DICOM (.dcm, .dic)
Background & Context

-
- MIME type: application/dicom
- DICOM medical imaging format.
- Commonly used in medical imaging equipment and picture archiving and communication systems.
- DICOM is an acronym for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine.
- Stores multiple raster images together with patient and device information.
- Binary format.
- Supports a variety of image encoding and data compression methods.
- DICOM Version 3.0 was introduced in 1993.
Import & Export

- Import["file.dcm"] imports a DICOM file, returning an Image object.
- Import["file.dcm",elem] imports the specified element from a DICOM file.
- The import format can be specified with Import["file","DICOM"] or Import["file",{"DICOM",elem,…}].
- Export["file.dcm",expr] exports graphics or any other expression as an image to a DICOM file.
- When exporting Wolfram Language graphics or arbitrary expressions to DICOM, the resulting image has the same raster size as its displayed form.
- Image objects are by default exported at their raster size.
- Because DICOM is a raster image format, all fonts are rasterized on export.
- See the following reference pages for full general information:
-
Import, Export import from or export to a file CloudImport, CloudExport import from or export to a cloud object ImportString, ExportString import from or export to a string ImportByteArray, ExportByteArray import from or export to a byte array
Import Elements

- General Import elements:
-
"Elements" list of elements and options available in this file "Summary" summary of the file "Rules" list of rules for all available elements - Data representation elements:
-
"Data" array of values "Graphics" Graphics object representing an image "Image" raster graphics given as an Image object "ImageList" a list of images -
"RawData" array of color map indices "RawPixelData" DICOM pixel data without scaling - Overlay elements:
-
"Overlays" an overlay image or a list of overlays - Import by default uses "Image" for single-frame DICOM files and "ImageList" for multi-frame DICOM files.
- Advanced Import elements:
-
"BitDepth" bits used to represent each color channel in the file "Channels" the number of color channels used in the file "ColorMap" color reduction palette, given as a list of color values "ColorSpace" color encoding used in the file "ImageSize" raster dimensions "MetaInformation" metainformation stored in the file "RawMetaInformation" raw metainformation stored in the file "Summary" summary of the file
Export Elements

- General Export element:
-
"Rules" a list of imported elements in the form of elemexpr - Export["file.dcm",{elem1->expr1,…},"Rules"] uses rules to specify the elements to be exported.
- Available Export elements:
-
"Data" numeric data "Image" an Image object "Image3D" an Image3D object "ImageList" a list of image frames "MetaInformation" an association of metadata tags and values "Overlays" a list of association - The "Overlays" associations can have the following keys:
-
"Description" the overlay description "Image" one or a list of overlay images "Label" the overlay label "Type" the type of the overlay "Subtype" the subtype of the overlay - Values for "Type" can be either "Graphics" or "RegionOfInterest". "Subtype" can be either "User" or "Automated".
Options



