-
See Also
- GeoPositionENU
- GeoPositionXYZ
- GeoGridPosition
- GeoDistance
- GeoDestination
- Latitude
- Longitude
- GeoAntipode
- FindGeoLocation
- $GeoLocation
- GeodesyData
- GeoVector
- GeoGraphics
- GeoPath
- GeoCircle
- GeoDisk
- LocalTime
-
- Entity Types
- GeographicRegion
-
- Interpreter Types
- GeoCoordinates
-
- Formats
- USGSDEM
- SDTSDEM
- GeoTIFF
- Related Guides
- Tech Notes
-
-
See Also
- GeoPositionENU
- GeoPositionXYZ
- GeoGridPosition
- GeoDistance
- GeoDestination
- Latitude
- Longitude
- GeoAntipode
- FindGeoLocation
- $GeoLocation
- GeodesyData
- GeoVector
- GeoGraphics
- GeoPath
- GeoCircle
- GeoDisk
- LocalTime
-
- Entity Types
- GeographicRegion
-
- Interpreter Types
- GeoCoordinates
-
- Formats
- USGSDEM
- SDTSDEM
- GeoTIFF
- Related Guides
- Tech Notes
-
See Also
GeoPosition[{lat,lon}]
represents a geodetic position with latitude lat and longitude lon.
GeoPosition[{lat,lon,h}]
represents a geodetic position with height h relative to the reference ellipsoid.
GeoPosition[{lat,lon,h},datum]
represents a geodetic position referring to the specified datum.
GeoPosition[{{lat1,lon1},{lat2,lon2},…},datum]
represents an array of geodetic positions.
GeoPosition[entity]
returns the geodetic position of the specified geographical entity.


GeoPosition
GeoPosition[{lat,lon}]
represents a geodetic position with latitude lat and longitude lon.
GeoPosition[{lat,lon,h}]
represents a geodetic position with height h relative to the reference ellipsoid.
GeoPosition[{lat,lon,h},datum]
represents a geodetic position referring to the specified datum.
GeoPosition[{{lat1,lon1},{lat2,lon2},…},datum]
represents an array of geodetic positions.
GeoPosition[entity]
returns the geodetic position of the specified geographical entity.
Details



- Latitude and longitude values in GeoPosition[{lat,lon}] can be given as decimal degrees, DMS strings, or Quantity angles.
- Height h in GeoPosition[{lat,lon,h}] can be given as a numeric object in meters or as a Quantity length.
- Height h in GeoPosition[{lat,lon,h}] is geodetic height, measured with respect to the reference ellipsoid.
- GeoPosition[{lat,lon,h,t}] includes a time t that can be given as a numeric object or as a DateObject specification. A numeric t represents GMT time measured in seconds since the beginning of January 1, 1900.
- Valid latitude angles range from
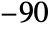 to 90 degrees. Longitude angles, traditionally between
to 90 degrees. Longitude angles, traditionally between 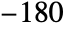 and 180 degrees, are unrestricted and interpreted modulo 360 degrees.
and 180 degrees, are unrestricted and interpreted modulo 360 degrees. - A GeoPosition object with no explicit height assumes height zero with respect to the reference ellipsoid. A GeoPosition object with no explicit time assumes the current date.
- GeoPosition[{lat,lon}] assumes the default datum "ITRF00".
- Standard datums can be specified by name. Typical named datums include:
-
"ITRF00" International Terrestrial Reference Frame 2000 "NAD27" North American Datum of 1927 "NAD83CORS96" North American Datum of 1983 (CORS96) - The complete list of named datums and reference ellipsoids is given by GeodesyData[].
- GeoPosition[GeoPosition[{lat,lon},datum1],datum2] converts between datums.
- GeoPosition[pos,datum] converts from any type of geographic position. The following coordinate types can be given: GeoPosition, GeoPositionXYZ, GeoPositionENU, GeoGridPosition.
- GeoPosition[pos] converts from any type of geographic position, keeping the same datum of pos.
- GeoPosition can represent a geodetic position on a body other than Earth using GeoPosition[coords,body], where body is an Entity object of domains "Planet", "MinorPlanet", or "PlanetaryMoon".
- For an image with Exif location information, GeoPosition[image] returns that information as a GeoPosition object.
- For extended entities, GeoPosition[entity] uses when possible the position of the geographic center of the entity.
- GeoPosition[…][prop] gives the specified property of a geo position.
