WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
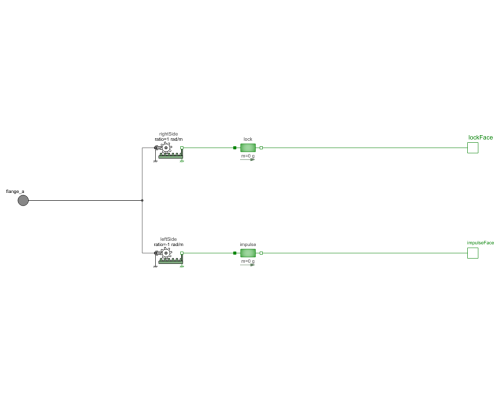
EscapementForkModel of escapement fork. |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["IndustryExamples.ConsumerProducts.PendulumClock.Components.EscapementFork"]
Information
The escapement fork here is modeled using two rotational to translational components with opposite signs on their ratios. When one face of the fork goes down, the other swings up.
Connectors (3)
| flange_a |
Type: Flange_a Description: One-dimensional rotational flange of a shaft (filled circle icon) |
|
|---|---|---|
| lockFace |
Type: Flange_b Description: One-dimensional translational flange (right, flange axis directed OUT OF cut plane) |
|
| impulseFace |
Type: Flange_b Description: One-dimensional translational flange (right, flange axis directed OUT OF cut plane) |
Components (4)
| lock |
Type: Mass Description: Sliding mass with inertia |
|
|---|---|---|
| impulse |
Type: Mass Description: Sliding mass with inertia |
|
| rightSide |
Type: IdealGearR2T Description: Gearbox transforming rotational into translational motion |
|
| leftSide |
Type: IdealGearR2T Description: Gearbox transforming rotational into translational motion |
Used in Examples (2)
|
IndustryExamples.ConsumerProducts.PendulumClock Main pendulum clock example. Clock has one hand that takes one step each second. The movement is controlled by a counterweight. |
|
|
IndustryExamples.ConsumerProducts.PendulumClock Expanded pendulum clock setup with two hands, the relative motion of the hands are controlled by gear ratios. |