Single-Aperture Scalar Diffraction
| Introduction | Perfectly Matched Layers in 3D Domains |
| Helmholtz Equations in Electromagnetism | Nomenclature |
| 2D Scalar Diffraction Model | References |
| Perfectly Matched Layers in 2D |
Introduction
The phenomenon of diffraction is fully described by the wave equation. The Huygens–Fresnel principle states that when a wave passes through an obstacle or aperture, every point surrounding the obstacle or inside the aperture acts as a point source of spherical waves. The superposition of those waves produces a wavefront with a characteristic shape [Born & Wolf, 1999]. The intensity profile ![]() [
[
Diffraction is the basic phenomenon behind several modern systems used for sensing and imaging, such as holographic microscopy, crystallography and astronomical observatories. Solving the wave equation is a relevant engineering problem, particularly in systems with sizes comparable with the electromagnetic wavelength ![]() , where integral methods such as Fourier transforms are not accurate [Born & Wolf, 1999].
, where integral methods such as Fourier transforms are not accurate [Born & Wolf, 1999].
Many of the animations of the simulation results shown in this tutorial are generated with a call to Rasterize. This is to reduce the disk space this tutorial requires. The downside is that the visual quality of the animations will not be as crisp as without it. To obtain high-quality graphics, remove or comment out the call to Rasterize.
The symbols and corresponding units used throughout this tutorial are summarized in the Nomenclature section.
Helmholtz Equations in Electromagnetism
In isotropic and non-dispersive media, diffraction can be modeled by the vector-valued source-free Helmholtz partial differential equation [Jackson, 1999]:
Here ![]() is the wave number in the medium
is the wave number in the medium ![]() and is related to the wavelength
and is related to the wavelength ![]() by
by ![]() . The wave number in a material is related to the free space wave number
. The wave number in a material is related to the free space wave number ![]() by
by ![]() , with
, with ![]() the relative permeability and
the relative permeability and ![]() the relative permittivity of the material.
the relative permittivity of the material. ![]() and
and ![]() are a measure of the magnetization and polarization of a material [Jackson, 1999]. In general,
are a measure of the magnetization and polarization of a material [Jackson, 1999]. In general, ![]() and
and ![]() are second-rank tensors. In isotropic materials,
are second-rank tensors. In isotropic materials, ![]() and
and ![]() are scalar constants.
are scalar constants.
As a first approach to numerically solve equation (1), only one component of the electric field is considered. In Cartesian coordinates, the Laplacian of a vector field is the Laplacian of each component ![]() , therefore equation (2) is a set of three independent scalar differential equations. It is worth mentioning that this holds only for materials with diagonal
, therefore equation (2) is a set of three independent scalar differential equations. It is worth mentioning that this holds only for materials with diagonal ![]() and
and ![]() tensors. In anisotropic materials with off-diagonal components, the PDE could have mixed dependent variables.
tensors. In anisotropic materials with off-diagonal components, the PDE could have mixed dependent variables.
It can be shown that the electric field vector describing the field oscillation direction is always perpendicular to the EM wave propagation direction [Born & Wolf, 1999]. This means that an EM wave propagating in the ![]() direction will only contain energy in the
direction will only contain energy in the ![]() and
and ![]() components.
components.
In the case that the field can be described by only one component, for example, in linearly polarized EM waves, the field is said to be a scalar quantity.
