gives the Hessenberg decomposition of a numerical matrix m.


HessenbergDecomposition
gives the Hessenberg decomposition of a numerical matrix m.
Details and Options
- The matrix m must be square.
- The result is given in the form {p,h}, where h is an upper Hessenberg matrix and p is a unitary matrix such that p.h.ConjugateTranspose[p]==m.
- An upper Hessenberg matrix
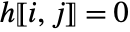 satisfies
satisfies 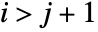 for
for 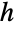 . That is, all the entries below its first subdiagonal are zero.
. That is, all the entries below its first subdiagonal are zero. - With the setting TargetStructure->"Structured", HessenbergDecomposition[m] returns the matrices {p,h} as structured matrices.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (9)
Basic Uses (5)
Find the Hessenberg decomposition of a machine-precision matrix:
Hessenberg decomposition of a complex matrix:
Hessenberg decomposition for an arbitrary-precision matrix:
Exact matrices must be numericized to be used with HessenbergDecomposition:
The Hessenberg decomposition of a large numerical matrix is computed efficiently:
Special Matrices (4)
Find the Hessenberg decomposition for sparse matrices:
Hessenberg decompositions of structured matrices:
Hessenberg decomposition of an identity matrix consists of two identity matrices:
Hessenberg decomposition of HilbertMatrix:
Options (2)
TargetStructure (2)
With TargetStructure->"Dense", the result of HessenbergDecomposition is a list of two dense matrices:
With TargetStructure->"Structured", the result of HessenbergDecomposition is a list containing an OrthogonalMatrix and a SparseArray:
With TargetStructure->"Dense", the result of HessenbergDecomposition is a list of two dense matrices:
With TargetStructure->"Structured", the result of HessenbergDecomposition is a list containing a UnitaryMatrix and a SparseArray:
Applications (2)
The Hessenberg decomposition is particularly useful for Hermitian matrices because the resulting ![]() matrix is tridiagonal. Generate a random 6×6 Hermitian matrix:
matrix is tridiagonal. Generate a random 6×6 Hermitian matrix:
Verify that the matrix is Hermitian:
Compute the Hessenberg decomposition:
If small numerical errors are ignored, the matrix is manifestly tridiagonal:
A matrix is tridiagonal if it is both upper and lower Hessenberg. The following shows that the small numbers discarded by Chop were in fact numerically insignificant:
A simple method for computing the Schur decomposition is the unshifted QR algorithm. Starting with ![]() , at each stage compute the QR decomposition
, at each stage compute the QR decomposition ![]() of
of ![]() , then let
, then let ![]() . In the limit,
. In the limit, ![]() converges to the desired
converges to the desired ![]() matrix (for well-behaved input matrices). A modification to speed up this algorithm is to let
matrix (for well-behaved input matrices). A modification to speed up this algorithm is to let ![]() be the
be the ![]() matrix of Hessenberg decomposition. Because so many entries are already zero, each QR step is much faster. Explore this for a randomly generated 25×25 real symmetric matrix:
matrix of Hessenberg decomposition. Because so many entries are already zero, each QR step is much faster. Explore this for a randomly generated 25×25 real symmetric matrix:
The matrix ![]() is real and symmetric:
is real and symmetric:
Do 2000 iterations of the unshifted QR algorithm using QRDecomposition:
As the eigenvalues of ![]() are real, they make up the diagonal of
are real, they make up the diagonal of ![]() up to small numerical error:
up to small numerical error:
The modification where the Hessenberg decomposition is computed first is roughly twice as fast:
Properties & Relations (7)
Compute its Hessenberg decomposition:
The matrix ![]() is upper Hessenberg:
is upper Hessenberg:
The original matrix ![]() is given by p.h.ConjugateTranspose[p]:
is given by p.h.ConjugateTranspose[p]:
For an upper Hessenberg ![]() matrix h, HessenbergDecomposition[h] returns
matrix h, HessenbergDecomposition[h] returns ![]() :
:
All 2×2 matrices are upper Hessenberg and are returned unchanged by HessenbergDecomposition:
Det[m] equals the determinant of the ![]() matrix of HessenbergDecomposition[m]:
matrix of HessenbergDecomposition[m]:
Tr[m] equals the trace of the ![]() matrix of HessenbergDecomposition[m]:
matrix of HessenbergDecomposition[m]:
The Hessenberg decomposition of a Hermitian matrix is tridiagonal:
Both the Hessenberg and Schur decompositions reduce real matrices to a Hessenberg matrix:
HessenbergDecomposition is based on row operations and preserves the top-left corner:
SchurDecomposition is based on eigenvalues; entries below the diagonal indicate complex values:
Possible Issues (1)
HessenbergDecomposition works only with matrices of approximate numerical values:
Use JordanDecomposition for exact matrices:
See Also
SchurDecomposition QRDecomposition
Function Repository: GaussianHessenbergDecomposition OrderedSchurDecomposition Pfaffian
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2004 (5.1) | Updated in 2024 (14.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2004), HessenbergDecomposition, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HessenbergDecomposition.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2004. "HessenbergDecomposition." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HessenbergDecomposition.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2004). HessenbergDecomposition. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HessenbergDecomposition.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_hessenbergdecomposition, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HessenbergDecomposition}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HessenbergDecomposition.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_hessenbergdecomposition, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HessenbergDecomposition}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HessenbergDecomposition.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}