Arg[z]
gives the argument of the complex number z.


Arg
Arg[z]
gives the argument of the complex number z.
Details

- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- Arg[z] is left unevaluated if z is not a numeric quantity.
- Arg[z] gives the phase angle of z in radians.
- The result from Arg[z] is always between
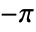 and
and 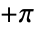 .
. - Arg[z] has a branch cut discontinuity in the complex z plane running from
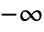 to 0.
to 0. - Arg[0] gives 0.
- Arg automatically threads over lists. »
- Arg can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (33)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
For real inputs, the result is exact:
For complex inputs, the precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
Compute the elementwise values of an array using automatic threading:
Or compute the matrix Arg function using MatrixFunction:
Arg can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Specific Values (6)
Visualization (5)
Function Properties (11)
Arg is defined for all real and complex inputs:
Function range of Arg for real inputs:
Except on the negative reals, ![]() :
:
Arg is not a differentiable function:
The difference quotient does not have a limit in the complex plane:
There is only a limit in certain directions, for example, the real direction:
Use ComplexExpand to get differentiable expressions for real-valued variables:
Arg is not an analytic function:
It has both singularities and discontinuities:
Over the complex plane, it is singular everywhere and discontinuous on the non-positive reals:
Arg is nonincreasing:
Arg is not injective:
Arg is not surjective:
Arg is non-negative:
Arg is neither convex nor concave:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Applications (3)
Polar decomposition of a complex number:
Color a plot according to value of Arg:
Expand multivalued functions without making assumptions about variables:
Properties & Relations (7)
Simplify expressions containing Arg:
Generate Arg from FullSimplify:
Use Arg as a target function in ComplexExpand:
Rescale Arg to run from 0 to 1:
Find the domain of positivity for a linear function:
Use Arg to specify assumptions about complex variables:
ComplexPlot plots the phase of a function using color and shades by the magnitude:
Possible Issues (4)
Degenerate cases give intervals as results:
Arg is a function of a complex variable and is therefore not differentiable:
As a complex function, it is not possible to write Arg[z] without involving Conjugate[z]:
In particular, the limit that defines the derivative is direction dependent and therefore does not exist:
Use ComplexExpand to get differentiable expressions for real-valued variables:
Numerical decision procedures with default settings cannot simplify this expression:
The machine-precision result is incorrect:
The arbitrary-precision result indicates that the result may be incorrect:
Using a larger setting for $MaxExtraPrecision gives the correct result:
The input contains a hidden zero, and simplifying the argument gets the correct answer:
The argument principle of complex analysis cannot be used because Arg has range ![]() :
:
Neat Examples (1)
See Also
ArcTan Sign Abs AbsArg Im Re Conjugate ToPolarCoordinates
Function Repository: UnwindingNumber
Tech Notes
Related Links
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2021 (13.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Arg, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Arg.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Arg." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Arg.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Arg. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Arg.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_arg, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Arg}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Arg.html}", note=[Accessed: 03-December-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_arg, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Arg}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Arg.html}, note=[Accessed: 03-December-2025]}