DiscreteMinLimit[f,k∞]
gives the min limit k∞f(k) of the sequence f as k tends to ∞ over the integers.
DiscreteMinLimit[f,{k1![]() ,…,kn
,…,kn![]() }]
}]
gives the nested min limit ![]() ⋯
⋯ ![]() f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.
f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.
DiscreteMinLimit[f,{k1,…,kn}{![]() ,…,
,…,![]() }]
}]
gives the multivariate min limit ![]() f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.
f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.




DiscreteMinLimit
DiscreteMinLimit[f,k∞]
gives the min limit k∞f(k) of the sequence f as k tends to ∞ over the integers.
DiscreteMinLimit[f,{k1![]() ,…,kn
,…,kn![]() }]
}]
gives the nested min limit ![]() ⋯
⋯ ![]() f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.
f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.
DiscreteMinLimit[f,{k1,…,kn}{![]() ,…,
,…,![]() }]
}]
gives the multivariate min limit ![]() f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.
f(k1,…,kn) over the integers.
Details and Options


- DiscreteMinLimit is also known as limit inferior, infimum limit, liminf, lower limit and inner limit.
- DiscreteMinLimit computes the largest lower bound for the limit and is always defined for real-valued sequences. It is often used to give conditions of convergence and other asymptotic properties that do not rely on an actual limit to exist.
- DiscreteMinLimit[f,k∞] can be entered as
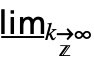 f. A template
f. A template 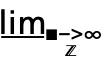 can be entered as
can be entered as  dmlim
dmlim , and
, and  moves the cursor from the underscript to the body.
moves the cursor from the underscript to the body. - DiscreteMinLimit[f,{k1,…,kn}{
 ,…,
,…,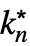 }] can be entered as
}] can be entered as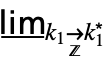 …
…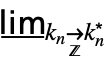 f.
f. - The possible limit points
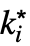 are ±∞.
are ±∞. - The min limit is defined as a limit of the min envelope sequence min[ω]:
-
DiscreteMinLimit[f,k∞] DiscreteLimit[min[ω],ω∞] DiscreteMinLimit[f,{k1,…,kn}{∞,…,∞}] DiscreteLimit[min[ω],ω∞] - DiscreteMinLimit[f[k],k-∞] is equivalent to DiscreteMinLimit[f[-l],l∞] etc.
- The definition uses the min envelope min[ω]MinValue[{f[k],k≥ω∧k∈
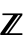 },k] for univariate f[k] and min[ω]MinValue[{f[k1,…,kn],k1≥ω∧⋯∧kn≥ω∧ki∈
},k] for univariate f[k] and min[ω]MinValue[{f[k1,…,kn],k1≥ω∧⋯∧kn≥ω∧ki∈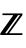 },{k1,…,kn}] for multivariate f[k1,…,kn]. The sequence min[ω] is monotone increasing as ω∞, so always has a limit, which may be ±∞.
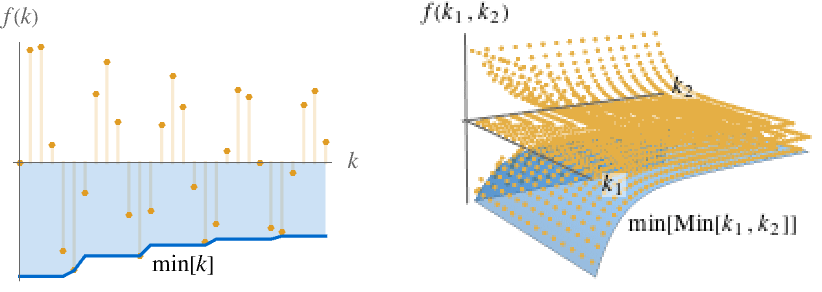
},{k1,…,kn}] for multivariate f[k1,…,kn]. The sequence min[ω] is monotone increasing as ω∞, so always has a limit, which may be ±∞. - The illustration shows min[k] and min[Min[k1,k2]] in blue.
- DiscreteMinLimit returns unevaluated when the min limit cannot be found.