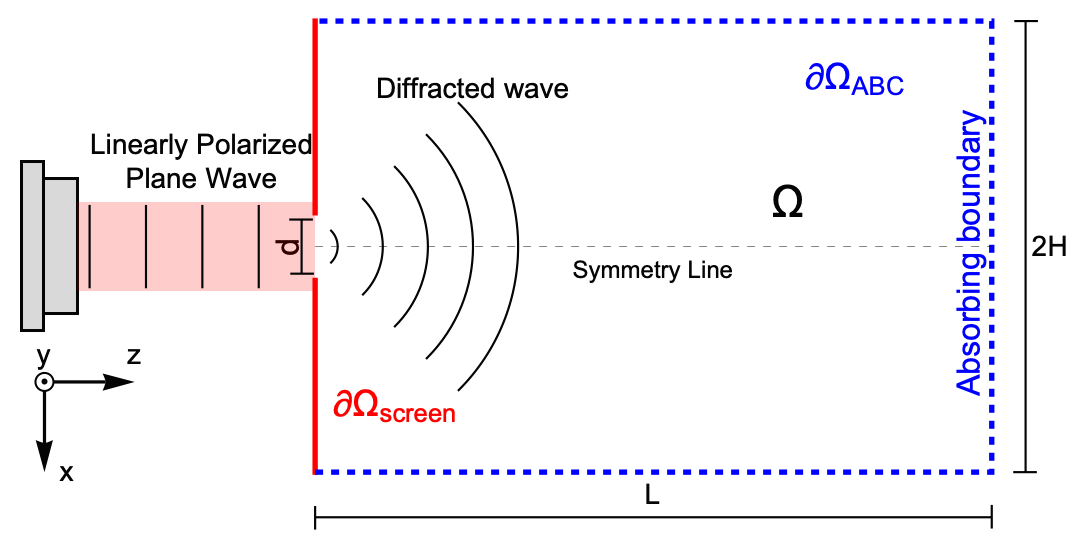
2D Scalar Diffraction Model
This application example considers a helium-neon laser with a free space wavelength ![]() illuminating an opaque screen with an aperture width of
illuminating an opaque screen with an aperture width of ![]() . The aperture is a slit and assumed to be infinitely large in the
. The aperture is a slit and assumed to be infinitely large in the ![]() direction, so there will be no disturbances to the diffracted wave in the
direction, so there will be no disturbances to the diffracted wave in the ![]() direction, hence a system in 2D can be modeled. The laser and aperture itself will be modeled by a radiation boundary condition. The opaque screen is made of a fully absorbing material where light cannot be transmitted or reflected. The boundary
direction, hence a system in 2D can be modeled. The laser and aperture itself will be modeled by a radiation boundary condition. The opaque screen is made of a fully absorbing material where light cannot be transmitted or reflected. The boundary ![]() is an artificial boundary that absorbs incoming light to mimic an open system where light propagates indefinitely without any reflections, therefore the only source of light is the aperture, as the field is
is an artificial boundary that absorbs incoming light to mimic an open system where light propagates indefinitely without any reflections, therefore the only source of light is the aperture, as the field is ![]() in the other boundaries. The simulation domain then has dimensions
in the other boundaries. The simulation domain then has dimensions ![]() and
and ![]() . The laser emits
. The laser emits ![]() polarized plane waves in the
polarized plane waves in the ![]() direction. In an
direction. In an ![]() polarized EM field, there is no energy in the
polarized EM field, there is no energy in the ![]() component. The refractive index inside the region
component. The refractive index inside the region ![]() is 1.
is 1.
The scheme above is rotated 90 degrees for better visualization; in the following, the propagation ![]() axis will be the vertical axis. Also note that the geometry is symmetric along the
axis will be the vertical axis. Also note that the geometry is symmetric along the ![]() direction and that the
direction and that the ![]() direction points outward from the screen.
direction points outward from the screen.
Parameters Setup
Set up the incoming scalar EM wave parameters and the Helmholtz differential operator in equation (3) for the diffracted scalar wave ![]() .
.
The differential operator is in Inactive form to allow for NeumannValue boundary conditions. For more information, read the Formal Partial Differential Equation section.
The HelmholtzPDEComponent could be used to set up the PDE model. However, since perfectly matched layers will be utilized at a later stage, the HelmholtzPDEComponent is less practical for this purpose. To maintain consistency in the workflow across different sections, the PDE is modeled using the basic PDE modeling terms.
Domain
Next, the simulation domain is set up. The simulation domain ![]() is symmetric with the axis of symmetry being the
is symmetric with the axis of symmetry being the ![]() axis, so it is sufficient to simulate half the domain in the
axis, so it is sufficient to simulate half the domain in the ![]() direction.
direction.
The black numbers are the boundary element markers. Marker 1 is assigned to the symmetry line boundary (dashed line), marker 2 indicates the ![]() boundary (blue lines), marker 3 is the
boundary (blue lines), marker 3 is the ![]() boundary (red line), and marker 4 represents half of the aperture boundary, referred to as
boundary (red line), and marker 4 represents half of the aperture boundary, referred to as ![]() (black line) from now on. Recall that
(black line) from now on. Recall that ![]() is an opening, but the incident light is modeled by a boundary condition there.
is an opening, but the incident light is modeled by a boundary condition there.
Now, an element mesh is created from the boundary mesh. Normally, five elements per wavelength are enough to resolve the wave [Jin, 1993]. It is worth mentioning that ![]() is a recommended initial discretization constraint. In some systems, a smaller constant has to be used to provide a precise result. In this case,
is a recommended initial discretization constraint. In some systems, a smaller constant has to be used to provide a precise result. In this case, ![]() will be used to obtain a smoother curve.
will be used to obtain a smoother curve.
