MaterialShading["material"]
is a three-dimensional graphics directive specifying that surfaces that follow are to be drawn with the material "material" appearance.
MaterialShading[{"material",col}]
uses the specified color col as the base color.
MaterialShading[parm1val1,parm2val2,…]
uses the specified parameters parms.


MaterialShading
MaterialShading["material"]
is a three-dimensional graphics directive specifying that surfaces that follow are to be drawn with the material "material" appearance.
MaterialShading[{"material",col}]
uses the specified color col as the base color.
MaterialShading[parm1val1,parm2val2,…]
uses the specified parameters parms.
Details








- MaterialShading is also known as physically based shading or PBR shader.
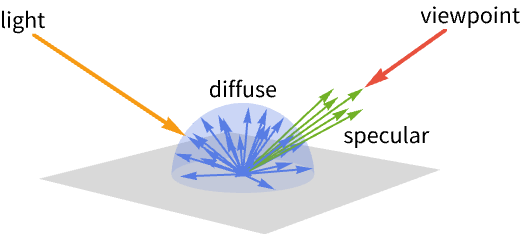
- MaterialShading is typically used to render surfaces in a way that models some key aspect of light and material interaction in the real world.
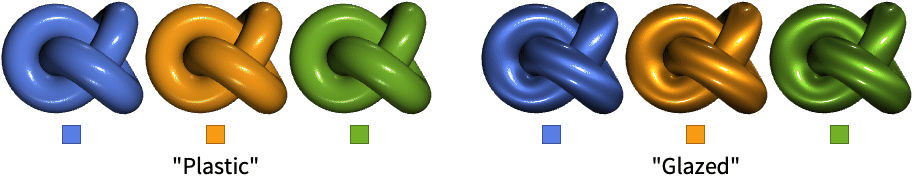
- MaterialShading["material"] specifies that reflectance on the surface should well approximate optical properties of the material "material".
- Possible materials include:
- MaterialShading[{"material",col}] specifies the base color for the material "material".
- MaterialShading[<|parm1val1,…|>] specifies that reflectance on the surface should approximate the reflectance equation based on physical, geometric and lighting properties parmi.
- Possible color parameters parmi of the material include:
-
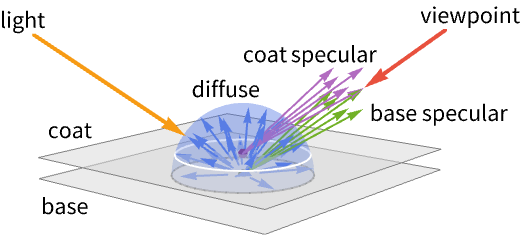
"BaseColor" base color of the material "EmissionColor" color of the light emitted accross the surface "SpecularColor" color of the light of a specular reflection - Values vali for color parameters parmi can be given in the following forms:
-
col a color Texture[image] a 2D texture based on an image {…,s} fraction of the color contribution to the final color - Possible physical parameters parmi include:
-
"MetallicCoefficient" metallic coefficient of the materal surface "RoughnessCoefficient" roughness coefficient of the materal surface - Values vali for physical parameters parmi can be given in the following forms:
-
s fraction of the property on the surface Texture[image] a 2D texture based on an image - Possible geometric parameters parmi include:
-
"SurfaceNormals" normal vectors of the surface - Values vali for geometric parameters parmi can be given in the following forms:
-
Texture[image] a 2D texture based on an image {…,s} fraction of surface normals - Possible parameters parmi of the clear coat covering of the material include:
-
"CoatColor" color of the coat covering "CoatRoughnessCoefficient" roughness cooefficient of the coat covering - Possible anisotropy parameters parmi include:
-
"SpecularAnisotropyCoefficient" anisotropy coefficient of specular reflection "CoatAnisotropyCofficient" anisotropy coefficient of coat reflection - Values vali for anisotropy parameters parmi can be given in the following forms:
-
s fraction of the reflection with respect to the view angle {s,θ} rotation of the reflection - Possible parameters parmi of the material at grazing angles include:
-
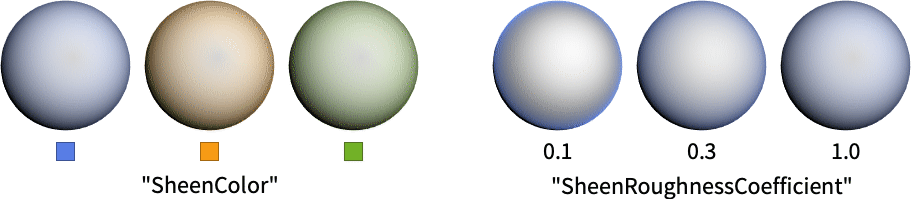
"SheenColor" color of the light of reflections "SheenRoughnessCoefficient" roughness coefficient - Possible light parameters parmi include:
-
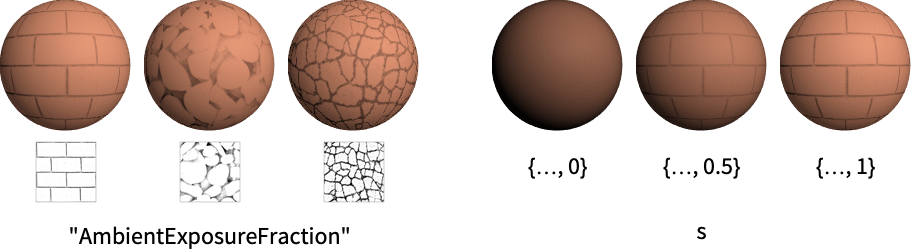
"AmbientExposureFraction" fraction of the ambient light on the surface - Values vali for light parameters parmi can be given in the following forms:
-
s fraction of the ambient light on the surface Texture[image] a 2D texture based on an image - MaterialShading[] is effectively equivalent to MaterialShading[<|"BaseColor"White|>].
- MaterialShading will override any color, Opacity, Texture, Glow or Specularity settings.

