finds a Hamiltonian cycle in the graph g.
FindHamiltonianCycle[g,k]
finds at most k Hamiltonian cycles.
FindHamiltonianCycle[{vw,…},…]
uses rules vw to specify the graph g.


FindHamiltonianCycle
finds a Hamiltonian cycle in the graph g.
FindHamiltonianCycle[g,k]
finds at most k Hamiltonian cycles.
FindHamiltonianCycle[{vw,…},…]
uses rules vw to specify the graph g.
Details and Options

- A Hamiltonian cycle visits each vertex exactly once.
- FindHamiltonianCycle returns a list of paths consisting of Hamiltonian cycles.
- FindHamiltonianCycle returns the list {} if no Hamiltonian cycles exist.
- FindHamiltonianCycle[g] is equivalent to FindHamiltonianCycle[g,1].
- FindHamiltonianCycle[g,All] finds all Hamiltonian cycles in the graph g.
- FindHamiltonianCycle works with undirected graphs, directed graphs, multigraphs, and mixed graphs.
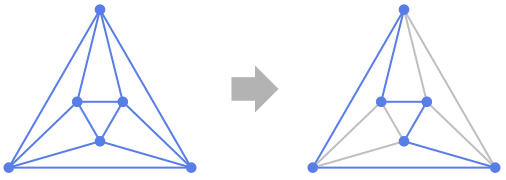
Background & Context
- FindHamiltonianCycle attempts to find one or more distinct Hamiltonian cycles, also called Hamiltonian circuits, Hamilton cycles, or Hamilton circuits. Cycles are returned as a list of edge lists or as {} if none exist. A Hamiltonian cycle (more properly called a Hamiltonian circuit when the cycle is identified using an explicit path with particular endpoints) is a consecutive sequence of distinct edges such that the first and last edges coincide at their endpoints and in which each vertex appears exactly once. A Hamiltonian cycle is therefore a graph cycle of length
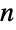 , where
, where 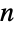 is the number of nodes in the graph. Hamiltonian cycles are used to reconstruct genome sequences, to solve some games (most obviously the Icosian game), to find a knight's tour on a chessboard, and to find attractive circular embeddings for regular graphs. A graph possessing a Hamiltonian cycle is known as a Hamiltonian graph.
is the number of nodes in the graph. Hamiltonian cycles are used to reconstruct genome sequences, to solve some games (most obviously the Icosian game), to find a knight's tour on a chessboard, and to find attractive circular embeddings for regular graphs. A graph possessing a Hamiltonian cycle is known as a Hamiltonian graph. - FindHamiltonianCycle[g,k] attempts to find k Hamiltonian cycles, where the count specification k may be omitted (in which case it is taken as 1), may be a positive integer, or may be All.
- Finding a Hamiltonian cycle is an NP-complete problem. However, various heuristic algorithms exist that sometimes (but not always) can find Hamiltonian cycles very quickly. For this reason, simply permuting the vertices in a graph may give a different runtime for FindHamiltonianCycle.
- A graph may be tested to see if it is Hamiltonian using HamiltonianGraphQ. FindShortestTour is another function that attempts to find a single Hamiltonian cycle on a graph (or a more generally specified set of vertices), with the advantage that it sometimes succeeds more quickly than FindHamiltonianCycle.
- While Hamiltonian cycles in an
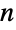 -node graph correspond to cycles of length
-node graph correspond to cycles of length 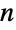 , a cycle of arbitrary length may be found using FindCycle. Hamiltonian cycles visit all vertices, but do not necessarily pass through each edge. A cycle that visits each edge exactly once is known as an Eulerian cycle and may be found using FindEulerianCycle.
, a cycle of arbitrary length may be found using FindCycle. Hamiltonian cycles visit all vertices, but do not necessarily pass through each edge. A cycle that visits each edge exactly once is known as an Eulerian cycle and may be found using FindEulerianCycle.
Examples
open all close allScope (8)
FindHamiltonianCycle works with undirected graphs:
Find several Hamiltonian cycles:
Use rules to specify the graph:
FindHamiltonianCycle returns an empty result for non-Hamiltonian graphs:
FindHamiltonianCycle works with large graphs:
Applications (5)
Solve the Icosian game [MathWorld] by finding a Hamiltonian cycle along the edges of the dodecahedron:
On a labeled dodecahedron, find Hamiltonian cycles that contain a given sequence of labels:
Obtain cycles containing the sequence B, C, P, N, M:
Find a sequence of moves by a knight chess piece that visits each square of an 8×8 chessboard exactly once:
Graph-based assembly of a circular genome "ATGGCGTGCA" with vertices as k-mers and edges as pairwise alignments:
The Gray code of order ![]() is a Hamiltonian cycle of the hypercube graph
is a Hamiltonian cycle of the hypercube graph ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (5)
Use GraphData for an extensive collection of Hamiltonian graphs:
Test whether a graph has a Hamiltonian cycle by using HamiltonianGraphQ:
Hamiltonian graphs are biconnected:
The line graph of a Hamiltonian graph has a Hamiltonian cycle:
The line graph of an Eulerian graph has a Hamiltonian cycle:
An undirected graph with ![]() vertices and minimal degree greater than
vertices and minimal degree greater than ![]() has a Hamiltonian cycle:
has a Hamiltonian cycle:
A directed graph with ![]() vertices and minimum degree greater than
vertices and minimum degree greater than ![]() has a Hamiltonian cycle:
has a Hamiltonian cycle:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2010 (8.0) | Updated in 2012 (9.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2015 (10.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), FindHamiltonianCycle, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindHamiltonianCycle.html (updated 2015).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "FindHamiltonianCycle." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2015. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindHamiltonianCycle.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). FindHamiltonianCycle. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindHamiltonianCycle.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_findhamiltoniancycle, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FindHamiltonianCycle}", year="2015", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindHamiltonianCycle.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_findhamiltoniancycle, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FindHamiltonianCycle}, year={2015}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindHamiltonianCycle.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}