WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
DragForceComponent calculating the magnus force |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["EducationExamples.Physics.FreeKick.Components.DragForce"]
Information
The drag force is dependent on the geometry and size of the object, the density of the air, the velocity of the object, and the so-called Reynolds number. In this implementation, the equation describing the drag force has been taken from the book Physics for Game Programmers, equation 7.51 on page 191, defined as:
- FD = 1/2 ρ v^2 A CD
where ρ is the air density, v is the velocity of the ball, A is the cross-sectional area of the ball, and CD is the drag coefficient. The drag coefficient is dependent on the Reynolds number, which is in turn dependent on the air density, the velocity of the object, the cross-sectional area, and the viscosity. In Physics for Game Programmers, experimental data is used to describe CD. This results in the following:
- CD = 0.47 if Re< 100000
- CD = 0.47 - 0.25*(Re -100000)/35000 if 100000 < Re < 135000
- CD = 0.22 if Re > 135000
where Re is the Reynolds number.
Parameters (1)
| rho |
Value: 1.225 Type: Density (kg/m³) Description: Density of the fluid (1.225 kg/m^3 for air) |
|---|
Connectors (1)
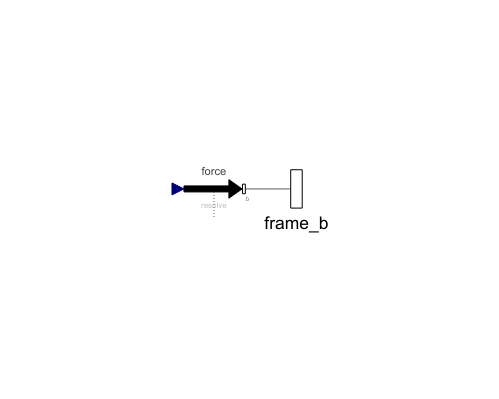
| frame_b |
Type: Frame_b Description: Coordinate system fixed to the component with one cut-force and cut-torque (non-filled rectangular icon) |
|---|
Components (1)
| force |
Type: WorldForce Description: MultiBody force component applying the drag force |
|---|
Used in Components (1)
|
EducationExamples.Physics.FreeKick.Components Ball subject to magnus forces. |