OrthogonalMatrix[omat]
converts the orthogonal matrix omat to a structured array.


OrthogonalMatrix
OrthogonalMatrix[omat]
converts the orthogonal matrix omat to a structured array.
Details and Options


- Orthogonal matrices, when represented as structured arrays, allow for a convenient specification and more efficient operations, including Inverse and LinearSolve.
- Matrix decompositions that use orthogonal matrices include QR, Hessenberg, Schur and singular value decompositions.
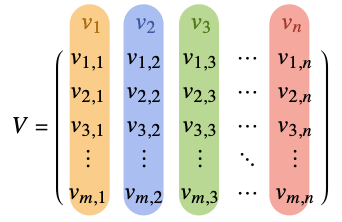
- For an orthogonal matrix
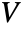 , the column vectors
, the column vectors 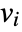 are orthonormal so that
are orthonormal so that ![v_i.v_j=TemplateBox[{{i, ,, j}}, KroneckerDeltaSeq] v_i.v_j=TemplateBox[{{i, ,, j}}, KroneckerDeltaSeq]](Files/OrthogonalMatrix.en/3.png) .
. - A square orthogonal matrix
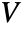 is a matrix whose transpose is equal to its inverse; that is, it satisfies the relation
is a matrix whose transpose is equal to its inverse; that is, it satisfies the relation ![TemplateBox[{V}, Transpose]=TemplateBox[{V}, Inverse] TemplateBox[{V}, Transpose]=TemplateBox[{V}, Inverse]](Files/OrthogonalMatrix.en/6.png) .
. - The inverse of a square orthogonal matrix is also orthogonal.
- A matrix
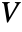 of dimensions p×q is orthogonal if p≥q and
of dimensions p×q is orthogonal if p≥q and ![TemplateBox[{V}, Transpose]V TemplateBox[{V}, Transpose]V](Files/OrthogonalMatrix.en/8.png) is the q×q identity matrix, or p≤q and
is the q×q identity matrix, or p≤q and ![VTemplateBox[{V}, Transpose] VTemplateBox[{V}, Transpose]](Files/OrthogonalMatrix.en/9.png) is the p×p identity matrix.
is the p×p identity matrix. - Orthogonal matrices are closed under matrix multiplication, so
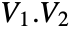 is again an orthogonal matrix.
is again an orthogonal matrix. - For an OrthogonalMatrix sa, the following properties "prop" can be accessed as sa["prop"]:
-
"Matrix" orthogonal matrix, represented as a full array "Properties" list of supported properties "Structure" type of structured array "StructuredData" internal data stored by the structured array "StructuredAlgorithms" list of functions with special methods for the structured array "Summary" summary information, represented as a Dataset - Normal[OrthogonalMatrix[…]] gives the orthogonal matrix as an ordinary matrix.
- OrthogonalMatrix[…,TargetStructure->struct] returns the orthogonal matrix in the format specified by struct. Possible settings include:
-
Automatic automatically choose the representation returned "Dense" represent the matrix as a dense matrix "Structured" represent the matrix as a structured array - OrthogonalMatrix[…,TargetStructureAutomatic] is equivalent to OrthogonalMatrix[…,TargetStructure"Structured"].
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Construct an orthogonal matrix:
Normal can convert an OrthogonalMatrix to its ordinary representation:
Scope (5)
Matrices corresponding to isometric transformations (reflections and rotations) are orthogonal:
Real reflection matrices are both orthogonal and symmetric:
The matrix is orthogonal, but not unitary:
A rectangular orthogonal matrix:
Its transpose is also orthogonal:
OrthogonalMatrix objects include properties that give information about the matrix:
The "Summary" property gives a brief summary of information about the matrix:
The "StructuredAlgorithms" property lists the functions that have structured algorithms:
Options (1)
Applications (5)
Matrices drawn from CircularRealMatrixDistribution are orthogonal:
Orthogonal matrices preserve the standard inner product on ![]() . In other words, if
. In other words, if ![]() is orthogonal and
is orthogonal and ![]() and
and ![]() are vectors, then
are vectors, then ![]() :
:
This means the angles between the vectors are unchanged:
Since the norm is derived from the inner product, norms are preserved as well:
Any orthogonal matrix represents a rotation and/or reflection. If the matrix has determinant ![]() , it is a pure rotation. If it the determinant is
, it is a pure rotation. If it the determinant is ![]() , the matrix includes a reflection. Consider the following matrix:
, the matrix includes a reflection. Consider the following matrix:
Thus, it is a pure rotation; the Cartesian unit vectors ![]() and
and ![]() maintain their relative positions:
maintain their relative positions:
The following matrix is orthogonal but has determinant ![]() :
:
Thus, it includes a reflection; the Cartesian unit vectors ![]() and
and ![]() reverse their relative positions:
reverse their relative positions:
Orthogonal matrices play an important role in many matrix decompositions:
The matrix ![]() is always orthogonal for any nonzero real vector
is always orthogonal for any nonzero real vector ![]() :
:
![]() is called a Householder reflection; as a reflection, its determinant is
is called a Householder reflection; as a reflection, its determinant is ![]() :
:
It represents a reflection through a plane perpendicular to ![]() , sending
, sending ![]() to
to ![]() :
:
Any vector perpendicular to ![]() is unchanged by
is unchanged by ![]() :
:
In matrix computations, ![]() is used to set to zero selected components of a given column vector
is used to set to zero selected components of a given column vector ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (1)
The transpose of an OrthogonalMatrix is equivalent to the inverse of the original matrix:
See Also
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2024), OrthogonalMatrix, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/OrthogonalMatrix.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2024. "OrthogonalMatrix." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/OrthogonalMatrix.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2024). OrthogonalMatrix. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/OrthogonalMatrix.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_orthogonalmatrix, author="Wolfram Research", title="{OrthogonalMatrix}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/OrthogonalMatrix.html}", note=[Accessed: 05-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_orthogonalmatrix, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={OrthogonalMatrix}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/OrthogonalMatrix.html}, note=[Accessed: 05-March-2026]}