represents a half-normal distribution with scale inversely proportional to parameter θ.


HalfNormalDistribution
represents a half-normal distribution with scale inversely proportional to parameter θ.
Details
- The probability density for value
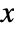 in a half-normal distribution is proportional to
in a half-normal distribution is proportional to 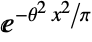 for
for 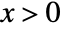 , and is zero for
, and is zero for 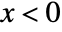 .
. - HalfNormalDistribution allows θ to be any positive real number.
- HalfNormalDistribution allows θ to be a quantity of any unit dimension. »
- HalfNormalDistribution can be used with such functions as Mean, CDF, and RandomVariate. »
Background & Context
- HalfNormalDistribution[θ] represents a continuous statistical distribution defined on the interval
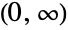 and parametrized by a positive real number θ that determines the overall height and steepness of the associated probability density function (PDF). The PDF of the half-normal distribution is smooth and monotonically decreasing with tails that are "thin," in the sense that the PDF decreases exponentially for large values of
and parametrized by a positive real number θ that determines the overall height and steepness of the associated probability density function (PDF). The PDF of the half-normal distribution is smooth and monotonically decreasing with tails that are "thin," in the sense that the PDF decreases exponentially for large values of 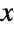 . (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) The half-normal distribution may be referred to as a folded or a doubly truncated normal distribution (see NormalDistribution), both of which are references to generalizations of NormalDistribution that can be formalized in a way that yields HalfNormalDistribution as a special case.
. (This behavior can be made quantitatively precise by analyzing the SurvivalFunction of the distribution.) The half-normal distribution may be referred to as a folded or a doubly truncated normal distribution (see NormalDistribution), both of which are references to generalizations of NormalDistribution that can be formalized in a way that yields HalfNormalDistribution as a special case. - The half-normal distribution has a sparse but colorful past dating back to the late 1940s, though it failed to become the focal point for considerable research until the 1960s. Derived as a special case of NormalDistribution in which the sign of the random variate is always positive, the half-normal distribution has been used to study various phenomena, including deviations in automotive part manufacturing, and has been utilized as a modeling tool in areas such as economics, industry, physiology, and quality control. The half-normal distribution has also been used in Bayesian statistics as a prior distribution for the standard deviations of certain distributions.
- RandomVariate can be used to give one or more machine- or arbitrary-precision (the latter via the WorkingPrecision option) pseudorandom variates from a half-normal distribution. Distributed[x,HalfNormalDistribution[θ]], written more concisely as xHalfNormalDistribution[θ], can be used to assert that a random variable x is distributed according to a half-normal distribution. Such an assertion can then be used in functions such as Probability, NProbability, Expectation, and NExpectation.
- The probability density and cumulative distribution functions may be given using PDF[HalfNormalDistribution[θ],x] and CDF[HalfNormalDistribution[θ],x]. The mean, median, variance, raw moments, and central moments may be computed using Mean, Median, Variance, Moment, and CentralMoment, respectively.
- DistributionFitTest can be used to test if a given dataset is consistent with a half-normal distribution, EstimatedDistribution to estimate a half-normal parametric distribution from given data, and FindDistributionParameters to fit data to a half-normal distribution. ProbabilityPlot can be used to generate a plot of the CDF of given data against the CDF of a symbolic half-normal distribution and QuantilePlot to generate a plot of the quantiles of given data against the quantiles of a symbolic half-normal distribution.
- TransformedDistribution can be used to represent a transformed half-normal distribution, CensoredDistribution to represent the distribution of values censored between upper and lower values, and TruncatedDistribution to represent the distribution of values truncated between upper and lower values. CopulaDistribution can be used to build higher-dimensional distributions that contain a half-normal distribution, and ProductDistribution can be used to compute a joint distribution with independent component distributions involving half-normal distributions.
