WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
JoystickReturnTrajectoryModel simulating response of three joystick designs to circularly varying test force |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["EducationExamples.MechanicalEngineering.Joystick.JoystickReturnTrajectory"]
Information
This model compares the return trajectory of three analog joysticks after being suddenly released after being displaced from the center equilibrium position. Each joystick has a handle re-centering mechanism based on a symmetrical arrangement of a different number of tension springs.
The other model in this example is JoystickForceResponse, which compares the response of the three joysticks to a circularly varying test force.
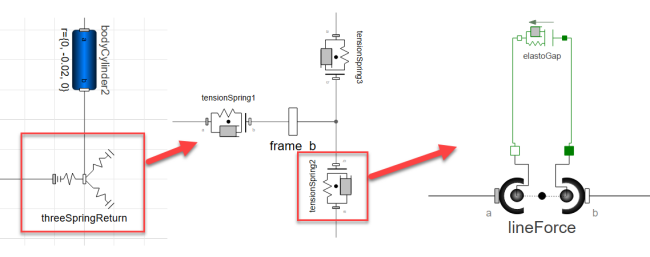
Hierarchical Modeling
The joystick model is constructed hierarchically. Double-click on a component such as fourSpringReturn to see its model diagram. Inside fourSpringReturn double-click on one of the tension springs to see its model diagram, and so on:
Simulation & Animation
To simulate the model and view a 3D animation of it, follow the steps below:
Click the Simulate button:
Click the Animate button:
Use your mouse or trackpad to drag the animation into a good angle, and zoom in with your scroll wheel or by using the trackpad. Then click the play button to play the animation.
Change the Time Scale at the bottom of the animation window to 0.1 to watch the joystick in slow motion.
The animation shows the trajectory of the joystick handle as it springs back after being suddenly released from a position away from the center equilibrium:
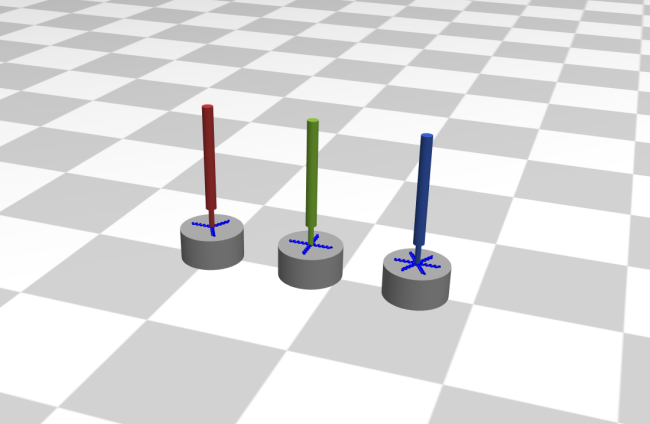
Note that the handle does not return along a linear trajectory. The joysticks with a larger number of symmetrically spaced springs (four or six) follow a path that is more nearly linear.
Visualization
After simulating the model, look at the stored plots to see parametric plots of the path along which each joystick returns.
The parametric plots look like this:
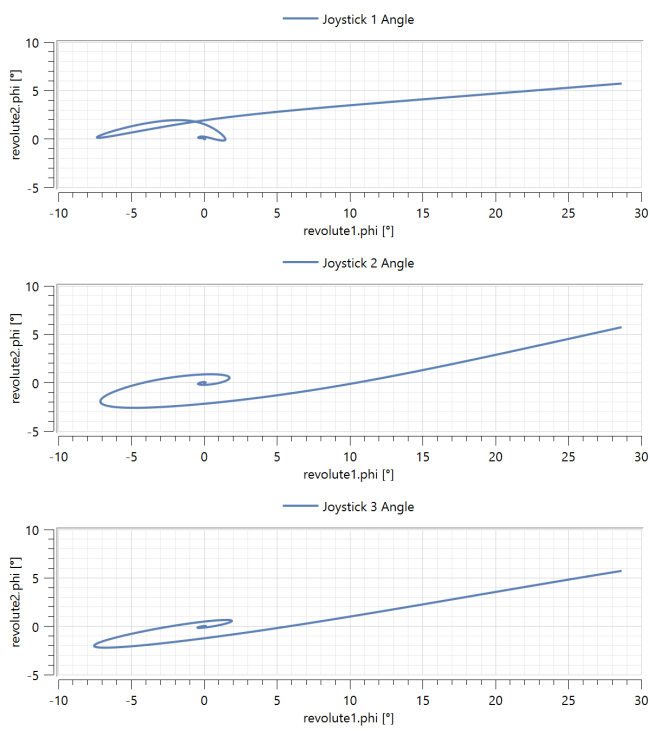
You can see that the six-spring arrangement leads to the most linear return trajectory.
