

Audio
Details and Options


- Audio is an object that can be input and output to functions, displayed as an audio player.
- The audio data can be stored in-memory or in a local or remote file, which can be streamed for playback and processing.
- Supported file formats include AIFF, FLAC, MP3, MP4, Ogg, QuickTime and WAV.
- Possible storage locations are:
-
File[…] data in a local file CloudObject[…] data in a public or private cloud object LocalObject[…] data in a local object URL[…] data in a URL - When constructing an audio object by just keeping a link, the byte count of the representative object and therefore the containing notebook will be smaller.
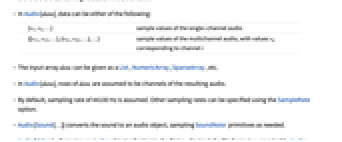
- In Audio[data], data can be either of the following:
-
{v1,v2,…} sample values of the single-channel audio {{v11,v12,…},{v21,v22,…},…} sample values of the multichannel audio, with values vij corresponding to channel i - The input array data can be given as a List, NumericArray, SparseArray, etc.
- In Audio[data], rows of data are assumed to be channels of the resulting audio.
- By default, sampling rate of 44100 Hz is assumed. Other sampling rates can be specified using the SampleRate option.
- Audio[Sound[…]] converts the sound to an audio object, sampling SoundNote primitives as needed.
- Audio[Video[…]] creates an Audio object referring to the first audio track for file formats supported by Audio.
- Audio[data,"type"] can be used to create an audio object of a different type. Values in data are coerced to the specified type by rounding or clipping. By default, "Real32" is assumed.
- Possible settings for "type" include:
-
"SignedInteger8" signed 8-bit integers from 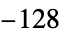 through
through 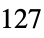
"SignedInteger16" signed 16-bit integers from 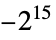 through
through 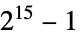
"SignedInteger32" signed 32-bit integers from 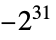 through
through 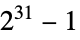
"Real32" single-precision real (32 bit) "Real64" double-precision real (64 bit) - Audio is treated as a raw object by functions like AtomQ and for purposes of pattern matching.
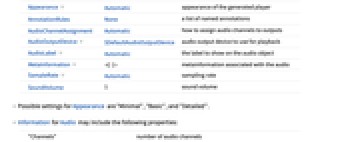
- The following options can be specified:
-
Appearance Automatic appearance of the generated player AnnotationRules None a list of named annotations AudioChannelAssignment Automatic how to assign audio channels to outputs AudioOutputDevice $DefaultAudioOutputDevice audio output device to use for playback AudioLabel Automatic the label to show on the audio object MetaInformation metainformation associated with the audio SampleRate Automatic sampling rate SoundVolume 1 sound volume - Possible settings for Appearance are "Minimal", "Basic", and "Detailed".
- Information for Audio may include the following properties:
-
"Channels" number of audio channels "DataType" underlying data type "Duration" duration of the audio signal "Length" number of audio samples "ResourcePath" path to the audio file "SampleRate" sampling rate

Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (10)
Basic Uses (5)
Import an Audio object from a file:
An audio object linking to a local file:
An audio object linking to a URL:
An audio object linking to a CloudObject:
Options (5)
AudioLabel (1)
AudioOutputDevice (1)
By default, $DefaultAudioOutputDevice is used for playback:
Check the list of available devices:
Use the device specified as the default by the operating system:
MetaInformation (1)
Add custom metainformation to an audio object:
Use Options to extract the metainformation:
Properties & Relations (7)
Use AudioQ to check for valid audio expressions:
Audio objects are atoms and cannot be subdivided:
Different audio types use different bit depths. Use smaller bit depth for compression:
Audio[file] and Audio[url] are not importing the underlying data into the memory:
Extract ByteCount of the generated player:
Compare with the byte count of the original file:
Use ToMemory to bring the data in out-of-core audio objects into memory:
Use AudioGenerator to create various oscillators and noises:
Use AudioPlot to visualize the waveform of an audio object:
Related Guides
Related Workflows
- Record a Sound
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), Audio, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Audio.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "Audio." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Audio.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). Audio. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Audio.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_audio, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Audio}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Audio.html}", note=[Accessed: 23-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_audio, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Audio}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Audio.html}, note=[Accessed: 23-February-2026]}