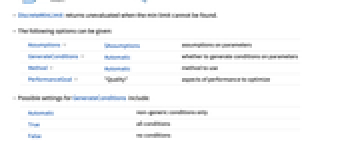
- The following options can be given:
-
Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions on parameters GenerateConditions Automatic whether to generate conditions on parameters Method Automatic method to use PerformanceGoal "Quality" aspects of performance to optimize - Possible settings for GenerateConditions include:
-
Automatic non-generic conditions only True all conditions False no conditions None return unevaluated if conditions are needed - Possible settings for PerformanceGoal include $PerformanceGoal, "Quality" and "Speed". With the "Quality" setting, DiscreteMinLimit typically solves more problems or produces simpler results, but it potentially uses more time and memory.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Use ![]() dmlim
dmlim![]() to enter the template
to enter the template ![]() and
and ![]() to move from the underscript to the body:
to move from the underscript to the body:
TraditionalForm typesetting:
Scope (22)
Basic Uses (4)
Elementary Function Sequences (6)
Integer Function Sequences (3)
Sequences involving Factorial:
Sequence involving FactorialPower:
Compute the limit of a sequence involving Fibonacci:
Periodic Sequences (3)
Piecewise Function Sequences (2)
Options (6)
Assumptions (1)
GenerateConditions (3)
Return a result without stating conditions:
This result is only valid if x>1:
Return unevaluated if the results depend on the value of parameters:
By default, conditions are generated that return a unique result:
By default, conditions are not generated if only special values invalidate the result:
With GenerateConditions->True, even these non-generic conditions are reported:
Method (1)
PerformanceGoal (1)
DiscreteMinLimit computes limits involving sequences of arbitrarily large periods:
Use PerformanceGoal to avoid potentially expensive computations in such cases:
The Method option overrides PerformanceGoal:
Applications (3)
Compute the asymptotic minimum of a sequence:
Plot the sequence and the asymptotic minimum:
Verify that the following sequence does not have a limit:
Show that DiscreteMaxLimit and DiscreteMinLimit are not equal:
Confirm that the limit does not exist by using DiscreteLimit:
An algorithm runtime function ![]() is said to be "big-omega of
is said to be "big-omega of ![]() ", written
", written ![]() , if
, if ![]() :
:
Similarly, ![]() is said to be "big-theta of
is said to be "big-theta of ![]() ", written
", written ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
It is possible for two functions to share neither relationship:
Hence, ![]() defines a reflexive partial order on the space of algorithm runtimes similar to
defines a reflexive partial order on the space of algorithm runtimes similar to ![]() :
:
If ![]() and
and ![]() , then
, then ![]() , which implies that
, which implies that ![]() is an equivalence relation:
is an equivalence relation:
Properties & Relations (11)
A real-valued function always has a (possibly infinite) min limit:
The corresponding limit may not exist:
If ![]() and
and ![]() have finite min limits, then
have finite min limits, then ![]() :
:
In this case, there is strict inequality:
Positive multiplicative constants can be moved outside a limit:
For a real-valued sequence, if DiscreteLimit exists, DiscreteMinLimit has the same value:
DiscreteMinLimit is less than or equal to DiscreteMaxLimit:
If DiscreteMinLimit equals DiscreteMaxLimit, the limit exists and equals their common value:
If the min limit is ![]() , then the max limit and thus the limit are also
, then the max limit and thus the limit are also ![]() :
:
DiscreteMinLimit can be computed as -DiscreteMaxLimit[-f,…]:
If the two max limits are equal—as in this example—then ![]() has a limit:
has a limit:
This is a generalization of the "squeezing" or "sandwich" theorem:
MinLimit is always less than or equal to DiscreteMinLimit:
Possible Issues (1)
DiscreteMinLimit is only defined for real-valued sequences:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), DiscreteMinLimit, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteMinLimit.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "DiscreteMinLimit." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteMinLimit.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). DiscreteMinLimit. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteMinLimit.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_discreteminlimit, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DiscreteMinLimit}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteMinLimit.html}", note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_discreteminlimit, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DiscreteMinLimit}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteMinLimit.html}, note=[Accessed: 13-March-2026]}