By simulating the other model in this example, JoystickForceResponse, you can also obtain the following parametric plots of the response of each joystick to a circularly varying test force:
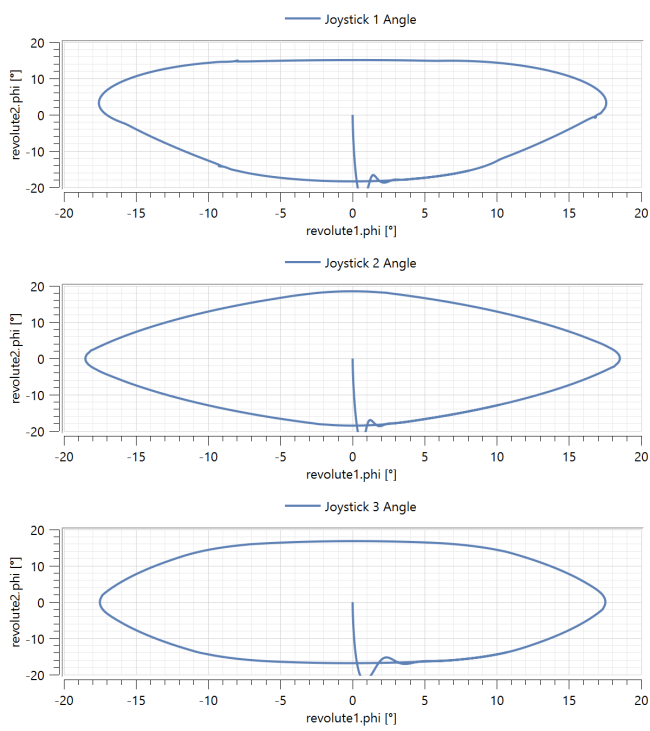
You can see that the-six spring arrangement leads to the most circular force response.
Parameters (2)
| initialAngles |
Value: {0.5, 0.1} Type: Angle[2] (rad) Description: Initial angles of the joysticks, first rotating aroung the X-axis and then rotating around the Y-axis |
|---|---|
| springConstants |
Value: 100 Type: TranslationalSpringConstant (N/m) Description: Base spring constant of the joystick springs |
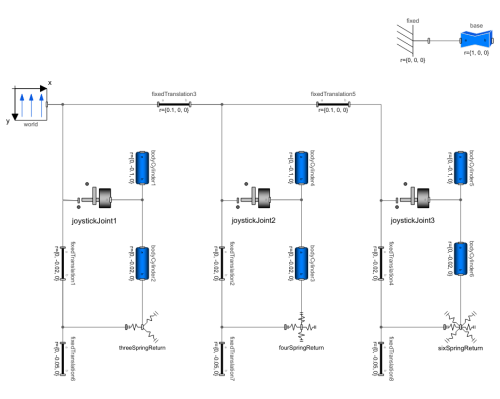
Components (23)
| world |
Type: World Description: World coordinate system + gravity field + default animation definition |
|
|---|---|---|
| joystickJoint1 |
Type: JoystickJoint Description: Two degree-of-freedom joystick joint |
|
| bodyCylinder1 |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Rigid body with cylinder shape. Mass and animation properties are computed from cylinder data and density (12 potential states) |
|
| bodyCylinder2 |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Rigid body with cylinder shape. Mass and animation properties are computed from cylinder data and density (12 potential states) |
|
| threeSpringReturn |
Type: ThreeSpringReturn Description: Joystick re-centering mechanism with three tension springs |
|
| fixedTranslation1 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| fixedTranslation2 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| fourSpringReturn |
Type: FourSpringReturn Description: Joystick re-centering mechanism with four tension springs |
|
| bodyCylinder3 |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Rigid body with cylinder shape. Mass and animation properties are computed from cylinder data and density (12 potential states) |
|
| bodyCylinder4 |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Rigid body with cylinder shape. Mass and animation properties are computed from cylinder data and density (12 potential states) |
|
| joystickJoint2 |
Type: JoystickJoint Description: Two degree-of-freedom joystick joint |
|
| fixedTranslation3 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| joystickJoint3 |
Type: JoystickJoint Description: Two degree-of-freedom joystick joint |
|
| bodyCylinder5 |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Rigid body with cylinder shape. Mass and animation properties are computed from cylinder data and density (12 potential states) |
|
| bodyCylinder6 |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Rigid body with cylinder shape. Mass and animation properties are computed from cylinder data and density (12 potential states) |
|
| sixSpringReturn |
Type: SixSpringReturn Description: Joystick re-centering mechanism with six tension springs |
|
| fixedTranslation4 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| fixedTranslation5 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| base |
Type: FixedShape2 Description: Visualizing an elementary shape with dynamically varying shape attributes (has two frame connectors) |
|
| fixed |
Type: Fixed Description: Frame fixed in the world frame at a given position |
|
| fixedTranslation6 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| fixedTranslation7 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |
|
| fixedTranslation8 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Fixed translation of frame_b with respect to frame_a |