AbsArgPlot[f,{x,xmin,xmax}]
generates a plot of Abs[f] colored by Arg[f] as a function of x∈ from xmin to xmax.
AbsArgPlot[{f1,f2,…},{x,xmin,xmax}]
plots several functions.
AbsArgPlot[{…,w[fi],…},…]
plots fi with features defined by the symbolic wrapper w.
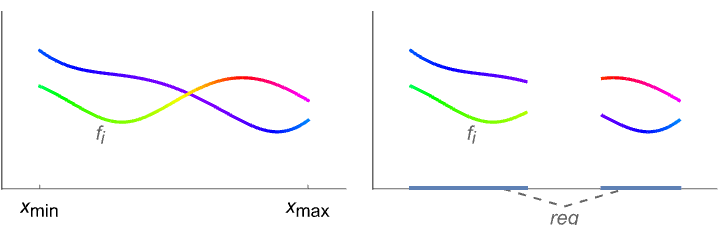
AbsArgPlot[…,{x}∈reg]
takes the variable x to be in the geometric region reg.




AbsArgPlot
AbsArgPlot[f,{x,xmin,xmax}]
generates a plot of Abs[f] colored by Arg[f] as a function of x∈ from xmin to xmax.
AbsArgPlot[{f1,f2,…},{x,xmin,xmax}]
plots several functions.
AbsArgPlot[{…,w[fi],…},…]
plots fi with features defined by the symbolic wrapper w.
AbsArgPlot[…,{x}∈reg]
takes the variable x to be in the geometric region reg.
Details and Options








- AbsArgPlot evaluates f at different values of x to create smooth curves of the form {x,Abs[f[x]]} colored by {x,Arg[f[x]]}.
- Gaps are left at any x where the fi evaluate to non-numeric values.
- The region reg can be any RegionQ object in 1D.
- AbsArgPlot treats the variable x as local, effectively using Block.
- AbsArgPlot has the attribute HoldAll and evaluates f only after assigning specific numerical values to x.
- In some cases, it may be more efficient to use Evaluate to evaluate f symbolically before specific numerical values are assigned to x.
- Wrappers apply to both Re[f] and Im[f].
- The following wrappers w can be used for the fi:
-
Annotation[fi,label] provide an annotation for the fi Button[fi,action] evaluate action when the curve for fi is clicked Callout[fi,label] label the function with a callout Callout[fi,label,pos] place the callout at relative position pos EventHandler[fi,events] define a general event handler for fi Highlighted[fi,effect] dynamically highlight fi with an effect Highlighted[fi,Placed[effect,pos]] statically highlight fi with an effect at position pos Hyperlink[fi,uri] make the function a hyperlink Labeled[fi,label] label the function Labeled[fi,label,pos] place the label at relative position pos Legended[fi,label] identify the function in a legend PopupWindow[fi,cont] attach a popup window to the function StatusArea[fi,label] display in the status area on mouseover Style[fi,styles] show the function using the specified styles Tooltip[fi,label] attach a tooltip to the function Tooltip[fi] use functions as tooltips - Wrappers w can be applied at multiple levels:
-
w[fi] wrap the fi w[{f1,…}] wrap a collection of fi w1[w2[…]] use nested wrappers - Callout, Labeled and Placed can use the following positions pos:
-
Automatic automatically placed labels Above, Below, Before, After positions around the curve x near the curve at a position x Scaled[s] scaled position s along the curve {s,Above},{s,Below},… relative position at position s along the curve {pos,epos} epos in label placed at relative position pos of the curve - AbsArgPlot has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
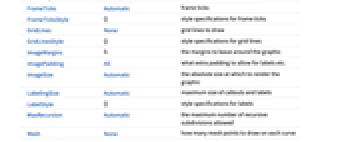
AspectRatio 1/GoldenRatio ratio of height to width Axes True whether to draw axes ClippingStyle None what to draw where curves are clipped ColorFunction Automatic how to determine the coloring of curves ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale arguments to ColorFunction EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate at every function evaluation Exclusions Automatic points in x to exclude ExclusionsStyle None what to draw at excluded points Filling None filling to insert under each curve FillingStyle Automatic style to use for filling LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels MaxRecursion Automatic the maximum number of recursive subdivisions allowed Mesh None how many mesh points to draw on each curve MeshFunctions {#1&} how to determine the placement of mesh points MeshShading None how to shade regions between mesh points MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh points Method Automatic the method to use for refining curves PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotHighlighting Automatic highlighting effect for curves PlotLabel None overall label for the plot PlotLabels None labels to use for curves PlotLegends None legends for curves PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points PlotRange {Full,Automatic} the range of y or other values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to specify the style for each curve PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot RegionFunction (True&) how to determine whether a point should be included ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations - Possible settings for ClippingStyle are:
-
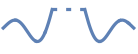
Automatic use a dotted line for the clipped portion 
None omit the clipped portion of the curve 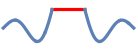
style use style for the clipped portion - With the default settings Exclusions->Automatic and ExclusionsStyle->None, AbsArgPlot breaks curves at discontinuities and singularities it detects. Exclusions->None joins across discontinuities and singularities.
