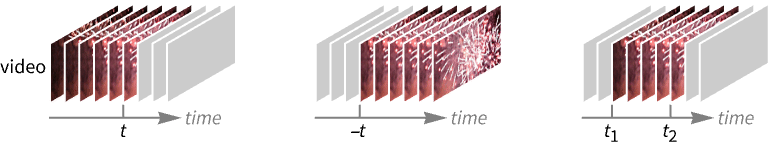
VideoTrim[video,t]
returns the first t seconds of video.
VideoTrim[video,-t]
returns the last t seconds of video.
VideoTrim[video,{t1,t2}]
returns video starting at time t1 and ending at time t2 of video.
VideoTrim[video,{{t11,t12},…}]
returns a list of video objects for all given intervals {ti1,ti2}.


VideoTrim
VideoTrim[video,t]
returns the first t seconds of video.
VideoTrim[video,-t]
returns the last t seconds of video.
VideoTrim[video,{t1,t2}]
returns video starting at time t1 and ending at time t2 of video.
VideoTrim[video,{{t11,t12},…}]
returns a list of video objects for all given intervals {ti1,ti2}.
Details and Options

- VideoTrim can be used to either extract interesting parts of a recording or remove uninteresting parts.
- VideoTrim places the new video under the "Video" directory in $WolframDocumentsDirectory.
- The time t can be any of the following:
-
t time given in seconds Quantity[t,"unit"] time given in "unit" compatible with seconds Quantity[t,"Frames"] time given as number of frames - By default, VideoTrim places the new video under the "Video" directory in $WolframDocumentsDirectory.
- The following options can be specified:
-
AudioEncoding Automatic audio encoding to use CompressionLevel Automatic compression level to use GeneratedAssetFormat Automatic the file format of the result GeneratedAssetLocation $GeneratedAssetLocation location of the generated assets OverwriteTarget Automatic whether to overwrite an existing file SubtitleEncoding Automatic subtitle encoding to use VideoEncoding Automatic video encoding to use VideoTransparency False whether the output video should have a transparency channel
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (7)
Trim the first 10 seconds of a video:
Trim from second 10 to second 20:
Trim using a valid time Quantity:
Compute multiple trims on the same video:
Trim the first and last 10 seconds of a video:
Trim a part of a remote video file:
Note that the trimmed video is stored as a local video object:
Options (2)
AudioEncoding (1)
Applications (3)
Extract an interesting portion of a video based on audio properties.
Import the audio track and use AudioLocalMeasurements to find the time when the audio has the greatest high-frequency content:
Extract the timestamp of the loudest partition:
Trim 3 seconds on either side of the interval:
Extract an interesting portion of a video based on image properties:
Define a function to detect whether an image has almost constant pixel values:
Use VideoMapTimeSeries to apply the function to each frame and plot the result:
Compute the intervals of constant and non-constant frames:
Find and trim the largest non-constant interval:
Use VideoTrim to partition a video file into smaller segments:
Partition the video into fixed-sized chunks of 20 seconds:
Compute and plot the mean intensity per frame for each video partition:
Perform an analysis of mean intensity value per frame on a specific segment:
Apply edge detection to video frames in a specific segment, generating a new video:
Properties & Relations (4)
If the requested time is beyond the duration of the video, only the available data is returned:
Negative times are also clipped to 0:
Properties of the original video object are typically preserved:
Compare with the properties of the generated video:
It is not always possible to preserve all properties when changing the encoding:
Some audio encodings support specific sample rates:
Video options such as RasterSize and track selection options are used when creating the trimmed video. Create a video object with nondefault option settings:
The trimmed video has the specified raster size:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), VideoTrim, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoTrim.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "VideoTrim." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoTrim.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). VideoTrim. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoTrim.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_videotrim, author="Wolfram Research", title="{VideoTrim}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoTrim.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_videotrim, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={VideoTrim}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoTrim.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}