Boundary Conditions
All that is left is to set up the conditions for each boundary. Following the theory, the boundary ![]() should be at infinity to eliminate all contributions due to reflections in the boundary [Jin, 1993]. Since the solution over an infinitely larger domain cannot be computed, an artificial absorbing boundary has to be placed on the edge
should be at infinity to eliminate all contributions due to reflections in the boundary [Jin, 1993]. Since the solution over an infinitely larger domain cannot be computed, an artificial absorbing boundary has to be placed on the edge ![]() to avoid reflections. The absorbing boundary condition can also be used for
to avoid reflections. The absorbing boundary condition can also be used for ![]() , as it is an opaque screen that absorbs all the incoming light. Using a first-order Padé absorbing boundary condition (ABC) [Jin, 1993]:
, as it is an opaque screen that absorbs all the incoming light. Using a first-order Padé absorbing boundary condition (ABC) [Jin, 1993]:
More information about absorbing boundary conditions and radiation conditions can be found in Acoustics in the Time Domain.
The incoming wave illuminating the aperture in ![]() can be modeled with a radiation boundary condition of the form:
can be modeled with a radiation boundary condition of the form:
with ![]() the boundary normal,
the boundary normal, ![]() the incoming EM wave propagation direction and
the incoming EM wave propagation direction and ![]() the EM wave amplitude. The boundary condition is a sum of two terms, a light incidence term
the EM wave amplitude. The boundary condition is a sum of two terms, a light incidence term ![]() and an absorbing boundary condition term
and an absorbing boundary condition term ![]() .
.
The second term is needed to ensure that the boundary ![]() does not reflect EM waves and only the incident light flows outward from the boundary. In this case, both the boundary normal and the wave propagation direction are in the
does not reflect EM waves and only the incident light flows outward from the boundary. In this case, both the boundary normal and the wave propagation direction are in the ![]() direction, therefore the inner product is 1.
direction, therefore the inner product is 1. ![]() will be set to 1.
will be set to 1.
The axis of symmetry on the element boundary marker 1 can be modeled with a Neumann 0 value. This is the default boundary condition if nothing else is specified on a boundary.
Model Evaluation
Compute the numeric solution of the PDE with NDSolve.
Visualization
See this note about improving the visual quality of the animation.
See this note about improving the visual quality of the image.
The intensity plot above shows that the electric field concentrates around the ![]() axis; therefore, using an overly fine mesh far away from the center region may be unnecessarily computationally expensive. A variable max cell measure, set up with a MeshRefinementFunction, can reduce the number of mesh elements while conserving precision in relevant regions.
axis; therefore, using an overly fine mesh far away from the center region may be unnecessarily computationally expensive. A variable max cell measure, set up with a MeshRefinementFunction, can reduce the number of mesh elements while conserving precision in relevant regions.
As indicated above, absorbing boundary conditions (![]() ) are an approximate boundary condition to model infinite domains. In the plot above, fluctuations can be seen as
) are an approximate boundary condition to model infinite domains. In the plot above, fluctuations can be seen as ![]() approaches
approaches ![]() . These fluctuations are due to undesired reflections at the absorbing boundary condition. In the following section, a different, more accurate approach to truncating the computational domain of an open system is introduced.
. These fluctuations are due to undesired reflections at the absorbing boundary condition. In the following section, a different, more accurate approach to truncating the computational domain of an open system is introduced.
Perfectly Matched Layers in 2D
Absorbing boundary conditions ![]() , like those used above, are not a perfect absorbing boundary. Some reflection may occur when the incidence angles of the wave deviate too much from the surface normal [Jin, 1993]. As a result, undesired fluctuations can appear. A better approach to truncating the computational domain is perfectly matched layers (PML).
, like those used above, are not a perfect absorbing boundary. Some reflection may occur when the incidence angles of the wave deviate too much from the surface normal [Jin, 1993]. As a result, undesired fluctuations can appear. A better approach to truncating the computational domain is perfectly matched layers (PML).
