DimensionReduce[{example1,example2,…}]
projects the examples examplei to a lower-dimensional approximating manifold.
DimensionReduce[examples,n]
projects onto an approximating manifold in n-dimensional space.


DimensionReduce
DimensionReduce[{example1,example2,…}]
projects the examples examplei to a lower-dimensional approximating manifold.
DimensionReduce[examples,n]
projects onto an approximating manifold in n-dimensional space.
Details and Options



- DimensionReduce can be used on many types of data, including numerical, textual, sounds, and images, as well as combinations of these.
- Each examplei can be a single data element, a list of data elements, an association of data elements, or a Dataset object.
- DimensionReduce[examples] automatically chooses an appropriate dimension for the approximating manifold.
- DimensionReduce[examples] is equivalent to DimensionReduce[examples,Automatic].
- The following options can be given:
-
FeatureExtractor Identity how to extract features from which to learn FeatureNames Automatic names to assign to elements of the examplei FeatureTypes Automatic feature types to assume for elements of the examplei Method Automatic which reduction algorithm to use PerformanceGoal Automatic aspect of performance to optimize RandomSeeding 1234 what seeding of pseudorandom generators should be done internally TargetDevice "CPU" the target device on which to perform training - Possible settings for PerformanceGoal include:
-
"Quality" maximize reduction quality "Speed" maximize reduction speed - Possible settings for Method include:
-
Automatic automatically chosen method "Autoencoder" use a trainable autoencoder "Hadamard" project data using a Hadamard matrix "Isomap" isometric mapping "LatentSemanticAnalysis" latent semantic analysis method "Linear" automatically choose the best linear method "LLE" locally linear embedding "MultidimensionalScaling" metric multidimensional scaling "PrincipalComponentsAnalysis" principal components analysis method "TSNE" 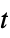 -distributed stochastic neighbor embedding algorithm
-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding algorithm"UMAP" uniform manifold approximation and projection - For Method"TSNE", the following suboptions are supported:
-
"Perplexity" Automatic perplexity value to be used "LinearPrereduction" False whether to perform a light linear pre-reduction before running the t-SNE algorithm - Possible settings for RandomSeeding include:
-
Automatic automatically reseed every time the function is called Inherited use externally seeded random numbers seed use an explicit integer or strings as a seed - DimensionReduce[…,FeatureExtractor"Minimal"] indicates that the internal preprocessing should be as simple as possible.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (6)
Create and visualize random 3D vectors:
Visualize this dataset reduced to two dimensions:
Reduce the dimension of a dataset of images:
Reduce the dimension of textual data:
Reduce the dimension of a list of DateObject:
Options (6)
FeatureExtractor (1)
FeatureTypes (1)
Reduce the dimension of a simple dataset:
The first feature has been interpreted as numerical. Use FeatureTypes to enforce the interpretation of the first feature as nominal:
Method (2)
PerformanceGoal (1)
Reduce the dimension of the images data with the setting PerformanceGoal"Quality" and measure the training time:
Perform the same operation using PerformanceGoal"Speed":
TargetDevice (1)
Reduce the dimension of vectors using a fully connected "AutoEncoder" on the system's default GPU and look at its AbsoluteTiming:
Compare the previous timing with the one obtained by using the default CPU computation:
Applications (1)
Dataset Visualization (1)
Load the Fisher iris dataset from ExampleData:
Reduce the dimension of the features:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2015), DimensionReduce, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DimensionReduce.html (updated 2018).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2015. "DimensionReduce." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2018. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DimensionReduce.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2015). DimensionReduce. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DimensionReduce.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_dimensionreduce, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DimensionReduce}", year="2018", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DimensionReduce.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_dimensionreduce, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DimensionReduce}, year={2018}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DimensionReduce.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}