ElectrostaticPDEComponent[vars,pars]
yields an electrostatic PDE term with variables vars and parameters pars.


ElectrostaticPDEComponent
ElectrostaticPDEComponent[vars,pars]
yields an electrostatic PDE term with variables vars and parameters pars.
Details





- ElectrostaticPDEComponent is typically used to generate an electrostatic equation with model variables vars and model parameters pars.
- ElectrostaticPDEComponent returns a sum of differential operators to be used as a part of partial differential equations:
- ElectrostaticPDEComponent models static electric fields produced by stationary charges in insulating, or dielectric materials.
- ElectrostaticPDEComponent models electrostatic phenomena with the dependent variable
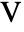 , the electric scalar potential.
, the electric scalar potential. 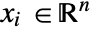 is in units of volt [
is in units of volt [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "V", volts, "Volts"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "V", volts, "Volts"}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/6.png) ], independent variables
], independent variables  in units of [
in units of [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "m", meters, "Meters"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "m", meters, "Meters"}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/8.png) ].
]. - Stationary variables vars are vars={V[x1,…,xn],{x1,…,xn}}.
- ElectrostaticPDEComponent generally does not produces a time-dependent PDE.
- ElectrostaticPDEComponent is based on a diffusion, a source and a derivative PDE term:
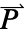 is the vacuum permittivity in units of [
is the vacuum permittivity in units of [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"F", , "/", , "m"}, farads per meter, {{(, "Farads", )}, /, {(, "Meters", )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"F", , "/", , "m"}, farads per meter, {{(, "Farads", )}, /, {(, "Meters", )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/11.png) ],
], 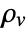 the polarization vector in units of [
the polarization vector in units of [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/13.png) ] and
] and 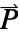 the volume charge density in units of [
the volume charge density in units of [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, coulombs per meter cubed, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, coulombs per meter cubed, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/15.png) ].
]. - The polarization vector
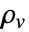 specifies the density of permanent or induced electric dipole moments inside a material.
specifies the density of permanent or induced electric dipole moments inside a material. - The volume charge density
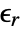 models charge distributions, negative or positive.
models charge distributions, negative or positive. - ElectrostaticPDEComponent can produce different equations, depending on the constitutive relationship.
- For linear materials, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation simplifies to:
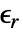 is the unitless relative permittivity.
is the unitless relative permittivity.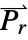 can be isotropic, orthotropic or anisotropic.
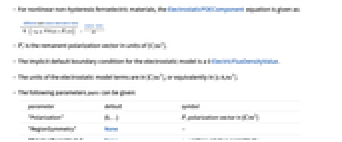
can be isotropic, orthotropic or anisotropic.- For nonlinear non-hysteresis ferroelectric materials, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation is given as:
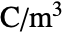 is the remanent polarization vector in units of [
is the remanent polarization vector in units of [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/23.png) ].
].- The implicit default boundary condition for the electrostatic model is a 0 ElectricFluxDensityValue.
- The units of the electrostatic model terms are in [
![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, coulombs per meter cubed, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, coulombs per meter cubed, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/24.png) ], or equivalently in [
], or equivalently in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"s", , "A", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, second amperes per meter cubed, {{(, {"Amperes", , "Seconds"}, )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"s", , "A", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, second amperes per meter cubed, {{(, {"Amperes", , "Seconds"}, )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/25.png) ].
]. - The following parameters pars can be given:
-
parameter default symbol "Polarization" {0,…} 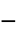 , polarization vector in [
, polarization vector in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/27.png) ]
]"RegionSymmetry" None 
"RelativePermittivity" 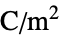 , unitless relative permittivity
, unitless relative permittivity
"RemanentPolarization" {0,…} 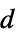 , remanent polarization vector in [
, remanent polarization vector in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, coulombs per meter squared, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/31.png) ]
]"Thickness" 1 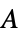 , thickness in [
, thickness in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "m", meters, "Meters"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "m", meters, "Meters"}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/33.png) ]
] "CrossSectionalArea" 1 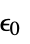 , cross-sectional area in [
, cross-sectional area in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {{"m", ^, 2}}, meters squared, {"Meters", ^, 2}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {{"m", ^, 2}}, meters squared, {"Meters", ^, 2}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/35.png) ]
] "VacuumPermittivity" 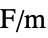
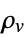 , vacuum permittivity in [
, vacuum permittivity in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"F", , "/", , "m"}, farads per meter, {{(, "Farads", )}, /, {(, "Meters", )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"F", , "/", , "m"}, farads per meter, {{(, "Farads", )}, /, {(, "Meters", )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/38.png) ]
] "VolumeChargeDensity" 0 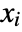 , volume charge density in [
, volume charge density in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, coulombs per meter cubed, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"C", , "/", , {"m", ^, 3}}, coulombs per meter cubed, {{(, "Coulombs", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 3}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.en/40.png) ]
] - All parameters may depend on the spacial variable
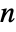 and dependent variable
and dependent variable 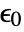 .