The basic ideal of PML is to add an additional layer around the simulation domain that is highly absorptive. As soon as the wave leaves the regular simulation domain and enters the PML, the wave will be attenuated quickly. A PML layer can be understood as a highly absorbing inhomogeneous orthotropic material. Orthotropic materials are a subgroup of anisotropic materials where only the main directions ![]() of a material differ but not the off-diagonal directions, so
of a material differ but not the off-diagonal directions, so  . In this case, orthotropic materials are described by a position-dependent permittivity tensor
. In this case, orthotropic materials are described by a position-dependent permittivity tensor ![]() . In absorbing media, the relative permittivity is complex valued
. In absorbing media, the relative permittivity is complex valued ![]() , where
, where ![]() describes the medium's polarizability and
describes the medium's polarizability and ![]() the absorptive properties of the material. In the 2D model, the values
the absorptive properties of the material. In the 2D model, the values ![]() are used for the
are used for the ![]() and
and ![]() directions.
directions.
A more detailed introduction to PML can be found in the acoustic time and frequency domain tutorials.
Domain
To make use of PMLs, the physical region ![]() needs to be extended by an extra layer of length
needs to be extended by an extra layer of length ![]() , which will be the PML region. In this region, the incoming wave will be damped out.
, which will be the PML region. In this region, the incoming wave will be damped out.
Boundaries 1 to 4 are the same as before, but now boundaries 2 are not absorbing boundary conditions, as the domain is truncated with a PML region. Boundaries with marker 5 (green) mark the end of the PML region, and boundaries with marker 6 (orange) are needed to define three separate regions with different PML parameters.
Earlier, an uniform element mesh was created with a constant max cell measure. However, it was observed from the intensity profiles that the intensity in regions far away from the ![]() axis is negligible. To address this, a MeshRefinementFunction can be applied to generate a finer mesh in areas with specific coordinates and to set up region markers for the PML regions. In 2D, a MeshRefinementFunction operates based on the element area. The area of the mesh's triangle elements can be approximated by the area of an equilateral triangle. The area satisfying the
axis is negligible. To address this, a MeshRefinementFunction can be applied to generate a finer mesh in areas with specific coordinates and to set up region markers for the PML regions. In 2D, a MeshRefinementFunction operates based on the element area. The area of the mesh's triangle elements can be approximated by the area of an equilateral triangle. The area satisfying the ![]() constraint is
constraint is ![]() .
.
The use of Rasterize above helps to reduce the size of the graphics. For a better visual appearance, the Rasterize can be removed.
Parameter Setup
As the PML layer ![]() is a diagonal tensor, (4) can still be applied. Inside the physical region,
is a diagonal tensor, (4) can still be applied. Inside the physical region, ![]() and
and ![]() to obtain the same PDE as in the initial example. In the PML region,
to obtain the same PDE as in the initial example. In the PML region, ![]() will be an increasing function with maximum value
will be an increasing function with maximum value ![]() .
.
The use of Rasterize above helps to reduce the size of the graphics. For a better visual appearance, the Rasterize can be removed.
In the ![]() function plots, it can be seen that the absorbing coefficient behaves as a wall in each direction outside the region
function plots, it can be seen that the absorbing coefficient behaves as a wall in each direction outside the region ![]() , while leaving the electric field unchanged inside the region
, while leaving the electric field unchanged inside the region ![]() .
.
Boundary Conditions
Use the same boundary conditions for the incident light boundary and screen. Recall that absorbing boundary conditions ![]() are not needed now.
are not needed now.
Boundaries 1, 2, 5 and 6 will have the default Neumann 0 value.
Model Evaluation
Visualization
See this note about improving the visual quality of the animation.
As ![]() approaches
approaches ![]() , no fluctuations are present with the PML approach.
, no fluctuations are present with the PML approach.
As observed, a regular fluctuating error exists between the two approaches, stemming from undesired reflections caused by the absorbing boundaries.
Model Verification
So far, the numerical solution of the absorbing boundary condition approach has been compared with the perfectly matched layer (PML) approach. Next, the PML solution will be verified against an analytical solution. To verify the model, the integral diffraction formula deduced with Green's method [Ishimarou, 1991] can be used
where ![]() is a surface enclosing the region of interest,
is a surface enclosing the region of interest, ![]() is the Green function of the system and
is the Green function of the system and ![]() is the normal derivative. The integral can be solved using three different types of boundary conditions (BC) for
is the normal derivative. The integral can be solved using three different types of boundary conditions (BC) for ![]() . Dirichlet
. Dirichlet ![]() or Neumann
or Neumann ![]() BC, often called type 1 or 2 Sommerfeld's conditions, respectively, or both Dirichlet and Neumann BC, which are called Kirchhoff's boundary conditions [Wolf & Marchand, 1964]. Although Kirchhoff's BC are the most commonly used, it is mathematically inconsistent, as the assumed BC are not retrieved from the solution [Wolf & Marchand, 1964]. It is worth mentioning that all three BC give the same result in the far field [Wolf & Marchand, 1964].
