HDF5 (.h5, .hdf5)
Background & Context

-
- MIME type: application/x-hdf5
- HDF data format Version 5.
- General-purpose format for representing multidimensional datasets and images.
- Datasets with compound data structures are supported.
- Used for storage, management, and exchange of scientific data.
- HDF is an acronym for Hierarchical Data Format.
- Originally developed by the US National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA).
- Currently maintained by The HDF Group.
- Binary file format.
- Incompatible with HDF Version 4 and earlier.
Import & Export

- Import["file.h5"] imports an HDF5 file, returning the names of the datasets stored in the file.
- Import["file.h5",elem] imports the specified element from an HDF5 file.
- The import format can be specified with Import["file","HDF5"] or Import["file",{"HDF5",elem,…}].
- Export["file.h5",expr] exports a numeric array to HDF5.
- Export["file.h5",{expr1,…},{"Datasets", {"dataset1",…}}] creates an HDF5 file, storing the data arrays {expr1,…} as separate datasets.
- Export["file.h5",expr,elem] exports the specified element to an HDF5 file.
- Export["file.h5",elem1->expr1,…,"Rules"] uses rules to specify the elements to be exported.
- See the following reference pages for full general information:
-
Import, Export import from or export to a file CloudImport, CloudExport import from or export to a cloud object ImportString, ExportString import from or export to a string ImportByteArray, ExportByteArray import from or export to a byte array
Import Elements




- General Import elements:
-
"Elements" list of elements and options available in this file "Summary" summary of the file "Rules" list of rules for all available elements - Structure elements:
-
"Datasets" names of all datasets "Groups" names of all groups "StructureGraph" a directed graph showing the structure of the datasets {"StructureGraph, groupname} a graph showing the structure under groupname "StructureGraphLegend" legend for the structure graph "Summary" summary of properties - Names of groups and datasets are given as the absolute paths starting with the root group name "/".
- Import by default uses the "Datasets" element for the HDF5 format.
- Data representation elements:
-
"Data" all datasets imported as an association {"Data",n} or n n 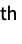 dataset
dataset{"Data",dataset} or dataset named dataset {"Data",groupname} an association of all datasets under groupname {"Data",groupname,lev} an association of datasets under groupname up to level lev - The following basic data types are supported:
-
"Integer8" 8-bit integers "Integer16" 16-bit integers "Integer32" 32-bit integers "Integer64" 64-bit integers "UnsignedInteger8" 8-bit unsigned integers "UnsignedInteger16" 16-bit unsigned integers "UnsignedInteger32" 32-bit unsigned integers "UnsignedInteger64" 64-bit unsigned integers "Real32" IEEE single‐precision numbers "Real64" IEEE double‐precision numbers "String" string of ASCII characters - The following structured data types are supported:
-
"ByteArray" a ByteArray of an arbitrary length "Array" an array of any supported data format "Enum" an enumeration "Compound" a compound dataset consisting of any other data format and other compound datasets - Complex numbers are typically stored and imported as compound types.
- Metadata elements:
-
"Attributes" attributes of all groups and datasets "DataEncoding" specifies how each dataset is compressed "DataFormat" type used to represent each dataset "Dimensions" data dimensions of each dataset {"metadata",n} metadata of the n 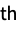 dataset
dataset{"metadata",dataset} metadata of the named dataset - The following data encodings are supported:
-
None no data compression is used "Fletcher32" adds the Fletcher checksum "GZIP" GZIP compression "ScaleOffset" performs a scale and/or offset operation "Shuffle" reorders so that consistent byte positions are placed together "SZIP" SZIP compression (Import only) - A single dataset can have multiple encodings, which will be specified as a list {enc1,enc2,…}.
Export Elements



- General Export element:
-
"Rules" a list of imported elements in the form of elemexpr - Export["file.h5",{elem1->expr1,…},"Rules"] uses rules to specify the elements to be exported.
- Available Export elements:
-
"Attributes" attributes associated to any object "Datasets" datasets and their associated elements "Groups" group names and their associated elements "NamedDataTypes" named data types and their associated elements - With the "Attributes" element, the following expressions can be given:
-
attr attributes associated to the root group "/" {path1attr1,…} attributes attri associated to the specified pathi - Attributes attri should be given in the form "attname"->attval.
- With the "Groups" element, the following expressions can be given:
-
{"gr1","gr2",…} a list of group paths {"gr1"grdata1,…} list of groups and their associated data - Group data grdatai can take the following keys:
-
"Attributes" group attributes "HardLinks" hard links to other objects "SoftLinks" soft links to other objects - Soft and hard links can be specified using "linkname"path.
- With the "Datasets" element, the following expressions can be given:
-
data stores data under "Dataset1" {"name1"data1,…} a list of dataset names and their associated data {"name1"ds1,…} specifies each dataset dsi using a list of rules - Datasets dsi can take the following keys:
-
"Attributes" dataset attributes "Data" array of data "DataFormat" data type "MaxDimensions" list of maximal dimensions for the dataset "SpaceSelection" part of the dataspace where the data will be written - With the "NamedDataTypes" element, the following expressions can be given:
-
{"name1"type1,…} a data type {"name1"<|"Type"type1,"Attributes"att1|>,…} an association specifying a type and its attributes - The type specification typei can take the following forms:
-
"simpletype" a simple data type such as "Integer64" <|"Class""ByteArray",…|> takes "Length" and "Tag" keys <|"Class""Array",…|> takes "DataFormat" and "Dimensions" keys <|"Class""Compound",…|> takes a "Structure" key
Options
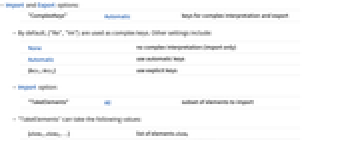

