DatePlus[date,n]
gives the date n days after date.
DatePlus[date,{n,step}]
gives the date n calendar steps after date.
DatePlus[date,{{n1,step1},{n2,step2},…}]
gives a date offset by ni steps of each specified size.
DatePlus[n]
gives the date n days after the current date.
DatePlus[offset]
gives the date with the specified offset from the current date.


DatePlus
DatePlus[date,n]
gives the date n days after date.
DatePlus[date,{n,step}]
gives the date n calendar steps after date.
DatePlus[date,{{n1,step1},{n2,step2},…}]
gives a date offset by ni steps of each specified size.
DatePlus[n]
gives the date n days after the current date.
DatePlus[offset]
gives the date with the specified offset from the current date.
Details and Options



- DatePlus shifts dates by any given amount of time, treated either as a physical duration or as a number of calendar steps.
- DatePlus[date,-n] gives the date n days before date.
- Dates can be specified in the following forms:
-
DateObject[…] date object {y,m,d} year, month, day {y,m} the first day of the specified month {y} January 1 of the year y "string" date as a string ("Jan. 1, 2000") {y,m,d,h,m,s} precise time time absolute time specification - Possible step sizes are calendar steps and day types "Year", "Quarter", "Month", "Week", "Day", "Hour", "Minute", "Second", "Weekday", "Weekend", Monday through Sunday, "EndOfMonth", "BeginningOfMonth" and "BusinessDay".
- Offsets can also be specified using the Quantity framework.
- {y,m,d} is taken to be equivalent to {y,m,d,0,0,0} etc.
- DatePlus[date,offset] gives results in the same general format as date.
- When date is a list, the result has the same length as date, possibly extended to include the smallest step in offset. »
- When date is a string, the result is in the form specified by $DateStringFormat.
- DatePlus takes the following options:
-
CalendarType "Gregorian" calendar in which the dates have been specified HolidayCalendar Automatic holiday schedule and subspecification for the business day and holiday computations Method Automatic date arithmetic method to use - For added time steps with variable duration (e.g. "Month"), date arithmetic can either convert the steps into a physical duration (continuous arithmetic) or treat them all as discrete calendar steps (discrete arithmetic).
- The option value Method"Continuous" implements continuous arithmetic. Discrete arithmetic is implemented with Methodrolling, where possible rolling methods are "RollForward", "RollBackward" and "RollOver", with the default being "RollBackward".
- For discrete arithmetic, adding, for example, a month may result in a date that does not exist (e.g. February 30). In such cases, there are three possible options for how that date should be resolved:
-
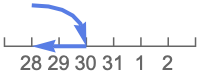
"RollBackward" roll back to the last existing date (Feb 28) 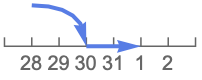
"RollForward" roll forward to the next existing date (Mar 1) 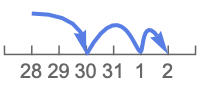
"RollOver" increment from the next existing date (Mar …)
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Scope (13)
Date Formats (5)
DatePlus can take dates in the standard {y,m,d,h,m,s} format of DateList:
DatePlus can take dates in any format supported by DateString:
If a date is given as {y,m,d}, DatePlus returns in the same form:
{y,m} is interpreted as the first day of the specified month:
Options (7)
CalendarType (2)
HolidayCalendar (2)
Method (3)
By default, adding a month to May 31 will roll back to June 30:
Using Method"RollForward" will roll forward to the next valid date, July 1:
DatePlus[date,"Year"] will move forward 365 or 366 days, depending on the year:
Quantity[1,"Years"] is equivalent to Quantity[365,"Days"] in the Quantity framework:
Therefore Method"Continuous" will always add 365 days:
Compare the results of different arithmetic methods when adding a month to January 30, 2021:
Compare the results of different rolling methods for January 27 through February 1:
Properties & Relations (2)
DatePlus adds calendar steps to dates, while DateDifference computes time distances between dates:
Use $DateStringFormat to set the default format for date strings:
Possible Issues (3)
Use DateList to disambiguate between different interpretations:
When list increments are specified, they are added from highest order to lowest:
The order in which calendar units are added can change the results of arithmetic operations, due to variable lengths for months and years:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), DatePlus, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DatePlus.html (updated 2023).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "DatePlus." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2023. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DatePlus.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). DatePlus. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DatePlus.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_dateplus, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DatePlus}", year="2023", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DatePlus.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_dateplus, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DatePlus}, year={2023}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DatePlus.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}