NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal
✖
NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal
represents an outward-pointing unit normal vector at the point ![]() on the boundary of a filled region.
on the boundary of a filled region.
Details


- NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal can be used to construct partial differential equation boundary conditions that depend on the unit normal vector
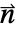 of the boundary.
of the boundary. - NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal can be used with NeumannValue, DirichletCondition and NIntegrate with the finite element method.
- NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal is used when non-normal flux values can be specified, like in AcousticRadiationValue or in ElectricCurrentDensityValue.
- NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal is generated by nonconservative boundary conditions for mass transport, like MassOutflowValue.
- For finite element approximations, the PDE is multiplied with a test function
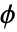 and integrated over
and integrated over 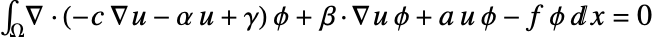 . Integration by parts gives
. Integration by parts gives 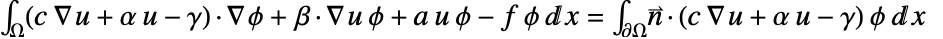 . The integrand
. The integrand 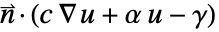 in the boundary integral is replaced with the NeumannValue
in the boundary integral is replaced with the NeumannValue 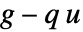 .
. - NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal can be used to model a boundary integration term of the form
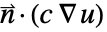 by specifying the NeumannValue as
by specifying the NeumannValue as 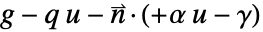 .
. - Conversely, when a PDE specifies a Neumann value as
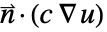 , NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal can be used to model a boundary integration term of the form
, NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal can be used to model a boundary integration term of the form 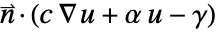 instead by specifying the NeumannValue as
instead by specifying the NeumannValue as 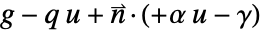 .
. - NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal will evaluate to a vector of length of the embedding dimension of the region
 when the boundary condition is discretized.
when the boundary condition is discretized. - NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal can be used to derive the tangent line (2D) and tangent plane (3D).
- Components of the boundary unit normal
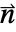 can be accessed with Indexed.
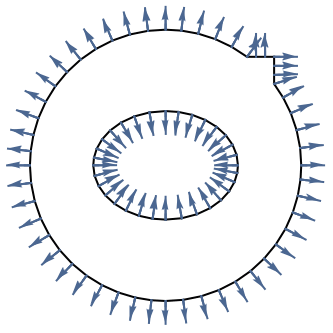
can be accessed with Indexed. - At internal boundaries of a region, the boundary unit normal is not uniquely defined.
- The value of the boundary unit normal
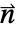 will be computed by solving
will be computed by solving 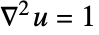 with a Dirichlet condition of
with a Dirichlet condition of 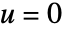 on all boundaries including internal boundaries over the entire region
on all boundaries including internal boundaries over the entire region  . The boundary unit normal is then the gradient of
. The boundary unit normal is then the gradient of 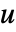 normalized with
normalized with 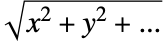 .
.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (2)Summary of the most common use cases
Set up a symbolic electric current density boundary condition with a non-surface normal current density:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-vw7olo
Specify a differential equation operator ![]() :
:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-72b1ry
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-lhb3x6
On the left, a NeumannValue is set up. The default Neumann boundary integrand for this equation is ![]() . To model a boundary integrand of the form
. To model a boundary integrand of the form ![]() , a NeumannValue
, a NeumannValue ![]() is set up:
is set up:

https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-s6o7xq
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-btsp
Scope (5)Survey of the scope of standard use cases
For nonconservative mass transport, boundary conditions like MassImpermeableBoundaryValue can produce NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal. Set up an impermeable boundary condition for a nonconservative model:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-gikt47
NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal can be used in NIntegrate to compute the flux through a boundary. Solve a Poisson equation on a unit Disk:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-yks3yb
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-fdx0b0
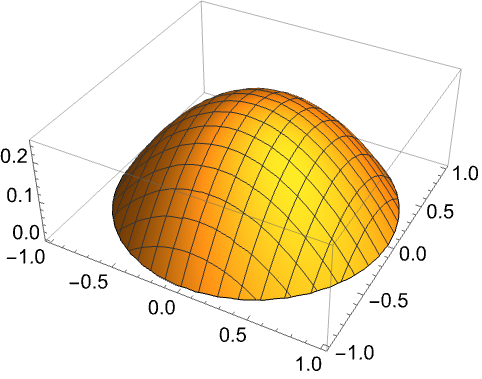
Compute the total flux through the boundary of the region through the boundary region:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-zi06e7
Compute the total flux through the boundary of a subregion:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-ohbdqg
Specify a time-dependent differential equation operator ![]() :
:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-0605j
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-gyyhbp
On the left, a NeumannValue is set up. The default Neumann boundary integrand for this equation is ![]() . To model a boundary integrand of the form
. To model a boundary integrand of the form ![]() , a NeumannValue
, a NeumannValue ![]() is set up:
is set up:

https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-ffp99r
Use a Neumann 0 boundary condition and solve the equation again:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-gsronc
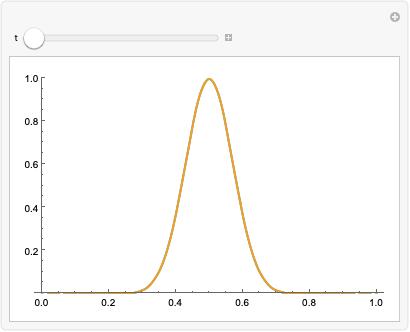
Inspect how the solutions start to differ over time:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-8wla0j
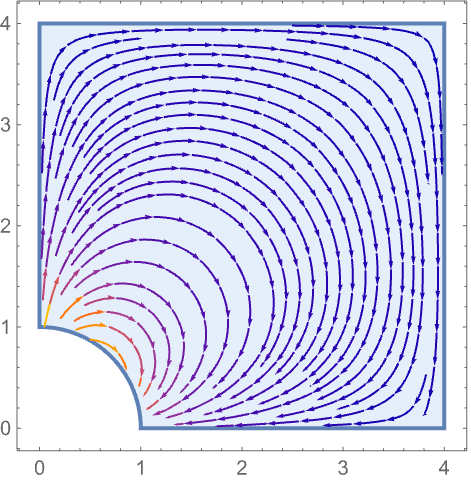
Create a tangential for a NeumannValue:

