colors as well as lighting:
Directional light yields rays parallel to the specified direction:
Point light yields rays toward all the directions from the position:
A spotlight emits conic rays toward the specified direction:
Possible Issues (5)
The default lighting may not be suitable for light surface colors:
Neutral lighting can be used to reflect surface colors more naturally:
If a color function is given to a plot, then neutral lighting is used automatically:
Restore the default colored lighting:
Flat surfaces may show little or no reflection:
A spotlight on a sphere may display a jagged boundary:
Increasing the spot exponent may reduce the effect:
Inline Lighting directives specifying light sources add those sources to any inherited specification:
Set LightingNone on the graphic to override the default LightingAutomatic setting:
Similarly, a sequence of Lighting{s1,…} specifications cumulatively adds the lights together:
Use list braces to ensure the lighting specification does not leak into subsequent specifications:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2020 (12.1) ▪ 2021 (12.3) ▪ 2021 (13.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Lighting, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Lighting.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Lighting." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Lighting.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Lighting. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Lighting.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_lighting, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Lighting}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Lighting.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_lighting, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Lighting}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Lighting.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}