SolidBoundaryLoadValue[pred,vars,pars]
represents a boundary load condition for PDEs with predicate pred indicating where it applies, with model variables vars and global parameters pars.
SolidBoundaryLoadValue[pred,vars,pars,lkeys]
represents a boundary load condition with local parameters specified in pars[lkey].


SolidBoundaryLoadValue
SolidBoundaryLoadValue[pred,vars,pars]
represents a boundary load condition for PDEs with predicate pred indicating where it applies, with model variables vars and global parameters pars.
SolidBoundaryLoadValue[pred,vars,pars,lkeys]
represents a boundary load condition with local parameters specified in pars[lkey].
Details

- SolidBoundaryLoadValue specifies a boundary condition for SolidMechanicsPDEComponent and is used as part of the modeling equation:
- SolidBoundaryLoadValue is typically used to apply a pressure or force at a boundary.
- SolidBoundaryLoadValue forces the movement of a solid with dependent variables
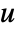 ,
, 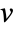 and
and 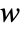 , independent variables
, independent variables 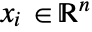 and time variable
and time variable 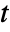 .
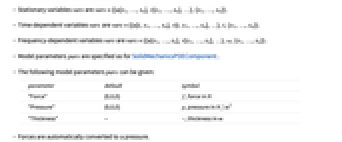
. - Stationary variables vars are vars={{u[x1,…,xn],v[x1,…,xn],…},{x1,…,xn}}.
- Time-dependent variables vars are vars={{u[t,x1,…,xn],v[t,x1,…,xn],…},t,{x1,…,xn}}.
- Frequency-dependent variables vars are vars={{u[x1,…,xn],v[x1,…,xn],…},ω,{x1,…,xn}}.
- Model parameters pars are specified as for SolidMechanicsPDEComponent.
- The following model parameters pars can be given:
-
parameter default symbol "Force" {0,0,0} 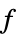 , force in
, force in 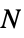
"Pressure" {0,0,0} 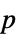 , pressure in
, pressure in 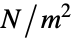
"Thickness" - 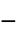 , thickness in
, thickness in 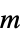
- Forces are automatically converted to a pressure.
- Forces or pressures acting normal to a surface can be modeled with NeumannBoundaryUnitNormal.
- In two dimensions, the parameter "Thickness" is taken into account to convert the pressure from units
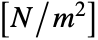 to
to 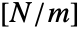 .
. - A boundary load value can be used with:
-
analysis type applicable Transient Yes Frequency Response Yes Eigenfrequency No Stationary Yes - SolidDisplacementCondition evaluates to a NeumannValue.
- The boundary predicate pred can be specified as in NeumannValue.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (7)
Create a pressure boundary load:
Create a pressure boundary load normal to a surface:
Create a force boundary load normal to a surface:
Create a time-dependent boundary load:
Create a time-dependent parametric boundary load:
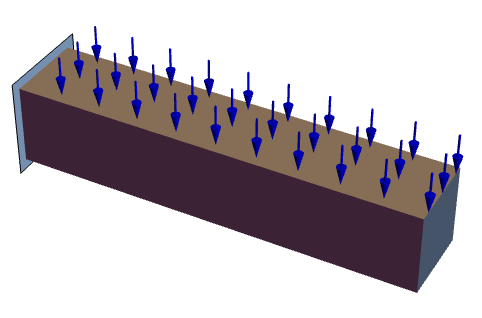
Compute the deflection of a beam held fixed at the left end and with a pressure applied in the negative ![]() axis at the right end:
axis at the right end:
Set up a geometry and the PDE:
Solve the equation with a pressure load:
Solve the equation with a force load:
Because the surface area that the pressure and force act on is 0.02 ![]() and since the force is equal to pressure per area
and since the force is equal to pressure per area ![]() , the displacements are the same:
, the displacements are the same:
Applications (1)
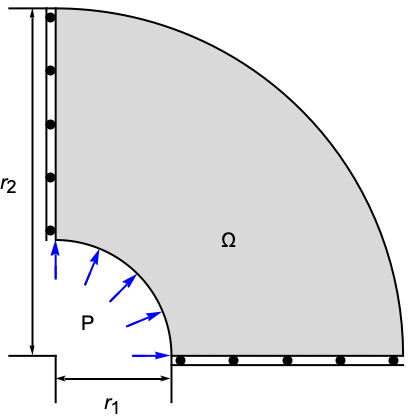
Apply a pressure normal to the inside of a pipe. The model domain ![]() is a quarter–cross section through a pipe, with matching units of an inner radius
is a quarter–cross section through a pipe, with matching units of an inner radius ![]() , an outer radius
, an outer radius ![]() and a thickness
and a thickness ![]() . At the left boundary, a symmetry constraint is added such that the pipe can move up and down, and at the right bottom, a second symmetry constraint is added such that the pipe can move left and right. A pressure of
. At the left boundary, a symmetry constraint is added such that the pipe can move up and down, and at the right bottom, a second symmetry constraint is added such that the pipe can move left and right. A pressure of ![]() is acting within the pipe in an outward direction. The remaining boundaries are free to move. Young's modulus is given as
is acting within the pipe in an outward direction. The remaining boundaries are free to move. Young's modulus is given as ![]() and Poisson's ratio is
and Poisson's ratio is ![]() .
.
Possible Issues (1)
In the case where boundary load values have predicates that do not overlap with the region boundary, results may be inaccurate. Set up a PDE:
Set up a boundary load with a discontinuity at ![]() and at
and at ![]() :
:
If the geometry does not reflect the discontinuity in the boundary condition, the result will be less accurate. The solution will be more accurate if the region ![]() reflects the discontinuities at
reflects the discontinuities at ![]() and at
and at ![]() . Set up two meshes:
. Set up two meshes:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), SolidBoundaryLoadValue, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SolidBoundaryLoadValue.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "SolidBoundaryLoadValue." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SolidBoundaryLoadValue.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). SolidBoundaryLoadValue. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SolidBoundaryLoadValue.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_solidboundaryloadvalue, author="Wolfram Research", title="{SolidBoundaryLoadValue}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SolidBoundaryLoadValue.html}", note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_solidboundaryloadvalue, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={SolidBoundaryLoadValue}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SolidBoundaryLoadValue.html}, note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}