BC, often called type 1 or 2 Sommerfeld's conditions, respectively, or both Dirichlet and Neumann BC, which are called Kirchhoff's boundary conditions [Wolf & Marchand, 1964]. Although Kirchhoff's BC are the most commonly used, it is mathematically inconsistent, as the assumed BC are not retrieved from the solution [Wolf & Marchand, 1964]. It is worth mentioning that all three BC give the same result in the far field [Wolf & Marchand, 1964].
In practice, the integration is not done along the entire surface, as explained in the 2D scalar diffraction model section. Only the ![]() boundary contributes to the integral. In 2D, the Green function is a Hankel function of second kind of order 0. Additionally, type 1 Sommerfeld's condition [Ishimarou, 1991] will be employed. The theoretical solution is:
boundary contributes to the integral. In 2D, the Green function is a Hankel function of second kind of order 0. Additionally, type 1 Sommerfeld's condition [Ishimarou, 1991] will be employed. The theoretical solution is:
where ![]() is the Euclidian distance between any point
is the Euclidian distance between any point ![]() at
at ![]() and a point
and a point ![]() inside the region
inside the region ![]() . As the aperture is a line, the normal is a vector in the
. As the aperture is a line, the normal is a vector in the ![]() direction.
direction.
The discrepancy between the theoretical and numerical solutions near ![]() can be attributed to the fact that the analytical solution does not retrieve the imposed BC; for instance, the Sommerfeld type 1 integral presents divergences near the
can be attributed to the fact that the analytical solution does not retrieve the imposed BC; for instance, the Sommerfeld type 1 integral presents divergences near the ![]() plane. Also, recall that the aperture boundary condition is the sum of light incidence and absorbing boundary conditions. This approximate absorbing boundary condition term in the radiation boundary condition
plane. Also, recall that the aperture boundary condition is the sum of light incidence and absorbing boundary conditions. This approximate absorbing boundary condition term in the radiation boundary condition ![]() may cause some fluctuations starting from
may cause some fluctuations starting from ![]() . Also note that these fluctuations reduce the further the wave travels into the domain.
. Also note that these fluctuations reduce the further the wave travels into the domain.
For more information about the analytical solution and Kirchhoff–Sommerfeld approaches, see [Buchwald & Yeang, 2016][Totzeck, 1991][Heurtley, 1973].
As a note, the high-frequency fluctuations in the error plot along the propagation direction can be eliminated by decreasing mesh element length to ![]() .
.
Perfectly Matched Layers in 3D Domains
In the previous section, a 2D PML was implemented. Now, the focus shifts to calculating the diffraction of waves by a 2D circular aperture in a 3D domain. Calculating 3D regions can be computationally expensive, so the analysis will be restricted to leveraging the symmetry of the system to analyze only a portion of the domain.
Parameters Setup
Set up the incoming scalar EM wave parameters to ![]() and the 3D Helmholtz differential operator with the orthotropic relative permittivity for the 3D PML region. The diffracted scalar wave will be labeled
and the 3D Helmholtz differential operator with the orthotropic relative permittivity for the 3D PML region. The diffracted scalar wave will be labeled ![]() .
.
Domain
First, set up a cubic domain in the positive octant including the PML region. Use OpenCascadeLink to join the regions, conserving the inner boundaries.
The OpenCascadeLink tutorial has more detailed information on generating objects with internal boundaries.
The green boundaries enclose the PML volume, the blue boundaries are the symmetry planes, and the red plane contains ![]() of the
of the ![]() and
and ![]() boundaries. The yellow disk represents one-quarter of the aperture. In some cases, it is hard to create separate boundaries for the aperture and screen, therefore a function will be used to set up the radiation and absorbing boundary condition at the same time in the red plane.
boundaries. The yellow disk represents one-quarter of the aperture. In some cases, it is hard to create separate boundaries for the aperture and screen, therefore a function will be used to set up the radiation and absorbing boundary condition at the same time in the red plane.
In this case, the MeshRefinementFunction will dependent on the volume of the mesh element. In this case, the recommended ![]() edge length will be used. The volume for the TetrahedronElement could be calculated as
edge length will be used. The volume for the TetrahedronElement could be calculated as ![]() to fulfill the
to fulfill the ![]() edge length constraint.
edge length constraint.
