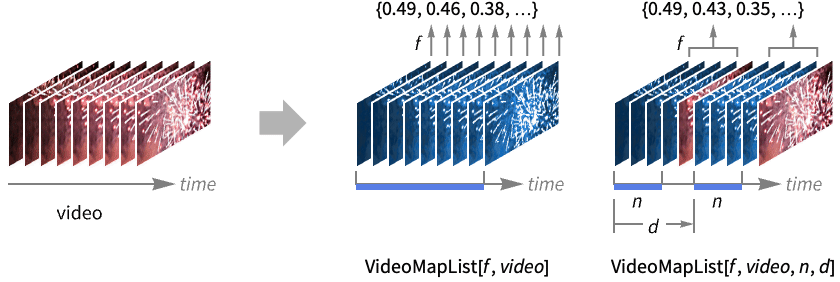
VideoMapList[f,video]
applies f to a chunk of data corresponding to one frame from the Video object video, returning a list of results.
VideoMapList[f,video,n]
applies f to overlapping partitions corresponding to n video frames.
VideoMapList[f,video,n,d]
applies f to partitions with offset d.
VideoMapList[f,{video1,video2,…},…]
applies f to a list of inputs extracted from each videoi.


VideoMapList
VideoMapList[f,video]
applies f to a chunk of data corresponding to one frame from the Video object video, returning a list of results.
VideoMapList[f,video,n]
applies f to overlapping partitions corresponding to n video frames.
VideoMapList[f,video,n,d]
applies f to partitions with offset d.
VideoMapList[f,{video1,video2,…},…]
applies f to a list of inputs extracted from each videoi.
Details and Options


- VideoMapList can be used to detect temporal or spatial events in videos, such as object detection, motion detection or activity recognition.
- VideoMapList returns a list of values corresponding to the results of f applied to an association including partial video data and their properties, such as video frames, audio data and time.
- Using VideoMapList[f,video,n], the partition slides by one image frame.
- The function f can access video and audio data using the following arguments:
-
#Image video frames as Image objects #Audio a chunk of the audio as an Audio object #Time time from the beginning of the video #TimeInterval beginning and end time stamps for the current partition #FrameIndex index of the current output frame #InputFrameIndex index of the current input frame - In VideoMapList[f,{video1,video2,…},…], data provided to each of the arguments is a list where the
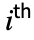 element corresponds to the data extracted from videoi.
element corresponds to the data extracted from videoi. - Frame variables n and d can be given as a scalar specifying the number of frames or a time Quantity object.
- The following options are supported:
-
Alignment Automatic alignment of the time stamps with partitions VideoPadding Automatic padding to use for frames beyond last frame - By default, the values of #Time are aligned with the center of each partition. Use Left, Right or a value between
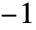 and
and 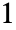 to specify a different alignment.
to specify a different alignment. - VideoMapList supports video containers and codecs specified by $VideoDecoders.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (4)
Function Specification (2)
The function f receives an Association holding data for each partition:
Check the keys of the provided association:
Process individual video frames:
The function f can operate on the audio data, provided as an Audio object:
Compute time-synchronous measurements on both image and audio data:
Partition Specification (2)
Options (2)
Alignment (1)
By default, the values of the "Time" keys are aligned with the center of each partition:
Use AlignmentRight to return the computed property at the end of each partition:
Use a custom alignment ranging from –1 (left) to 1 (right):
The boundaries of each partition are the start time for the first frame and the end time for the last frame of the partition. They can be queried using the "TimeInterval" key:
VideoPadding (1)
When video track is longer, black frames are used beyond its duration:
Use VideoPadding to specify a different color padding:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (2)
VideoMapList can return lists of varying dimensions for each evaluation:
VideoMapTimeSeries cannot store such results:
VideoMapList does not return times corresponding to results:
Use VideoMapTimeSeries to get times back as well:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), VideoMapList, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoMapList.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "VideoMapList." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoMapList.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). VideoMapList. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoMapList.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_videomaplist, author="Wolfram Research", title="{VideoMapList}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoMapList.html}", note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_videomaplist, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={VideoMapList}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/VideoMapList.html}, note=[Accessed: 11-March-2026]}