- Possible properties include:
-
"AbsoluteTime" date as number of seconds since Jan 1, 1900, 00:00 GMT "Count" number of positions in the GeoPosition object "Data" first argument of the GeoPosition object "DateList" date list {y,m,d,h,m,s} in GMT time "DateObject" full date object "Datum" datum of the GeoPosition object "Depth" point depth: 0 for a single position, 1 for a list of them, … "Dimension" number of coordinates for each position "Elevation" numeric elevation in meters, with respect to the ellipsoid "Latitude" numeric latitude in degrees "LatitudeLongitude" numeric {lat,lon} pair in degrees "Longitude" numeric longitude in degrees "LongitudeLatitude" numeric {lon,lat} pair in degrees "PackingType" Integer or Real if data is packed; None otherwise
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
A geodetic position in the default reference frame:
The current position of the International Space Station, including height and time information:
A position that explicitly refers to the ITRF00 reference frame:
Convert this position to NAD 83 (CORS96) coordinates:
Convert to Cartesian geocentric coordinates:
Scope (19)
Position Specification (9)
A geo position identified by values of latitude and longitude, respectively, both in degrees:
Specify time as well, in seconds since 1900:
Give an average location for a geographical entity:
Angles given as Quantity objects are converted into numeric angles, in degrees:
Heights and dates are also canonicalized to meters and seconds, respectively:
Write GeoPosition objects in DMS string form:
A GeoPosition object with no height information is assumed to have zero geodetic height:
A GeoPosition object with no time information is assumed to have the current date:
Extract Exif location information from an image:
A geo position that specifies its datum:
Transform to a different datum:
Transform to the original datum:
Height is modified in a change of datum, but not time:
These are the current locations of the magnetic poles, as determined by GeomagneticModelData:
Geo Position Arrays (4)
To speed up computations, use an array of points as the first argument:
All points are transformed at once:
Here each point is transformed individually:
Results coincide up to numerical error:
Changes of datum are also faster using an array of points as the first argument:
GeoPosition can contain nested lists of points, as long as all points have the same length and depth:
Manipulations will preserve the nesting structure:
However, this is not allowed, because the first point has a height specification, but not the second:
This is not allowed because the second point is deeper than the first:
Convert a list of geo positions into a single geo position array:
Coordinate Extraction (4)
Extract date information using DateValue:
Numeric time in GeoPosition is interpreted as GMT time. Convert to local time:
Extract the year as an integer number:
Extract the coordinates from a GeoPosition object:
Extract latitude, longitude or both, as Quantity angles:
Use properties to extract information from a GeoPosition object:
Use properties to extract information from a GeoPosition array:
It is a matrix of points, so it has point depth 2:
Each point has dimension 2, namely latitude and longitude:
RandomGeoPosition returns a GeoPosition object containing a packed array with type Real:
Any other property will return an array of values corresponding to the points of the array:
Datum Transformations (2)
Perform a datum transformation from the default "ITRF00" to the British datum "OGB7" of 1936:
To estimate the implied spatial change, compute geo distance ignoring the datum information:
The change is smaller for locations in the UK:
Convert a geo position array of locations from the American "NAD27" datum to the European "EURM":
Generalizations & Extensions (3)
Use positions on a sphere of 100 kilometers of radius:
The vector components are given in meters:
Transform back to a GeoPosition object on the sphere:
Use positions on an ellipsoid of given semiaxes:
Transform back to a GeoPosition object on the ellipsoid:
A position on a geo reference model other than the Earth:
Distance from the Tycho Brahe crater to the South Pole of Mars:
Computations are performed with an ellipsoid of these semiaxis lengths:
Applications (3)
GeoPosition is the main object in the Wolfram Language denoting point-like locations on the Earth:
Compute distance between two points:
Compute the initial bearing of a geodesic from p to q:
Draw the geodesic between them and respective geo circles:
Check that the end of the geodesic starting at p is actually the point q:
Geographical locations returned by EntityValue are given as GeoPosition objects:
They can also include height and time information:
Geographical polygons have their coordinates inside a GeoPosition head:
Properties & Relations (7)
Convert a geodetic location to a three-dimensional Cartesian vector with respect to the reference frame of the datum, assuming geodetic height 0:
Convert back to a GeoPosition specification, now with some small residual value of height:
Convert geodetic coordinates to Cartesian coordinates for an ellipsoid of these semiaxis lengths:
Take a point p of geodetic latitude 60°, zero longitude, and geodetic height 0.15:
Convert it to Cartesian coordinates:
Convert back to geodetic coordinates:
Take a point q of the same latitude and longitude, but zero height:
Represent the relation between the coordinates on a vertical cut of the ellipsoid:
The blue line is perpendicular to the tangent at q and forms an angle of 60° with the ![]() axis:
axis:
The geodetic height of p along the geodetic vertical is the distance between p and q:
Project a geodetic location using various geo projections, using their default parameters:
Convert back to a GeoPosition specification:
The antipode of a GeoPosition object is another GeoPosition object:
GeoPosition[{}] represents an empty array of geo positions:
GeoPosition[] is invalid syntax:
GeoPosition inside Graphics primitives marks coordinates as being in {lat,lon} notation:
Graphics primitives containing GeoPosition coordinates are formed by straight segments in the projected map:
Possible Issues (2)
See Also
GeoPositionENU GeoPositionXYZ GeoGridPosition GeoDistance GeoDestination Latitude Longitude GeoAntipode FindGeoLocation $GeoLocation GeodesyData GeoVector GeoGraphics GeoPath GeoCircle GeoDisk LocalTime
Entity Types: GeographicRegion
Interpreter Types: GeoCoordinates
Formats: USGSDEM SDTSDEM GeoTIFF
Function Repository: ElevateGeoPosition
Tech Notes
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), GeoPosition, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoPosition.html (updated 2019).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "GeoPosition." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2019. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoPosition.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). GeoPosition. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoPosition.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_geoposition, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GeoPosition}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoPosition.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_geoposition, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GeoPosition}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoPosition.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}