. - The number of independent variables
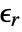 determines the dimensions of
determines the dimensions of 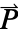 or
or 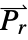 and the length of vectors
and the length of vectors 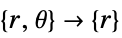 and
and 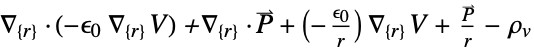 .
. - A possible choice for the parameter "RegionSymmetry" is "Axisymmetric".
- "Axisymmetric" region symmetry represents a truncated cylindrical coordinate system where the cylindrical coordinates are reduced by removing the angle variable as follows:
-
dimension reduction equation 1D 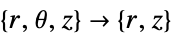
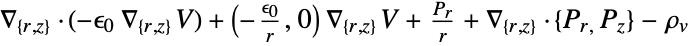
2D 
- In 2D, when a "Thickness"
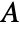 is specified, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation is given as:
is specified, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation is given as: - In 1D, when a "CrossSectionalArea"
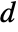 is specified, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation is given as:
is specified, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation is given as: - In a 1D axisymmetric, when a "Thickness"
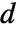 is specified, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation is given as:
is specified, the ElectrostaticPDEComponent equation is given as: - The input specification for the parameters is exactly the same as for their corresponding operator terms.
- If no parameters are specified, the default electrostatic PDE is:
- If the ElectrostaticPDEComponent depends on parameters
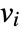 that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters
that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters 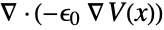 are replaced with
are replaced with  .
.
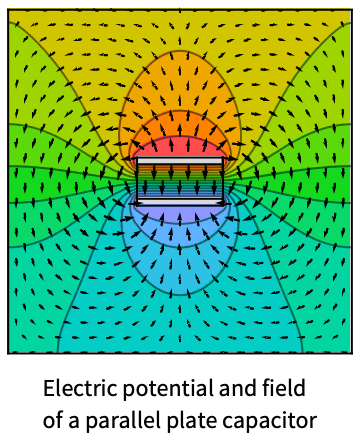
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (14)
1D (4)
Define a 1D electrostatic model with a cross-sectional area ![]() :
:
Model an electric potential field with two electric potential conditions at the sides.
Specify model variables and electrostatic parameters:
Set up and solve an electrostatic PDE:
Model an electric potential field with two electric potential conditions at the sides and a discontinuous relative permittivity.
Specify model variables and electrostatic parameters:
2D (5)
2D Axisymmetric (2)
3D (1)
Multi-material (2)
Applications (4)
1D (2)
Compute the electric potential distribution between two parallel plates separated by a distance ![]() [
[![]() ] and positioned normal to the
] and positioned normal to the ![]() axis. The left plate is maintained at a constant potential
axis. The left plate is maintained at a constant potential ![]() [
[![]() ], whereas the right plate is grounded,
], whereas the right plate is grounded, ![]() [
[![]() ]. The region between the plates is characterized by a relative permittivity
]. The region between the plates is characterized by a relative permittivity ![]() and a uniform electron charge density
and a uniform electron charge density ![]() [
[![]() ]. The equation to model is given by:
]. The equation to model is given by:
Set up the electrostatic model variables ![]() :
:
Specify electrostatic model parameters:
Specify the electric potential conditions:
Compute the electrical potential distribution between two parallel plates with the same distance and boundary conditions as in the previous example, but now with a nonuniform charge distribution given by: ![]()
Set up the electrostatic model variables ![]() :
:
Specify electrostatic model parameters:
2D (1)
Model an infinitely long rectangular box with metallic walls. The box has a width of ![]() [
[![]() ], and a height of
], and a height of ![]() [
[![]() ]. The side and bottom walls are maintained at zero electric potential, whereas the top wall has a fixed electric potential of
]. The side and bottom walls are maintained at zero electric potential, whereas the top wall has a fixed electric potential of ![]() . The region inside the box is free of charge
. The region inside the box is free of charge ![]() . The equation to model is given by:
. The equation to model is given by:
Define the model variables and parameters:
Set up a 2D electrostatic model:
The side and bottom walls at ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are maintained at a zero electric potential:
are maintained at a zero electric potential:
3D (1)
Model a dielectric material of a cylindrical capacitor with two electric potential conditions at the upper and lower boundaries, which represent the capacitor electrodes. The equation to model is given by:
Set up the electrostatic model variables ![]() :
:
Specify a relative permittivity ![]() :
:
Specify ground potential at the lower boundary:
Possible Issues (1)
For symbolic computation, the "VacuumPermittivity" or "RelativePermittivity" parameter should be given as a matrix:
For numeric values, the "VacuumPermittivity" or "RelativePermittivity" parameter is automatically converted to a matrix of proper dimensions:
This automatic conversion is not possible for symbolic input:
Not providing the properly dimensioned matrix will result in an error:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2024), ElectrostaticPDEComponent, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2024. "ElectrostaticPDEComponent." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2024). ElectrostaticPDEComponent. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_electrostaticpdecomponent, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ElectrostaticPDEComponent}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.html}", note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_electrostaticpdecomponent, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ElectrostaticPDEComponent}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ElectrostaticPDEComponent.html}, note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}