See this note about improving the visual quality of the image.
The mesh appears finer near the left corner and coarser at the upper-right corner. Please note that the aperture depicted in yellow is included for visualization purposes only and is not part of the mesh.
Visualizing 3D meshes can be complicated. A Manipulate provides an easier way to visualize the 3D regions and ElementMarker in 3D individually. To reduce the size of this notebook, a second element mesh is generated for visualization purposes only.
Visualize the boundary element markers groups to find the ElementMarker for the aperture.
Boundary Conditions
Earlier, the ![]() and
and ![]() boundaries were separated, but setting up proper boundaries can be challenging for complex geometries or 3D regions. A better approach for those cases is to use a function to distinguish between the conditions
boundaries were separated, but setting up proper boundaries can be challenging for complex geometries or 3D regions. A better approach for those cases is to use a function to distinguish between the conditions ![]() and
and ![]() . From equation (5), it is evident that setting
. From equation (5), it is evident that setting ![]() to
to ![]() restores equation (6). Therefore, both conditions
restores equation (6). Therefore, both conditions ![]() and
and ![]() can be set using a function that is
can be set using a function that is ![]() at the aperture and
at the aperture and ![]() at the screen.
at the screen.
The next step is to create a function for a circular aperture of diameter ![]() .
.
Now, the unified boundary condition ![]() can be created.
can be created.
The surface boundaries with ElementMarker 1 and 5 are the surfaces of symmetry for this region and can be modeled with a Neumann 0 value. This is the default boundary condition if nothing else is specified on a boundary.
Perfectly Matched Layer Parameter Setup
Knowing the region markers, the PML absorbing coefficients can now be set up.
Model Evaluation
Visualization
See this note about improving the visual quality of the animation.
See this note about improving the visual quality of the animation.
The density plot shows the characteristic ring-like pattern of circular apertures. For long propagation distances, this pattern will evolve into a order-0 Bessel function of the first kind.
Model Verification
In 3D, the Green function of the system is spherical waves of the form ![]() . Replacing the Green function in equation (7) results in:
. Replacing the Green function in equation (7) results in:
where ![]() is the Euclidian distance between any point
is the Euclidian distance between any point ![]() at
at ![]() and a point
and a point ![]() inside the region
inside the region ![]() . To make use of the analytical result, a helper function is set up.
. To make use of the analytical result, a helper function is set up.
As a summary, absorbing boundary conditions (ABCs) are useful for a quick problem setup, but if accuracy is essential, perfectly matched layers (PMLs) are a better choice.
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description | Unit |
| E | Electric field | [V/m] |
| λn | Wavelength | [m] |
| kn | Wave number | [1/m] |
| μr | Relative permeability | N/A |
| ϵr | Relative permittivity | N/A |
| L | Propagation region length | [μm] |
| H | Propagation region width | [μm] |
| d | Aperture size | [m] |
| Γscreen | Opaque screen boundary | N/A |
| Γaperture | Aperture boundary | N/A |
| ΓABC | Absorbing boundary | N/A |
| Ω | Propagation region | N/A |
References
1. Born, M. and Wolf, E. (1999). Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light (7th ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
2. Jackson, J. D. Classical Electrodynamics. New York :Wiley, 1999.
3. Jin, J.-M. The Finite Element Method in Electromagnetics. John Wiley & Sons, 2015.
4. A. Ishimarou, Electromagnetic Wave Propagation, Radiation, and Scattering. Prentice Hall, 1991.
5. Wolf, E. and Marchand, E. W. "Comparison of the Kirchhoff and the Rayleigh–Sommerfeld Theories of Diffraction at an Aperture." Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1964, 54(5), p. 587. doi:10.1364/josa.54.000587
6. Buchwald, J. Z. and Yeang, C. P. "Kirchhoff’s Theory for Optical Diffraction, Its Predecessor and Subsequent Development: The Resilience of an Inconsistent Theory." Archive for History of Exact Sciences 70, pp. 463–511 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00407-016-0176-1
7. Totzeck, M. (1991). "Validity of the Scalar Kirchhoff and Rayleigh–Sommerfeld Diffraction Theories in the Near Field of Small Phase Objects." Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1991, 8(1), p. 27. doi:10.1364/josaa.8.000027
8. Heurtley, J. C. "Scalar Rayleigh–Sommerfeld and Kirchhoff Diffraction Integrals: A Comparison of Exact Evaluations for Axial Points*." Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1973, 63(8), p. 1003. doi:10.1364/josa.63.001003