GaborMatrix[r,k]
gives a matrix that corresponds to the real part of a Gabor kernel of radius r and wave vector k.
GaborMatrix[r,k,ϕ]
uses phase shift ϕ.
GaborMatrix[{r,σ},…]
uses the specified standard deviation σ.
GaborMatrix[{{r1,r2,…}},…]
gives an array corresponding to a Gabor kernel with radius ri in the i![]() index direction.
index direction.


GaborMatrix
GaborMatrix[r,k]
gives a matrix that corresponds to the real part of a Gabor kernel of radius r and wave vector k.
GaborMatrix[r,k,ϕ]
uses phase shift ϕ.
GaborMatrix[{r,σ},…]
uses the specified standard deviation σ.
GaborMatrix[{{r1,r2,…}},…]
gives an array corresponding to a Gabor kernel with radius ri in the i![]() index direction.
index direction.
Details and Options

- GaborMatrix[{r,σ},k,ϕ] gives values proportional to
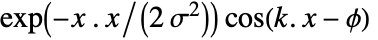 at index position
at index position 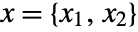 from the center.
from the center. - GaborMatrix[r,k] is equivalent to GaborMatrix[{r,r/2},k,0].
- By default, the matrix is rescaled so that the elements of Abs[GaborMatrix[r,k,0]+I GaborMatrix[r,k,π/2]] sum to 1.
- For integer r, GaborMatrix[r,…] yields a
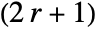 ×
×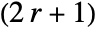 matrix.
matrix. - For noninteger r, the value of r is effectively rounded to an integer.
- Either of the r or σ can be lists, specifying different values for different directions.
- With GaborMatrix[{r,{σ1,σ2,…}},k], σ1 is the standard deviation along k, and σ2, … are standard deviations perpendicular to k. The i
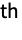 direction is defined by the i
direction is defined by the i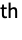 column of RotationMatrix[{{1,0,…},k}].
column of RotationMatrix[{{1,0,…},k}]. - For data arrays with n dimensions and a wave vector {k1,…,kn}, ki is pointing in the same direction as the i
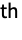 dimension of data. For images, the filter is effectively applied to ImageData[image].
dimension of data. For images, the filter is effectively applied to ImageData[image]. - The following options can be specified:
-
Standardized True whether to rescale the matrix to account for truncation WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision with which to compute matrix elements
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (9)
Gabor matrix using a 45° wave vector. Notice that the wave vector is perpendicular to the wave front:
Specify an isotropic standard deviation ![]() :
:
Specify an anisotropic standard deviation ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Decrease the wave number to get a Gabor matrix with a larger wavelength:
Create a rectangular Gabor matrix:
An anisotropic Gabor matrix with a large wavelength and a node at the center:
Visualize a 1D Gabor vector with different wave number and phase shift:
Visualize the magnitude spectrum of a 1D Gabor vector for different values of the wavenumber:
Options (2)
Standardized (1)
The default setting is True:
Use StandardizedFalse:
WorkingPrecision (1)
MachinePrecision is used by default:
Properties & Relations (3)
GaborFilter is equivalent to a convolution with a GaborMatrix:
Visualize the 1D Gabor kernel on its equivalent Gabor wavelet function:
With a zero-length wave vector, Gabor matrix is equivalent to GaussianMatrix:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), GaborMatrix, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborMatrix.html (updated 2015).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "GaborMatrix." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2015. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborMatrix.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). GaborMatrix. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborMatrix.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_gabormatrix, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GaborMatrix}", year="2015", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborMatrix.html}", note=[Accessed: 23-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_gabormatrix, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GaborMatrix}, year={2015}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborMatrix.html}, note=[Accessed: 23-February-2026]}