FeatureExtract[examples]
extracts features for each example using a feature extractor trained on the examples given.
FeatureExtract[examples,spec]
extracts features using the specified feature extractor method spec.


FeatureExtract
FeatureExtract[examples]
extracts features for each example using a feature extractor trained on the examples given.
FeatureExtract[examples,spec]
extracts features using the specified feature extractor method spec.
Details and Options








- FeatureExtract is typically used to process raw data into usable features (e.g. for training a machine learning algorithm)
- FeatureExtract can be used on many types of data, including numerical, textual, sounds, images, graphs, time series and combinations of these.
- Possible values of examples are:
-
example a single unitary example without training {example1,…} a list of training examples Dataset[…] a Dataset object Tabular[…] a Tabular object - Each examplei can be a single data element, a list of data elements, an association of data elements, or a Dataset object.
- Possible values for spec include:
-
extractor use the specified extractor method partextractor apply the extractor to the specific example part {part1extractor1,…} specify extractors for specific parts - In FeatureExtract[examples,{part1extractor1,…}], the extractori are all applied separately to examples.
- Possible feature extractor methods include:
-
Automatic automatic extraction Identity give data unchanged "ConformedData" conformed images, colors, dates, etc. "NumericVector" numeric vector from any data "name" a named extractor method f applies function f to each example {extractor1,extractor2,…} use a sequence of extractors in turn - Possible forms of part are:
-
All all parts of each example i i 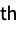 part of each example
part of each example{i1,i2,…} parts i1, i2, … of each example "key" part with the specified key in each example {"key1","key2",…} parts with names "keyi" in each example - When explicitly specifying parts, any unmentioned parts are dropped when extracting features.
- FeatureExtract[examples] is equivalent to FeatureExtract[examples, Automatic] which is typically equivalent to FeatureExtract[examples, "NumericVector"].
- The "NumericVector" method will typically convert examples to numeric vectors, impute missing data, and reduce the dimension using DimensionReduction.
- Feature extractor methods specific to a single data type are applied only to data elements with whose types they are compatible. Other data elements are returned unchanged.
- Not all specific feature extractors are available when only one example is provided - for example vector processors will assume a list of is a list of scalar features.
- The specific extractors are:
- Numeric data:
-
"DiscretizedVector" discretized numerical data "DimensionReducedVector" reduced-dimension numeric vectors "MissingImputed" data with missing values imputed "StandardizedVector" numeric data processed with Standardize - Nominal data:
-
"IndicatorVector" nominal data "one-hot encoded" with indicator vectors "IntegerVector" nominal data encoded with integers - Text:
-
"LowerCasedText" text with each character lowercase "SegmentedCharacters" text segmented into characters "SegmentedWords" text segmented into words "SentenceVector" semantic vector from a text "TFIDF" term frequency-inverse document frequency vector "WordVectors" semantic vectors sequence from a text (English only) - Images:
-
"FaceFeatures" semantic vector from an image of a human face "ImageFeatures" semantic vector from an image "PixelVector" vector of pixel values from an image - Audio objects:
-
"AudioFeatures" sequence of semantic vectors from an audio object "AudioFeatureVector" semantic vector from an audio object "LPC" audio linear prediction coefficients "MelSpectrogram" audio spectrogram with logarithmic frequencies bins "MFCC" audio mel-frequency cepstral coefficients vectors sequence "SpeakerFeatures" sequence of semantic speaker vectors "SpeakerFeatureVector" semantic vector for a speaker "Spectrogram" audio spectrogram - Video objects:
-
"VideoFeatures" sequence of semantic vectors from a video object "VideoFeatureVector" semantic vector from a video object - Graphs:
-
"GraphFeatures" numeric vector summarizing graph properties - Molecules:
-
"AtomPairs" Boolean vector from pairs of atoms and the path lengths between them "MoleculeExtendedConnectivity" Boolean vector from enumerated molecule subgraphs "MoleculeFeatures" numeric vector summarizing molecule properties "MoleculeTopologicalFeatures" Boolean vector from circular atom neighborhoods - The following options can be given:
-
FeatureNames Automatic names to assign to elements of the examplei FeatureTypes Automatic feature types to assume for elements of the examplei RandomSeeding 1234 what seeding of pseudorandom generators should be done internally - Possible settings for RandomSeeding include:
-
Automatic automatically reseed every time the function is called Inherited use externally seeded random numbers seed use an explicit integer or strings as a seed - FeatureExtract[…] is equivalent to FeatureExtraction[…,"ExtractedFeatures"].
Extractors
Options
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (26)
Input Shape (9)
Extract from a list of examples with multiple features:
Extract features on a mixed-type dataset:
Extract features from a dataset formatted as a list of associations:
Extract features from data given as feature lists:
Feature extract from a Tabular:
Feature extract from a Dataset:
Extract features from a dataset that contains missing values:
Extract features from a single example using an extractor that requires no training:
Extractor Specifications (8)
Specify the feature extractor "SentenceVector" on a single textual feature:
Extract features using the "SentenceVector" method followed by dimension reduction "DimensionReducedVector":
Extract features on texts and images using the text-only "TFIDF" method:
Features have only been extracted from the text part, since "TFIDF" does not apply to images.
Specify feature extraction on multiple features by position:
Extract features with the "IndicatorVector" method on the second nominal variable only:
Use the Identity extractor method to copy the first variable as well:
A variable can be copied multiple times:
Specify the feature extraction on multiple features by key:
Generate a feature extractor using a custom function:
Chain the custom extractor with the "StandardizedVector" method:
Feature Types (9)
Extract features on textual data:
Compute term frequency-inverse document frequency vectors from texts:
By default, texts will be segmented into words. This gives the same result:
Extract features with the "IndicatorVector" method on nominal variables:
Extract features from a list of DateObject instances:
Train a feature extractor on a list of Graph instances:
Train a feature extractor on a list of TimeSeries instances:
Extract features from Molecule data:
Extract features from a selection of Audio instances:
Extract features from a dataset that contains missing values:
Options (2)
FeatureNames (1)
Use FeatureNames to name features, and refer to their names in part specifications:
FeatureTypes (1)
Extract features with the "IndicatorVector" method on a simple dataset:
The first feature has been interpreted as numerical, and since the "IndicatorVector" method only acts on nominal features, the first feature is unchanged.
Use FeatureTypes to enforce the interpretation of the first feature as nominal:
Applications (1)
Dataset Visualization (1)
Construct a dataset of dog images:
Extract features from this dataset:
Reduce the dimension of the extracted vectors to 2:
Visualize the images at their feature positions:
A similar visualization can be directly obtained using FeatureSpacePlot:
Properties & Relations (2)
Extract features with no training examples is the equivalent of FeatureExtraction[None,...]:
FeatureExtract[…] is equivalent to FeatureExtraction[…,"ExtractedFeatures"]:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2016 (11.0) | Updated in 2017 (11.2) ▪ 2020 (12.1) ▪ 2020 (12.2) ▪ 2021 (12.3) ▪ 2025 (14.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), FeatureExtract, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FeatureExtract.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "FeatureExtract." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FeatureExtract.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). FeatureExtract. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FeatureExtract.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_featureextract, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FeatureExtract}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FeatureExtract.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_featureextract, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FeatureExtract}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FeatureExtract.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}