represents a loss layer that computes a loss based on a distance metric and a target that specifies whether the distance should be minimized or maximized.
ContrastiveLossLayer[margin]
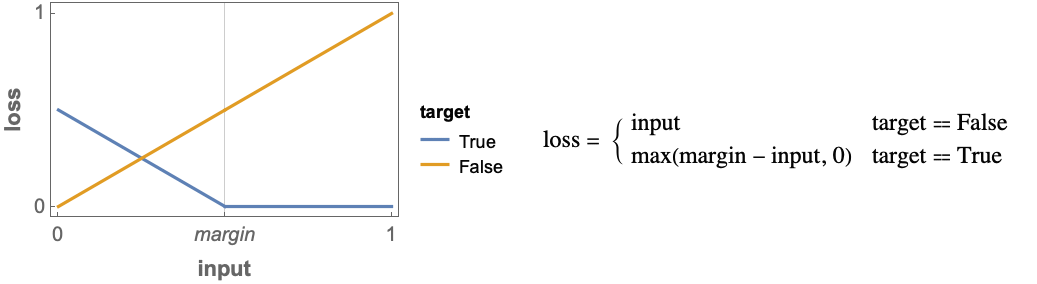
specifies a distance above which the loss is zero for True targets.


ContrastiveLossLayer
represents a loss layer that computes a loss based on a distance metric and a target that specifies whether the distance should be minimized or maximized.
ContrastiveLossLayer[margin]
specifies a distance above which the loss is zero for True targets.
Details and Options

- ContrastiveLossLayer is typically used in conjunction with NetPairEmbeddingOperator in order to learn an embedding from an input into a vector space, such that similar inputs cluster together in the vector space and dissimilar inputs are separated.
- ContrastiveLossLayer exposes the following ports for use in NetGraph etc.:
-
"Input" a real number representing a distance "Target" True if the distance should be maximized, False if it should be minimized "Loss" a real number - ContrastiveLossLayer[margin] computes the following loss:
- ContrastiveLossLayer[…][<|"Input"in,"Target"target|>] explicitly computes the loss from applying the layer.
- ContrastiveLossLayer[…][<|"Input"{in1,in2,…},"Target"{target1,target2,…}|>] explicitly computes losses for each of the ini and targeti.
- When given a NumericArray as input, the output will be a NumericArray.
- ContrastiveLossLayer is typically used inside NetGraph to construct a training network for a learned embedding.
- A ContrastiveLossLayer[…] can be provided as the third argument to NetTrain when training a specific network.
- When appropriate, ContrastiveLossLayer is automatically used by NetTrain if an explicit loss specification is not provided.
- Options[ContrastiveLossLayer] gives the list of default options to construct the layer. Options[ContrastiveLossLayer[…]] gives the list of default options to evaluate the layer on some data.
- Information[ContrastiveLossLayer[…]] gives a report about the layer.
- Information[ContrastiveLossLayer[…],prop] gives the value of the property prop of ContrastiveLossLayer[…]. Possible properties are the same as for NetGraph.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Create a ContrastiveLossLayer with a given margin:
Create a ContrastiveLossLayer:
If the target is True, the loss is nonzero only when the input distance is less than the default margin of 0.5:
If the target is False, the loss is proportional to the input distance:
Applications (1)
Train a multilayer perceptron to embed a synthetic dataset based only on its topology. First, create the training data on a spiral-like manifold that is dense in the plane:
Create a loss network to measure the performance of the embedding:
Create a generator that will sample pairs of points and associate them with True if their parameterization on the manifold differs by more than Pi:
Train the network, using a generator to sample pairs of points, and classify them as the same if their original parameterization was close:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), ContrastiveLossLayer, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ContrastiveLossLayer.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "ContrastiveLossLayer." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ContrastiveLossLayer.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). ContrastiveLossLayer. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ContrastiveLossLayer.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_contrastivelosslayer, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ContrastiveLossLayer}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ContrastiveLossLayer.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_contrastivelosslayer, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ContrastiveLossLayer}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ContrastiveLossLayer.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}