- Exclusions->{x1,x2,…} is equivalent to Exclusions->{x==x1,x==x2,…}.
- PlotLabels->"Expressions" uses the fi as the label text.
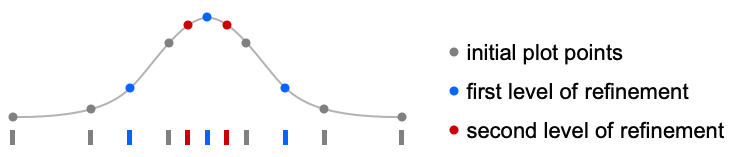
- AbsArgPlot initially evaluates f at a number of equally spaced sample points specified by PlotPoints. Then it uses an adaptive algorithm to choose additional sample points, subdividing a given interval at most MaxRecursion times.
- Since only a finite number of sample points are used, it is possible for AbsArgPlot to miss features of f. Increasing the settings for PlotPoints and MaxRecursion will often catch such features.
- Themes that affect curves include:
-

"ThinLines" thin plot lines 
"MediumLines" medium plot lines 
"ThickLines" thick plot lines - The arguments supplied to functions in MeshFunctions and RegionFunction are x, y. Functions in ColorFunction are by default supplied with scaled versions of these arguments.
- ScalingFunctions->"scale" scales the
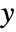 coordinate; ScalingFunctions{"scalex","scaley"} scales both the
coordinate; ScalingFunctions{"scalex","scaley"} scales both the 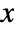 and
and 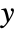 coordinates.
coordinates. - Possible highlighting effects for Highlighted and PlotHighlighting include:
-
style highlight the indicated curve 
"Ball" highlight and label the indicated point in a curve 
"Dropline" highlight and label the indicated point in a curve with droplines to the axes 
"XSlice" highlight and label all points along a vertical slice 
"YSlice" highlight and label all points along a horizontal slice 
Placed[effect,pos] statically highlight the given position pos - Highlight position specifications pos include:
-
x, {x} effect at {x,y} with y chosen automatically {x,y} effect at {x,y} {pos1,pos2,…} multiple positions posi -
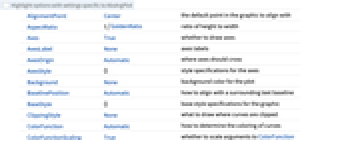
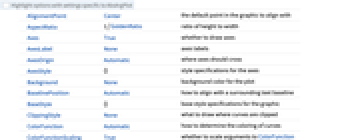
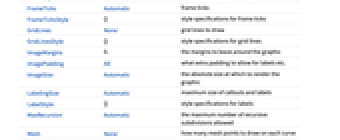
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio 1/GoldenRatio ratio of height to width Axes True whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ClippingStyle None what to draw where curves are clipped ColorFunction Automatic how to determine the coloring of curves ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale arguments to ColorFunction ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate at every function evaluation Exclusions Automatic points in x to exclude ExclusionsStyle None what to draw at excluded points Filling None filling to insert under each curve FillingStyle Automatic style to use for filling FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame False whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels MaxRecursion Automatic the maximum number of recursive subdivisions allowed Mesh None how many mesh points to draw on each curve MeshFunctions {#1&} how to determine the placement of mesh points MeshShading None how to shade regions between mesh points MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh points Method Automatic the method to use for refining curves PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotHighlighting Automatic highlighting effect for curves PlotLabel None overall label for the plot PlotLabels None labels to use for curves PlotLegends None legends for curves PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points PlotRange {Full,Automatic} the range of y or other values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to specify the style for each curve PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RegionFunction (True&) how to determine whether a point should be included RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations
List of all options


Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Plot the modulus of a complex function of a real variable colored by its argument:
Compare Plot and AbsArgPlot:
Scope (18)
Sampling (8)
More points are sampled where the function changes quickly:
The plot range is selected automatically:
The curve is split when there are discontinuities in the function:
Use Exclusions->None to draw connected curves:
Use PlotPoints and MaxRecursion to control adaptive sampling:
The domain can be specified by a region:
Specify a domain using a MeshRegion:
Labeling and Legending (5)
Presentation (5)
Provide explicit styling to different curves:
Use ScalingFunctions to scale the axes:
Options (113)
AspectRatio (4)
By default, AbsArgPlot uses a fixed ratio of the height to the width of the plot:
Make the height the same as the width with AspectRatio1:
AspectRatioAutomatic determines the ratio from the plot ranges:
AspectRatioFull adjusts the height and width to tightly fit inside other constructs:
Axes (4)
By default, Axes is drawn for AbsArgPlot:
Use Frame instead of axes:
Use AxesOrigin to specify where the axes intersect:
AxesLabel (3)
AxesOrigin (2)
AxesStyle (4)
ColorFunction (4)
ColorFunction has higher priority than PlotStyle:
