VideoFrameMap[f,video]
applies f to each frame of the Video object video, returning a new Video object.
VideoFrameMap[f,video,n]
applies f to overlapping partitions of n video frames.
VideoFrameMap[f,video,n,d]
applies f to partitions with offset d.
VideoFrameMap[f,{video1,video2,…},…]
applies f to a list of inputs extracted from each videoi.


VideoFrameMap
VideoFrameMap[f,video]
applies f to each frame of the Video object video, returning a new Video object.
VideoFrameMap[f,video,n]
applies f to overlapping partitions of n video frames.
VideoFrameMap[f,video,n,d]
applies f to partitions with offset d.
VideoFrameMap[f,{video1,video2,…},…]
applies f to a list of inputs extracted from each videoi.
Details and Options


- VideoFrameMap is also known as a video filter.
- VideoFrameMap is typically used to improve video quality or modify video content, including noise reduction, brightness adjustments, video stabilization, stylization and more.
- VideoFrameMap returns a new Video object whose frames are the results of f applied to each video frame or partition of video frames.
- Using VideoFrameMap[f,video,n], the partition slides by one image frame.
- The function f should return an image for each frame or partition of frames.
- In VideoFrameMap[f,{video1,video2,…},…], data provided to f is a list where the
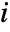
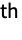 element corresponds to the frame or frames extracted from videoi.
element corresponds to the frame or frames extracted from videoi. - Frame variables n and d can be given as a scalar specifying the number of frames or a time Quantity object.
- To process partitions in parallel, use Parallelize[VideoFrameMap[…]].
- By default, VideoFrameMap places the new video under the "Video" directory in $WolframDocumentsDirectory.
- VideoFrameMap supports video containers and codecs specified by $VideoEncoders and $VideoDecoders.
- The following options can be given:
-
CompressionLevel Automatic compression level to use FrameRate Automatic the frame rate to use GeneratedAssetFormat Automatic the format of the result GeneratedAssetLocation $GeneratedAssetLocation the location of the result OverwriteTarget False whether to overwrite an existing file VideoEncoding Automatic video encoding to use VideoPadding Automatic padding scheme to use for video tracks VideoTransparency False whether the output video should have a transparency channel
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (4)
Specify a partition size corresponding to four frames:
Specify a partition size using a time Quantity:
By default, the offset between partitions is one frame:
Specify an offset of four frames:
Specify an offset using a time Quantity:
Use Scaled to specify an offset proportional to the partition size:
The function does not need to return an image with the same properties as the input:
Graphics objects returned by the function are automatically rasterized:
Options (3)
FrameRate (2)
Applications (5)
Visualize the gait of an animal by computing and highlighting its skeleton:
Define a function to binarize an image and compute the skeleton of the foreground:
Run the function on every frame:
Compute the difference between consecutive frames:
Extract one frame per second and create a video with the original frame rate:
Add a stylization effect to a video:
Create a side-by-side video showing an original and processed video:
Properties & Relations (1)
VideoFrameMap operates on the first video track of the input:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), VideoFrameMap, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoFrameMap.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "VideoFrameMap." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoFrameMap.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). VideoFrameMap. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoFrameMap.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_videoframemap, author="Wolfram Research", title="{VideoFrameMap}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoFrameMap.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_videoframemap, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={VideoFrameMap}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoFrameMap.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}