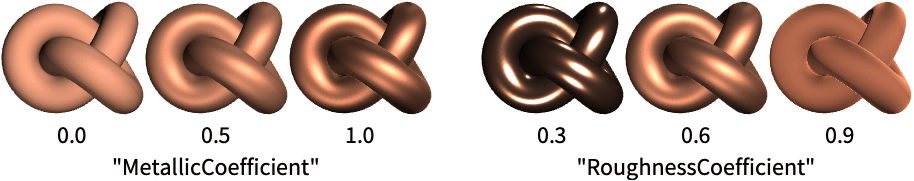
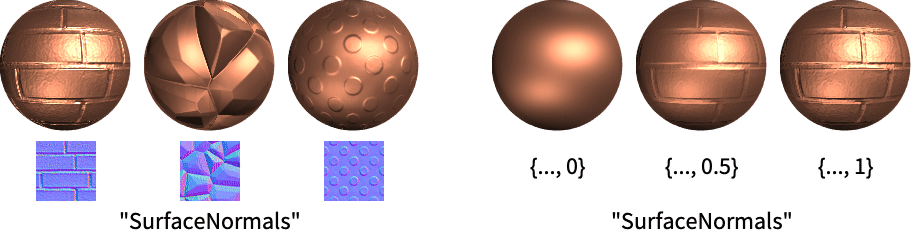
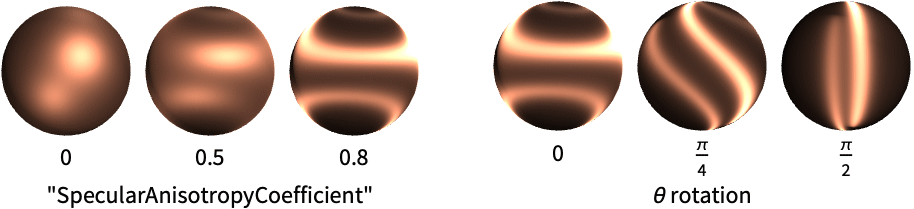
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (14)
Basic Uses (6)
Specification (5)
Specify a named material preset:
Use a material Entity:
Use a custom base color for a named material:
Specify the material parameters directly:
MaterialShading[] with no arguments uses a White base color:
Lighting (3)
MaterialShading works with all types of lights:
Use "ThreePoint" or "Accent" lighting to faithfully reproduce colors on the surface:
Applications (14)
Basic Applications (10)
Use the "BaseColor" parameter to set the base color of the material:
Use the "RoughnessCoefficient" parameter to set the shininess of the material:
Use the "SpecularColor" parameter to set the color of the specular highlight on shiny materials:
Specular highlights with the base color set to Black:
Use the "MetallicCoefficient" parameter to create metallic materials:
Use the "SpecularAnisotropyCoefficient" parameter to set the material's preference to reflect light along its tangent direction:
Set a custom angle for the tangent direction:
Use the "EmissionColor" parameter to set the light emitted by the material itself:
The emitted color does not require scene lighting:
Use the "SheenColor" parameter to add highlights on the edges of materials:
The "SheenRoughnessCoefficient" parameter sets the concentration of the sheen lighting:
Metallic materials do not have diffuse lighting and appear dark when perfectly smooth:
Use the "RoughnessCoefficient" parameter to increase the roughness of the metal:
The "AmbientExposureFraction" parameter has no effect with directional, point or spot lights:
Use an ambient light to view the effect of the "AmbientExposureFraction" parameter:
Properties & Relations (3)
MaterialShading with no arguments approximates the default system appearance:
Use VertexTextureCoordinates to specify vertex texture coordinates for a 2D texture:
Possible Issues (1)
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), MaterialShading, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MaterialShading.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "MaterialShading." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MaterialShading.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). MaterialShading. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MaterialShading.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_materialshading, author="Wolfram Research", title="{MaterialShading}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MaterialShading.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_materialshading, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={MaterialShading}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MaterialShading.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}