Exclusions (3)
ExclusionStyle (1)
Filling (4)
FillingStyle (2)
Frame (3)
FrameLabel (2)
FrameTicks (8)
FrameTicks are placed automatically by default:
Use frame ticks on the ![]() axes but not the
axes but not the ![]() axes:
axes:
Place frame ticks at specific positions:
Draw frame ticks at the specified positions with specific labels:
Specify the lengths for frame ticks as a fraction on graphics size:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for each frame tick:
Specify a style for each frame tick:
Construct a function that places frame ticks at the midpoint and extremes of the frame edge:
FrameTicksStyle (3)
ImageSize (7)
Use named sizes such as Tiny, Small, Medium and Large:
Specify the width of the plot:
Specify the height of the plot:
Allow the width and height to be up to a certain size:
Specify the width and height for a graphic, padding with space if necessary:
Setting AspectRatioFull will fill the available space:
Use maximum sizes for the width and height:
Use ImageSizeFull to fill the available space in an object:
Specify the image size as a fraction of the available space:
MaxRecursion (1)
Each level of MaxRecursion adaptively subdivides the initial mesh into a finer mesh:
Mesh (3)
MeshFunctions (2)
MeshShading (2)
MeshStyle (2)
PerformanceGoal (2)
PlotHighlighting (8)
Plots have interactive coordinate callouts with the default setting PlotHighlightingAutomatic:
Use PlotHighlightingNone to disable the highlighting for the entire plot:
Move the mouse over the curve to highlight it with a ball and label:
Move the mouse over the curve to highlight it with a label and droplines to the axes:
Move the mouse over the plot to highlight it with a slice showing ![]() values corresponding to the
values corresponding to the ![]() position:
position:
Move the mouse over the plot to highlight it with a slice showing ![]() values corresponding to the
values corresponding to the ![]() position:
position:
Use a component that shows the points on the curve closest to the ![]() position of the mouse cursor:
position of the mouse cursor:
Specify the style for the points:
Use a component that shows the coordinates on the curve closest to the mouse cursor:
Use Callout options to change the appearance of the label:
PlotLabels (6)
Modify the appearance of the labels:
Place the labels differently for each curve:
PlotLabels->"Expressions" uses functions as curve labels:
Use callouts to identify the curves:
Use None to not add a label:
PlotStyle (2)
ScalingFunctions (6)
By default, plots have linear scales in each direction:
Use a logarithm to scale the modulus but leave the argument (color) unscaled:
Use different scales in the ![]() and
and ![]() directions:
directions:
Domains that contain infinite values are scaled automatically:
Use "Reverse" scale in an infinite domain:
Use Interval to focus on a region of interest in an infinite domain:
Ticks (9)
Ticks are placed automatically on each axis:
Use ticks on the ![]() axis but not the
axis but not the ![]() axis:
axis:
Place tick marks at specific positions:
Draw tick marks at the specified positions with the specified labels:
Use specific ticks on one axis and automatic ticks on the other:
Specify the lengths for ticks as a fraction on graphics size:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for each tick:
Specify a style for each tick:
Construct a function that places ticks at the midpoint and extremes of the axis:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (8)
AbsArgPlot is a special case of Plot:
ComplexPlot shows the argument and magnitude of a function using color:
Use ComplexPlot3D to use the ![]() axis for the magnitude:
axis for the magnitude:
Use ReImPlot to plot real and imaginary components over the real numbers:
Use ComplexListPlot to show the location of complex numbers in the plane:
ComplexContourPlot plots curves over the complexes:
ComplexRegionPlot plots regions over the complexes:
ComplexStreamPlot and ComplexVectorPlot treat complex numbers as directions:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2019), AbsArgPlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsArgPlot.html (updated 2023).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2019. "AbsArgPlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2023. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsArgPlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2019). AbsArgPlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsArgPlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_absargplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{AbsArgPlot}", year="2023", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsArgPlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_absargplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={AbsArgPlot}, year={2023}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AbsArgPlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 04-March-2026]}