- Import and Export options:
-
"ImageTopOrientation" Top orientation of the image as stored in the file ImageSize Automatic overall image size IncludeMetaInformation All amount of metadata to import and export - Possible settings for IncludeMetaInformation include:
-
All include all available metadata None include no metadata "Anonymized" include anonymized metadata "FullyAnonymized" include fully anonymized metadata - Import option:
-
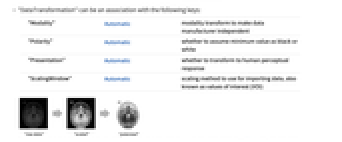
"DataTransformation" Automatic set of transformations applied to the data stored in the file - "DataTransformation" can be an association with the following keys:
-
"Modality" Automatic modality transform to make data manufacturer independent "Polarity" Automatic whether to assume minimum value as black or white "Presentation" Automatic whether to transform to human perceptual response "ScalingWindow" Automatic scaling method to use for importing data, also known as values of interest (VOI) - By default, the modality transformation specified in the file is used. Use "Modality"None to disable this transform.
- By default, the polarity transformation specified in the file is used. Possible settings are:
-
"Normal" assume minimum value to be black "Reverse" assume minimum value to be white - By default, the presentation transformation specified in the file is used. Use "Presentation"None to disable this transform.
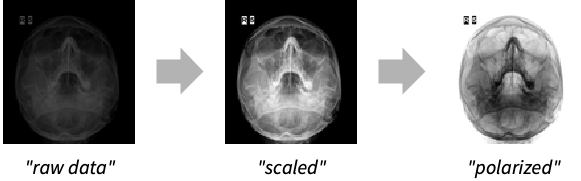
- "ScalingWindow" can take the following settings:
-
Automatic automatic scaling None no scaling "MinMax" scale to min and max of data in all frames "MinMaxPerFrame" scale to min and max of each frame {center,w} scale to the range {center-w,center+w} <|"Center"center,"Width"w|> scale to the range {center-w,center+w} <|"Min"min,"Max"max|> scale to the range {min,max} - With "ScalingWindow"->Automatic, values are scaled using scaling values stored in the file. If no scaling specification is stored, values are scaled using the "MinMax" method.
- Export options:
-
ColorSpace Automatic color space to be used in the file CompressionLevel Automatic compression level to use ImageSize Automatic overall image size "BitDepth" Automatic bit depth per channel used to store image data "ImageEncoding" None the image encoding to use "ImageTopOrientation" Automatic orientation of the image as stored in the file - Supported ColorSpace settings are "Grayscale" and "RGB".
- Possible values for "ImageEncoding" are "JPEGLossless", "JPEGLosslessNonhierarchical", "JPEGLSLossless", "JPEGLSLossy", "JPEGLossy8Bit", "JPEGLossy12Bit" and "RLE".
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (2)
Import Elements (15)
Available Elements (3)
Data Representation (4)
"Graphics" (1)
Import as a Graphics object:
"Image" (1)
Metadata (8)
"ColorSpace" (1)
Get the color encoding used on export:
Use ImageColorSpace to get the color space of an imported image:
"ImageSize" (1)
Get the dimensions of the image stored in the file:
Using ImageDimensions on an imported image gives the same result:
"RawMetaInformation" (2)
Unlike "MetaInformation", "RawMetaInformation" does not validate imported values against the DICOM Standard and does not perform any conversions to Wolfram Language expressions. Read the raw metainformation from a DICOM file:
A dataset of raw metainformation:
The "RawMetaInformation" element may return more tags than "MetaInformation":
Export Elements (10)
"Data" (1)
Export NumericArray as raw pixel values to a DICOM file:
"Graphics" (1)
"ImageList" (1)
"MetaInformation" (2)
Import Options (8)
ImageSize (1)
"ImageTopOrientation" (1)
"DataTransformation" (6)
Import the image with default data transformations applied:
Check the range of pixel values in the imported image:
Import the image without transformations:
Check the range of pixel values in the imported image:
Check the values of the window width and center stored in the file:
Import the image explicitly specifying the window width and center as stored in the file:
Import image scaling values between 500 and 600 to the full image data range:
Import the image with specific scaling values and reversed polarity:
Compare how disabling modality transformation and changing polarity affects the imported image:
Export Options (18)
BitDepth (3)
ColorSpace (3)
CompressionLevel (4)
The compression level should be between 0 and 1:
Use CompressionLevel0 for no compression and the best possible image quality:
This leads to a larger file size:
Use CompressionLevel1 for the most compression and the smallest possible file size:
This leads to a smaller file size:
"ImageEncoding" (3)
ImageSize (1)
IncludeMetaInformation (3)
Import the image with embedded metadata:
By default, embedded metadata is merged with the one specified in "MetaInformation" element:
With IncludeMetaInformationNone, embedded metadata is ignored:
Include embedded meta information with some anonymization:
Notice that the patient name is removed:
While some other metadata, such as procedure start time, persists:
"ImageTopOrientation" (1)
By default, the upright image is exported using "ImageTopOrientation"->Top:
Tech Notes
History
Introduced in 2003 (5.0) | Updated in 2016 (11.0) ▪ 2020 (12.1) ▪ 2020 (12.2) ▪ 2021 (12.3)