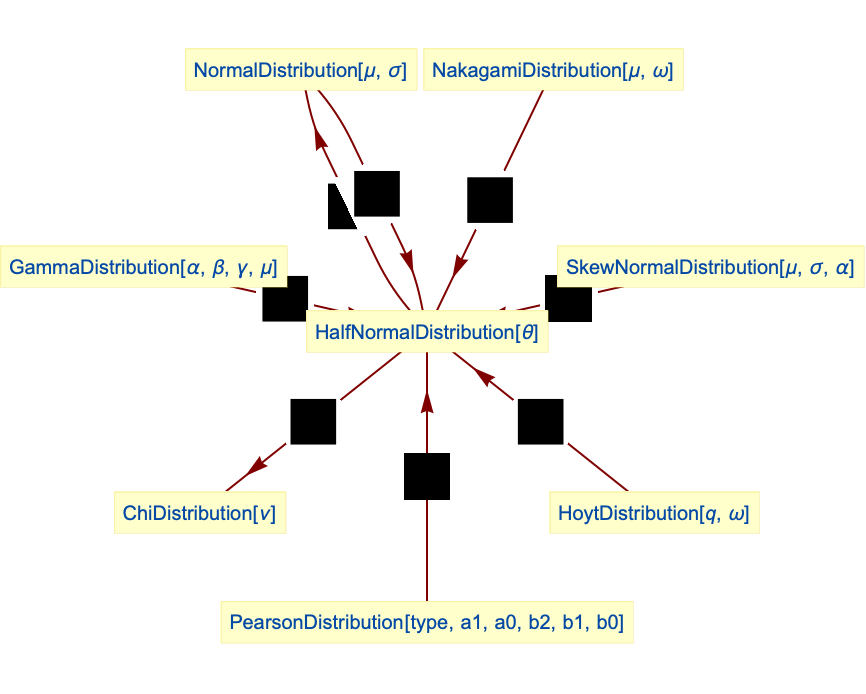
- HalfNormalDistribution is closely related to a number of other distributions. For example, HalfNormalDistribution[θ] can be viewed as both a truncation and a transformation of NormalDistribution, in the sense that its PDF is precisely the same as both TruncatedDistribution[{0,∞},NormalDistribution[0,
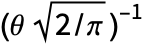 ]] and TransformedDistribution[Abs[x-μ],xNormalDistribution[μ,
]] and TransformedDistribution[Abs[x-μ],xNormalDistribution[μ,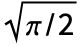 /θ]]. HalfNormalDistribution is also a special case of both GammaDistribution (the PDF of GammaDistribution[1/2,β,2,0] is the same as that of HalfNormalDistribution[
/θ]]. HalfNormalDistribution is also a special case of both GammaDistribution (the PDF of GammaDistribution[1/2,β,2,0] is the same as that of HalfNormalDistribution[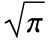 /β]) and NakagamiDistribution (the PDF of NakagamiDistribution[1/2,π/(2 θ2)] is precisely that of HalfNormalDistribution[θ]), and HalfNormalDistribution[θ] is a limiting case of SkewNormalDistribution[0,
/β]) and NakagamiDistribution (the PDF of NakagamiDistribution[1/2,π/(2 θ2)] is precisely that of HalfNormalDistribution[θ]), and HalfNormalDistribution[θ] is a limiting case of SkewNormalDistribution[0,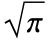 /(
/(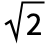 θ),α] as α tends to Infinity. HalfNormalDistribution is also related to PearsonDistribution, ChiDistribution, ChiSquareDistribution, StudentTDistribution, and HoytDistribution.
θ),α] as α tends to Infinity. HalfNormalDistribution is also related to PearsonDistribution, ChiDistribution, ChiSquareDistribution, StudentTDistribution, and HoytDistribution.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (7)
Generate a sample of pseudorandom numbers from a half-normal distribution:
Compare its histogram to the PDF:
Distribution parameters estimation:
Estimate the distribution parameters from sample data:
Compare the density histogram of the sample with the PDF of the estimated distribution:
Skewness and kurtosis are constant:
Different moments with closed forms as functions of parameters:
Closed form for symbolic order:
Consistent use of Quantity in parameters yields QuantityDistribution:
Applications (2)
Compute the ![]() -value for a
-value for a ![]() -test of a random variate
-test of a random variate ![]() under the null hypothesis
under the null hypothesis ![]() with alternative hypothesis
with alternative hypothesis ![]() :
:
Compare with Probability:
Measurement errors are independent and follow a centered normal distribution with standard deviation of 0.1 seconds. Find the distribution of the absolute errors:
Find the average absolute error:
Find the probability that the absolute error is greater than 0.2 seconds:
Properties & Relations (11)
Half-normal distribution is closed under scaling by a positive factor:
Variance is a power function of the mean:
Relationships to other distributions:
A half-normal distribution is a truncated NormalDistribution:
Normal and half-normal distributions:
Half-normal distribution is a transformation of NormalDistribution:
A half-normal distribution is a transformation of NormalDistribution:
The half-normal distribution with ![]() is equivalent to the ChiDistribution with
is equivalent to the ChiDistribution with ![]() :
:
A half-normal distribution is a special case of generalized GammaDistribution:
Scaled half-normal distribution is a special case of type 3 PearsonDistribution:
HalfNormalDistribution is a special case of NakagamiDistribution:
HalfNormalDistribution is the limiting case of SkewNormalDistribution:
Possible Issues (2)
HalfNormalDistribution is not defined when θ is not a positive real number:
Substitution of invalid parameters into symbolic outputs gives results that are not meaningful:
See Also
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), HalfNormalDistribution, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HalfNormalDistribution.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "HalfNormalDistribution." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HalfNormalDistribution.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). HalfNormalDistribution. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HalfNormalDistribution.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_halfnormaldistribution, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HalfNormalDistribution}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HalfNormalDistribution.html}", note=[Accessed: 05-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_halfnormaldistribution, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HalfNormalDistribution}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HalfNormalDistribution.html}, note=[Accessed: 05-March-2026]}