

Threshold
Details


- Thresholding is a mathematical segmentation operation to set values in a specific region to zero and occasionally diminish values outside the region.
- Threshold works with data arrays of any rank, as well as 2D and 3D images.
- Threshold[data] is equivalent to Threshold[data,{"Hard",10-10}].
- The threshold specification tspec can be of the form {tfun,pars}.
- Possible tfun names and options include:
- Available thresholding functions tfun and their parameters are (using input data
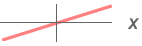 ):
): -
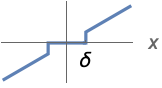
{"Hard",δ} ![ 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; x TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta; 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; x TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta;](Files/Threshold.en/3.png)
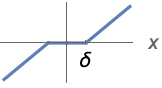
{"Soft",δ} ![ 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; sgn(x) (TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]-delta) TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta; 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; sgn(x) (TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]-delta) TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta;](Files/Threshold.en/5.png)
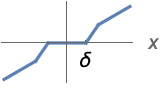
{"Firm",δ,r,p} ![ 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta-delta p r; 1/(delta r)sgn(x) (delta+delta r-delta p r) (TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]-delta+delta p r) delta-delta p r<TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta+delta (-p) r+delta r; x TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta+delta (-p) r+delta r; 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta-delta p r; 1/(delta r)sgn(x) (delta+delta r-delta p r) (TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]-delta+delta p r) delta-delta p r<TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta+delta (-p) r+delta r; x TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta+delta (-p) r+delta r;](Files/Threshold.en/7.png)
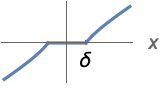
{"PiecewiseGarrote",δ} ![0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; x-(delta^2)/x TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; x-(delta^2)/x TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta](Files/Threshold.en/9.png)
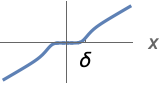
{"SmoothGarrote",δ,n} 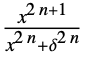
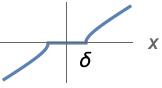
{"Hyperbola", 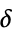 }
}![ 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; sgn(x) sqrt(x^2-delta^2) TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta; 0 TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]<=delta; sgn(x) sqrt(x^2-delta^2) TemplateBox[{x}, Abs]>delta;](Files/Threshold.en/14.png)
{"LargestValues",k} keep the largest k data points - In all cases
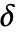 is assumed to be a positive number or a thresholding function tfunc to compute
is assumed to be a positive number or a thresholding function tfunc to compute 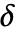 . Each tfunc[data] should return a positive number.
. Each tfunc[data] should return a positive number. - The parameter conditions for "Firm" are that
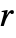 is a positive real and
is a positive real and 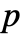 a real number between 0 and 1.
a real number between 0 and 1. - The parameter conditions for "SmoothGarrote" is to have
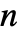 be a positive machine integer.
be a positive machine integer. - The threshold
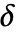 can be automatically computed using the following methods:
can be automatically computed using the following methods: -
{"BlackFraction",b} make a fraction b of all pixels be black "Cluster" cluster variance maximization (Otsu's algorithm) "Entropy" histogram entropy minimization (Kapur's method) "Mean" use the mean level as the threshold "Median" use the median pixel level as the threshold "MinimumError" Kittler–Illingworth minimum error thresholding method
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (14)
Data (7)
Threshold Specification (7)
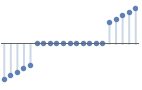
"Hard" thresholding replaces data values with absolute value below ![]() with 0:
with 0:
With "Soft" thresholding, data values below threshold ![]() are set to 0; others are diminished by
are set to 0; others are diminished by ![]() :
:
"Firm" thresholding is a compromise between "Hard" and "Soft" thresholding:
"PiecewiseGarrote" thresholding is similar to "Firm", but uses a single parameter:
"LargestValues" thresholding preserves ![]() samples with largest absolute values:
samples with largest absolute values:
Properties & Relations (7)
"Hard" thresholding sets to 0 all data values with absolute value below a certain threshold ![]() :
:
Vary the value of the threshold ![]() :
:
"Hard" thresholding is similar to Chop:
"Soft" thresholding performs a shrinking operation:
Vary the value of the threshold ![]() :
:
"Firm" thresholding is a compromise between "Hard" and "Soft" thresholding:
"Firm" thresholding has uniformly smaller variance than "Hard" thresholding:
In the limit β->∞, "Firm" threshold performs "Soft" thresholding:
In the limit β->η, "Firm" threshold performs "Hard" thresholding:
"PiecewiseGarrote" thresholding:
This is similar to "Firm" thresholding with the advantage of having a single parameter ![]() :
:
Vary the value of the threshold ![]() :
:
In the limit n∞, "SmoothGarrote" goes to "Hard" thresholding:
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), Threshold, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Threshold.html (updated 2012).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "Threshold." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2012. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Threshold.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). Threshold. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Threshold.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_threshold, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Threshold}", year="2012", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Threshold.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_threshold, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Threshold}, year={2012}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Threshold.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}