https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-vugv3d
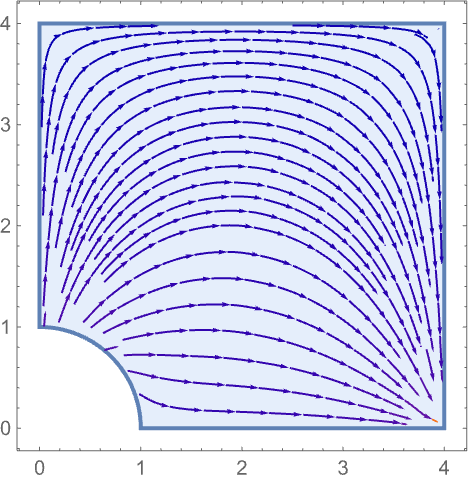
Make use of an Indexed component, the ![]() component, of a NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal to compute a NeumannValue:
component, of a NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal to compute a NeumannValue:

https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-e5szlb
Applications (1)Sample problems that can be solved with this function
The AcousticRadiationValue makes use of a NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal to automatically compute the sound direction vector. Define model variables vars for a frequency domain acoustic pressure field with model parameters pars:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-dcdeb2
Set up the equation with a radiation boundary at the left end and an acoustic absorbing boundary at the right end:
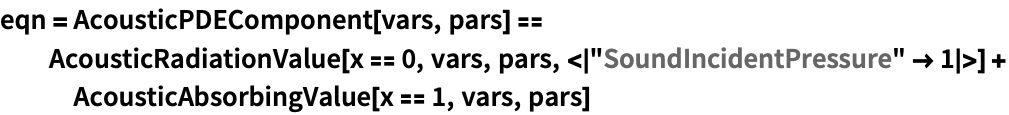
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-tgzhoh
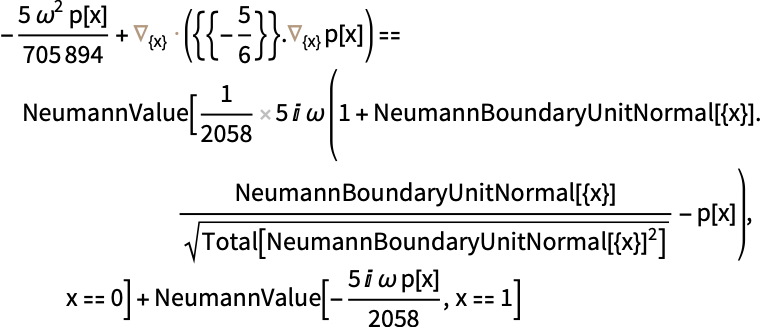
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-xht1ym
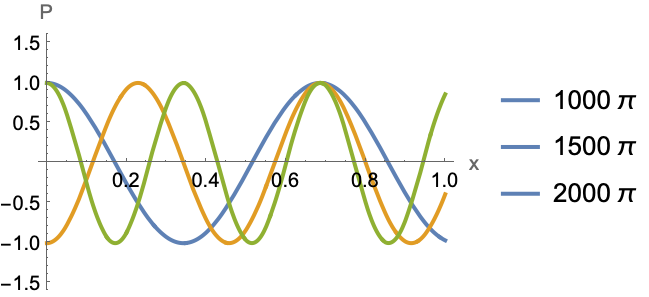
Convert the solution to the time domain and visualize the solution in the frequency domain at various frequencies ![]() :
:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-k3bcpi
Properties & Relations (1)Properties of the function, and connections to other functions
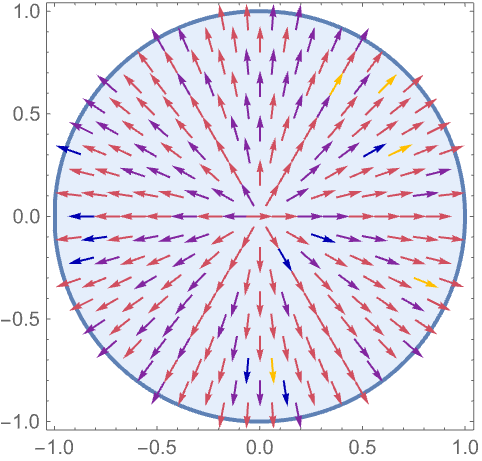
The boundary unit normal is computed by solving a Poisson equation over the region and specifying 0 Dirichlet conditions. Compute a Poisson equation over a unit Disk:

https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-tzjb00
Compute the normalized gradient of the potential:
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-zz9sy1
https://wolfram.com/xid/0itb2um6h1yvh2d7rj93q-9k549a
Wolfram Research (2025), NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html.Text
Wolfram Research (2025), NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html.
Wolfram Research (2025), NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html.CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html.
Wolfram Language. 2025. "NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html.APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html
Wolfram Language. (2025). NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.htmlBibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_neumannboundaryunitnormal, author="Wolfram Research", title="{NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html}", note=[Accessed: 13-April-2025
]}BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_neumannboundaryunitnormal, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.html}, note=[Accessed: 13-April-2025
]}