WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
HelicopterModelExample of how gyroscopic precession works on a simple helicopter model. |
|
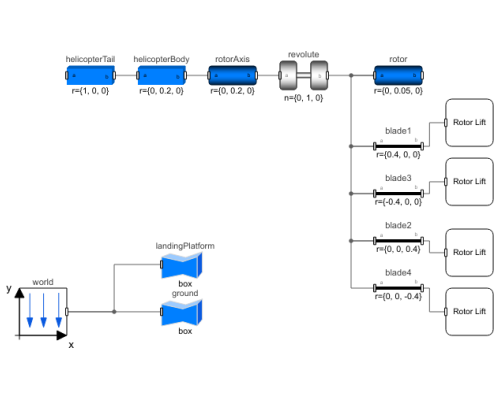
Diagram
Wolfram Language

SystemModel["EducationExamples.Physics.GyroscopicPrecession.HelicopterModel"]

Information
This model simulates how gyroscopic precession is used in a helicopter to make it move forward.
Helicopter Model
To get a helicopter to move forward is a bit more complex than it might seem. This is actually done by using gyroscopic precession. The principle is not more complicated than a plain gyro, but in reality, as usual, it takes a lot of effort to put the theories into practice. On a real helicopter, precession is achieved by controlling the blades of the rotor so that they produce extra force upward on the left side (provided the rotor is spinning counterclockwise), which introduces a clockwise torque on the helicopter body as seen from behind. This in turn generates a precession tilting the vehicle nose downward.
As decribed in the description of the gyro model in this example, you can think of this phenomenon as a 90 degree delay of the lift force; a force pushing upward on the left side manifests 90 degrees later, creating a lifting force on the rear side of the rotor that after tilting the nose of the helicopter downward propulses it forward.
In this example, the rotor is modeled as a solid circular disk with four forces acting on four evenly spaced points on the edge of the disk. The four forces act as periodic impulses on the "rotor blades", simulating the lift force coming from the change in pitch angle of the rotor blades on a helicopter.
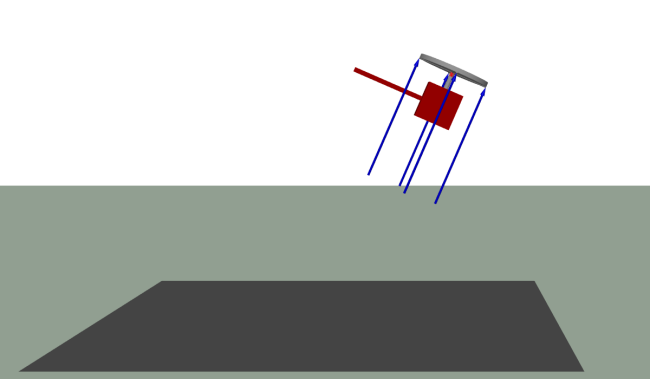
Simulation
By simulating the model, you can try different values of the parameters that are relevant for the precession. If you increase the amplitude of the lift force, for example, you will see that the helicopter rises up in the air faster, but also tilts forward more aggressively.
To simulate the model and see the generated 3D animation, follow the steps below:
Click the Simulate button:
Click the Animation button:
Use your mouse or trackpad to drag the animation to a good angle and zoom in with your scroll wheel or by using the trackpad. Then click the Play button:
To see exactly what the velocities or forces are, you can plot them by opening the Plot tab. Double click the PositionAndLifForce plot in the Stored Plots section to see a plot of the position of the helicopter and the lift forces affection the four blades.
Discussion
After simulating, you may notice that the helicopter does not move particularly smoothly. If you try to apply an external angular momentum directly to the body, you will see that the ride seems a lot smoother. The oscillating behavior of the vehicle is due to the fact that the momentum created by the periodic forces on the "rotor blades" are not continuous, but based on a fairly crude model. In a real helicopter, these kinds of problems are carefully controlled and compensated for. You also need to compensate for many other different factors that are not important for this example.
Parameters (2)
| rotorSpeed |
Value: 100 Type: AngularVelocity (rad/s) Description: Speed of the rotor |
|---|---|
| liftForce |
Value: 500 Type: Force (N) Description: Lift force per blade |
Components (16)
| world |
Type: World Description: World component. |
|
|---|---|---|
| helicopterBody |
Type: BodyBox Description: Helicopter body part. |
|
| rotorAxis |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Axis of the rotor. |
|
| rotor |
Type: BodyCylinder Description: Rotor of the helicopter. |
|
| revolute |
Type: Revolute Description: Joint to allow rotation of the rotor. |
|
| blade4 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Rotor blade 4. |
|
| blade2 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Rotor blade 2. |
|
| blade3 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Rotor blade 3. |
|
| blade1 |
Type: FixedTranslation Description: Rotor blade 1. |
|
| helicopterTail |
Type: BodyBox Description: Visualizer for the helicopter tail. |
|
| ground |
Type: FixedShape Description: Visualizer for the ground. |
|
| landingPlatform |
Type: FixedShape Description: visualizer for the helicopter platform. |
|
| rotorLiftForce1 |
Type: RotorLiftForce Description: Lift force applied to rotor blade 1. |
|
| rotorLiftForce3 |
Type: RotorLiftForce Description: Lift force applied to rotor blade 3. |
|
| rotorLiftForce2 |
Type: RotorLiftForce Description: Lift force applied to rotor blade 2. |
|
| rotorLiftForce4 |
Type: RotorLiftForce Description: Lift force applied to rotor blade 4. |