WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
FirstFirst example: simple drive train |
|
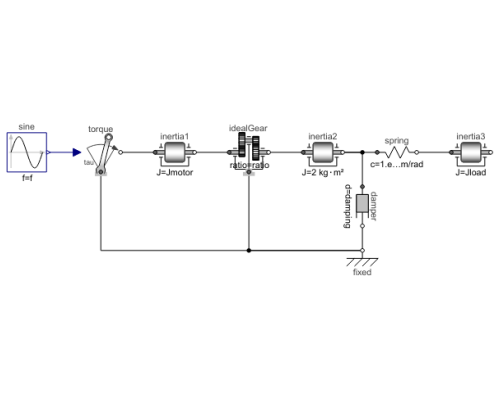
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["Modelica.Mechanics.Rotational.Examples.First"]
Information
This information is part of the Modelica Standard Library maintained by the Modelica Association.
The drive train consists of a motor inertia which is driven by a sine-wave motor torque. Via a gearbox the rotational energy is transmitted to a load inertia. Elasticity in the gearbox is modeled by a spring element. A linear damper is used to model the damping in the gearbox bearing.
Note, that a force component (like the damper of this example) which is acting between a shaft and the housing has to be fixed in the housing on one side via component Fixed.
Simulate for 1 second and plot the following variables:
angular velocities of inertias inertia2 and 3: inertia2.w, inertia3.w
Parameters (6)
| amplitude |
Value: 10 Type: Torque (N⋅m) Description: Amplitude of driving torque |
|---|---|
| f |
Value: 5 Type: Frequency (Hz) Description: Frequency of driving torque |
| Jmotor |
Value: 0.1 Type: Inertia (kg⋅m²) Description: Motor inertia |
| Jload |
Value: 2 Type: Inertia (kg⋅m²) Description: Load inertia |
| ratio |
Value: 10 Type: Real Description: Gear ratio |
| damping |
Value: 10 Type: Real Description: Damping in bearing of gear |
Components (9)
| fixed |
Type: Fixed Description: Flange fixed in housing at a given angle |
|
|---|---|---|
| torque |
Type: Torque Description: Input signal acting as external torque on a flange |
|
| inertia1 |
Type: Inertia Description: 1D-rotational component with inertia |
|
| idealGear |
Type: IdealGear Description: Ideal gear without inertia |
|
| inertia2 |
Type: Inertia Description: 1D-rotational component with inertia |
|
| spring |
Type: Spring Description: Linear 1D rotational spring |
|
| inertia3 |
Type: Inertia Description: 1D-rotational component with inertia |
|
| damper |
Type: Damper Description: Linear 1D rotational damper |
|
| sine |
Type: Sine Description: Generate sine signal |