TextPosition[text,form]
gives a list of the starting and ending positions at which instances of form occur in text.
TextPosition[text,{form1,form2,…}]
gives an association of results for all the types formi.
TextPosition[text,formspec,n]
gives the positions of the first n cases found.


TextPosition
Listing of Text Content Types »TextPosition[text,form]
gives a list of the starting and ending positions at which instances of form occur in text.
TextPosition[text,{form1,form2,…}]
gives an association of results for all the types formi.
TextPosition[text,formspec,n]
gives the positions of the first n cases found.
Details and Options
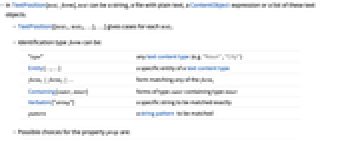

- In TextPosition[text,form], text can be a string, a file with plain text, a ContentObject expression or a list of these text objects.
- TextPosition[{text1,text2,…},…] gives cases for each texti.
- Identification type form can be:
-
"type" any text content type (e.g. "Noun", "City") Entity[…,…] a specific entity of a text content type form1|form2|… - form matching any of the formi
Containing[outer,inner] forms of type outer containing type inner Verbatim["string"] a specific string to be matched exactly pattern a string pattern to be matched - Possible choices for the property prop are:
-
"String" string of the identified text (default) "Position" start and end position of the string in text "Probability" estimated probability that the identification is correct "Interpretation" standard interpretation of the identified string "Snippet" a snippet around the identified string "HighlightedSnippet" a snippet with the identified string highlighted f apply f to the association containing all properties {prop1,prop2,…} a list of property specifications - The following options can be given:
-
AcceptanceThreshold Automatic minimum probability to accept identification PerformanceGoal Automatic favor algorithms with specific advantages TargetDevice "CPU" whether CPU or GPU computation should be used for entity detection VerifyInterpretation False whether interpretability should be verified
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Scope (4)
ContentObject and Files (2)
Alternatives and Containing (2)
Use Alternatives to match multiple types:
Find all sentences in a string that contain currency amounts:
Find all sentences in a string that contain countries:
Combine Alternatives and Containing to form highly structured queries:
Options (3)
AcceptanceThreshold (1)
By default, all the detected entities have an estimated probability higher than 0.5:
Get only the entities that are highly probable to be correct by setting a high AcceptanceThreshold:
PerformanceGoal (1)
Using PerformanceGoal->"Speed" can help to have faster detection, at the cost of lower accuracy:
VerifyInterpretation (1)
By default, some entities cannot be interpreted, either because they are not correct or because they are not yet in the knowledgebase. In these cases, a string is returned instead of an interpretation:
Use VerifyInterpretation to filter out the entities that cannot be interpreted:
Applications (6)
Word and Sentence Segmentation (2)
Word segmentation preserves syntactic elements such as email addresses, URLs and Twitter handles:
All the non-whitespace characters are grabbed with forms "Word" and "Punctuation":
Sentence segmentation intelligently ignores acronyms and other misleading boundaries:
Parts of Speech (2)
Entities and Interpretable Objects (2)
Return interpreted strings as Entity objects:
Properties & Relations (1)
TextPosition handles the same types as TextCases and TextContents, and always identify the same substrings as these functions for a given type:
TextCases is a generalization of TextPosition:
See Also
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2015), TextPosition, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TextPosition.html (updated 2019).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2015. "TextPosition." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2019. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TextPosition.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2015). TextPosition. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TextPosition.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_textposition, author="Wolfram Research", title="{TextPosition}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TextPosition.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_textposition, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={TextPosition}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TextPosition.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}