- Import and Export options:
-
"ComplexKeys" Automatic keys for complex interpretation and export - By default, {"Re","Im"} are used as complex keys. Other settings include:
-
None no complex interpretation (import only) Automatic use automatic keys {key1,key2} use explicit keys - Import option:
-
"TakeElements" All subset of elements to import - "TakeElements" can take the following values:
-
{elem1,elem2,…} list of elements elemi {m;;n;;s,...} elements m through n in steps of s {opt1val1,…} list of suboptions - The following suboptions opti are available for taking elements:
-
"Offset" {0,0,…} the offset along the dimensions of the dataset "Count" All the number of block to be imported along each dimension "Stride" {1,1,…} the step between beginnings of the blocks "Block" {1,1,…} number of elements in each block - Export option:
-
ByteOrdering $ByteOrdering what byte ordering to use OverwriteTarget True whether to overwrite an existing file "AppendMode" "Extend" how to append to existing objects - Using OverwriteTarget->"Append", new objects may be added to an existing file.
- Possible settings for "AppendMode" include:
-
"Extend" extends existing objects, if possible (default) "Overwrite" overwrites exisiting objects "Preserve" preserves existing objects
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (12)
Import (7)
Show all elements available in the file:
By default, a list of dataset names is returned:
Import the file structure, specifying the format explicitly:
Import contents of a dataset by specifying its name:
Import dimensions and data format for all datasets in the file:
Import dimensions and data format of a single dataset:
Import 8-bit RGB raster data and render it as an Image object:
Import Elements (22)
Attributes (4)
Data (4)
DataFormat (2)
Get data type description for every dataset in the file:
Simple numeric and string types have one-word descriptions:
"DataFormat" for a compound type shows class and structure:
"DataFormat" for enumerated types includes class, base data format and a list of values and names:
"DataFormat" for array types includes class, base data format and dimensions:
Dimensions (4)
StructureGraph (3)
Export Elements (28)
Attributes (4)
Attach attributes to the root group:
Specify data format for attributes:
Export dataset's attributes both in "Datasets" and "Attributes" elements:
Each attribute must have a name that is unique among all attributes attached to the same object:
Try to export a different attribute with an already existing name:
It is possible to overwrite existing attributes with "AppendMode" set to "Overwrite":
Datasets (13)
"Datasets" is the default export element. Data format and dimensions are automatically inferred from the expression:
Export expressions into different datasets, each of which can have a full path:
Inspect the structure of the HDF5 file:
Export a dataset with a custom data format:
Export a dataset with an attribute:
Create a scalar dataset with a single integer:
Create an array of integer numbers:
Export an array of real numbers:
Export a numeric array with complex numbers:
Note that complex numbers are exported to a compound dataset:
Use the "ComplexKeys" option to get complex numbers back:
Create a dataset with strings:
A ByteArray is stored as a "ByteArray" type (also called the opaque type in HDF5):
Associations with string keys are exported as elements of a compound type:
Create a dataset of initial size 2×2 that can later be extended to 10 rows and arbitrarily many columns:
Overwrite the first row with a list of 5 integers. This will extend the dataset to 5 columns:
Use the "SpaceSelection" subelement to overwrite the third and fourth columns:
Create a 3×4 dataset that can be arbitrarily extended:
Append a 3×3 array. This can only be done along the first dimension and Export will automatically detect that:
Sometimes data dimensions do not allow for automatic extensions of the dataset:
Groups (9)
HDF5 files always have a root group (with path "/"):
Export multiple groups by giving a list of paths:
Groups can have links to other groups or datasets:
Soft link names cannot contain the special character "/":
Soft link target must be a valid path, without "." or "..":
If a soft link target is missing, the link becomes a dangling link:
Create a file with two groups, a dataset and a hard link from one group to the dataset:
A hard link pointing to a nonexistent location cannot be added:
Create a new dataset under "/A/newDset":
Try to redirect the "newDset" link to point to group "B":
It is only possible with "Overwrite" mode:
Now the access to the second dataset is irreversibly lost. This is a resource leak as the dataset still occupies space in the file.
As with soft links, hard link name is always relative to the group path and must consist of exactly one path element:
The hard link target must be a valid path, without "." or "..":
Import Options (4)
"ComplexKeys" (1)
Export Options (8)
"AppendMode" (1)
When appending data to an existing file using OverwriteTarget"Append", the export behavior for appending data can be specified using the "AppendMode" option. By default, "AppendMode""Extend" is used.
Append some attributes to "gr1/ds1" and a hard link from "gr1" to "gr2":
"AppendMode""Extend" does not allow for modifying existing attributes or links:
With "AppendMode""Overwrite", it is possible to overwrite existing objects and add new ones:
With "AppendMode""Overwrite", it is possible to modify data in existing datasets as long as data format and dimensions match:
To append new objects to the file with the guarantee that no existing structures in the file will be modified, use "AppendMode""Preserve":
ByteOrdering (1)
HDF5 allows you to choose the byte ordering. Create a big-endian file using ByteOrdering-1:
The two files are actually different:
Import will work correctly independently of the byte ordering:
"ComplexKeys" (3)
By default, complex numbers are exported to a compound type using "Re" and "Im" keys:
To import the data as complex numbers, specify the keys in Import:
OverwriteTarget (3)
By default, with OverwriteTargetTrue, every call to Export writes a new file:
With OverwriteTargetFalse, the call to Export will fail if the output file already exists:
Export to certain formats, e.g. HDF5, supports the setting OverwriteTarget"Append", which makes Export act on the output file if it already exists, instead of overwriting it:
Properties & Relations (1)
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2004 (5.1) | Updated in 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2020 (12.2)