ImageAdjust
ImageAdjust[image]
adjusts the levels in image, rescaling them to cover the range 0 to 1.
ImageAdjust[image,corr]
adjusts the image according to the correction specification corr.
ImageAdjust[image,corr,{inmin,inmax}]
first rescales so that the range of input values inmin to inmax is mapped to 0 to 1.
ImageAdjust[image,corr,{inmin,inmax},{outmin,outmax}]
rescales so that the range of input values inmin to inmax is mapped to outmin to outmax.
Details
- ImageAdjust can be used for adjusting pixel values so that more of the image content is in the visible range or to correct for bad illumination or contrast.
- ImageAdjust works with arbitrary 2D and 3D images.
- Correction corr for contrast, brightness and gamma correction can take any of the following settings:
-
c adjusts the image contrast by c {c,b} also adjusts the image brightness by b {c,b,γ} also performs a gamma correction by raising the values to the power of γ - The correction transformation applied to every pixel value x is
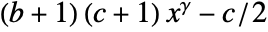 , rounded or clipped to the image type, if necessary.
, rounded or clipped to the image type, if necessary. - Zero adjustment corresponds to {0,0,1} correction.
- When rescaled values lie outside the range outmin to outmax, they are clipped.
- All correction and range parameters can be given as lists to specify different treatment for different channels in the image. »
- Range parameters can be set to Automatic to indicate the minimum or maximum of the values that occur in the image.
- When applied to color images, ImageAdjust always returns an RGB image.
Examples
open allclose allScope (9)
Data (3)
Contrast (2)
Brightness (1)
Applications (7)
Use gamma values in the range 0<γ<1 to see more details in dark areas of an image:
Use values γ>1 to see more details in a washed-out image:
Adjust to see relative distances returned by DistanceTransform:
Adjust to see out-of-range values returned by LaplacianGaussianFilter:
Symmetrically adjust the result of a Laplacian filter:
Use the maximum range in each channel:
Compare with the default adjustment:
Properties & Relations (5)
For grayscale images, ImageAdjust[Image[data]] is equivalent to Image[Rescale[data]]:
ImageAdjust[image] is equivalent to ImageAdjust[image,{0,0,1},{min,max},{0,1}], where {min,max} are the channel-wise pixel ranges in image:
ImageAdjust[image,-2] is equivalent to ColorNegate[image]:
ImageAdjust[image,-1] returns a constant image:
Image contrast increases as contrast value c is varied from -1 to ∞:
ImageAdjust[image,{c,b,γ}] is equivalent to ImageApply[Clip[(b+1)(c+1)#γ-c/2,{0,1}]&,image]:
When scaling is specified, it is applied before the other corrections:
The image is not changed if the input and the output range are identical:
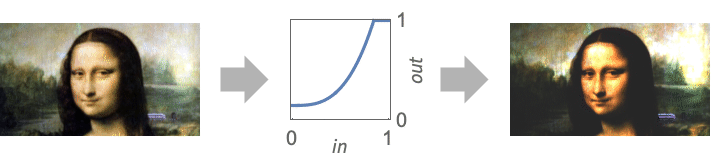
View the pixel transformation function and its effect on the example image and its histogram as the contrast, brightness and gamma parameters are changed:
Possible Issues (2)
Noise may get amplified for images with small color variation:
ImageAdjust may introduce new colors, as all channels are scaled independently:
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), ImageAdjust, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageAdjust.html (updated 2019).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "ImageAdjust." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2019. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageAdjust.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). ImageAdjust. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageAdjust.html