WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
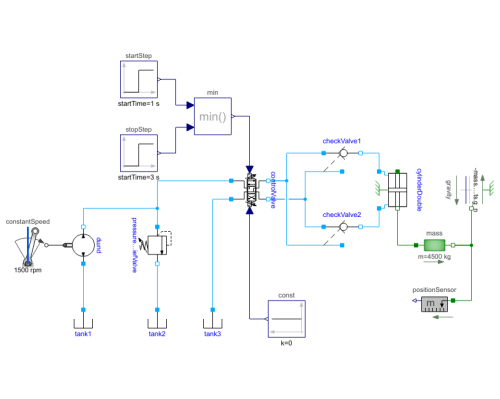
Servo3Example circuit of a cylinder moving a load |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["Hydraulic.Examples.Translation.Servo3"]
Information
Fig. 1 shows how the control valve moves to the upper state and then back to its center state. Fig. 2 shows how the check valves allow flow when the control valve is in its upper state. Fig. 3 shows how the cylinder moves when the control valve is in its upper state.
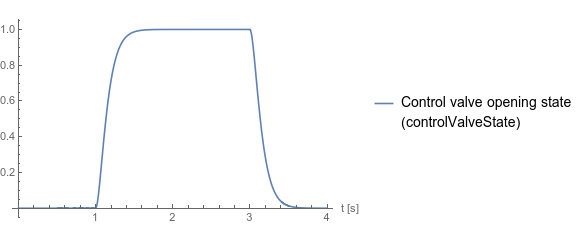
Fig. 1 Control valve opening state
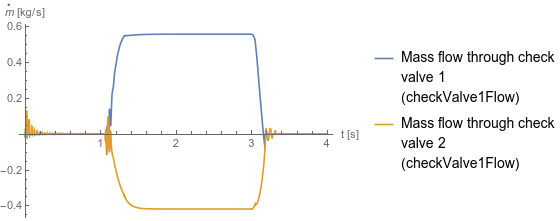
Fig. 2 Flow through check valves. The difference is caused by asymmetric piston areas. The rod diameter to the left of the piston is zero.
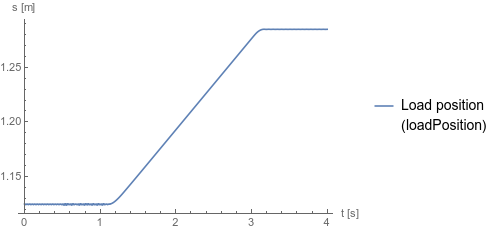
Fig. 3 Load position
Parameters (1)
| medium |
Value: Oil() Type: Medium Description: Medium in the component |
|---|
Components (18)
| medium |
Type: Medium Description: Medium in the component |
|
|---|---|---|
| startStep |
Type: Step Description: Generate step signal of type Real |
|
| tank1 |
Type: Tank Description: Simple tank with constant pressure |
|
| tank2 |
Type: Tank Description: Simple tank with constant pressure |
|
| pump |
Type: Pump Description: Model of a pump with fixed displacement and volumes |
|
| tank3 |
Type: Tank Description: Simple tank with constant pressure |
|
| positionSensor |
Type: PositionSensor Description: Ideal sensor to measure the absolute position |
|
| cylinderDouble |
Type: CylinderDouble Description: Double cylinder model |
|
| constantSpeed |
Type: ConstantSpeed Description: Constant speed, not dependent on torque |
|
| pressureReliefValve |
Type: PressureReliefValve Description: Pressure valve, controlled by the pressure difference between the ports |
|
| controlValve |
Type: PCVE43FloatingCenter Description: Electrically actuated proportional control valve with four ports and three states |
|
| gravity |
Type: ConstantForce Description: Constant force, not dependent on speed |
|
| min |
Type: Min Description: Pass through the smallest signal |
|
| stopStep |
Type: Step Description: Generate step signal of type Real |
|
| const |
Type: Constant Description: Generate constant signal of type Real |
|
| checkValve1 |
Type: PilotOperatedCheckValvePilotToOpen Description: Pilot-operated check valve with lumped volumes |
|
| checkValve2 |
Type: PilotOperatedCheckValvePilotToOpen Description: Pilot-operated check valve with lumped volumes |
|
| mass |
Type: Mass Description: Sliding mass with inertia |