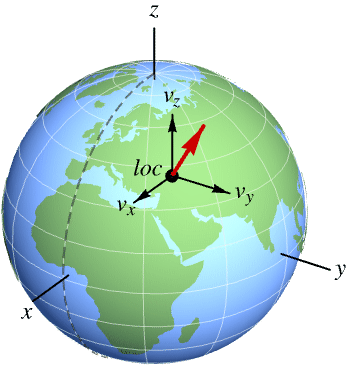
GeoVectorXYZ[loc{vX,vY,vZ}]
represents a three-dimensional vector of Cartesian components vX, vY, vZ in an orthonormal frame parallel to the geocentric frame, at location loc.
GeoVectorXYZ[{loc1,loc2,…}{vec1,vec2,…}]
represents a collection of vectors veci at respective geo locations loci.
GeoVectorXYZ[{loc1vec1,loc2vec2,…}]
represents the same collection of vectors.
GeoVectorXYZ[vec]
represents a geo vector whose associated location has been implicitly specified.


GeoVectorXYZ
GeoVectorXYZ[loc{vX,vY,vZ}]
represents a three-dimensional vector of Cartesian components vX, vY, vZ in an orthonormal frame parallel to the geocentric frame, at location loc.
GeoVectorXYZ[{loc1,loc2,…}{vec1,vec2,…}]
represents a collection of vectors veci at respective geo locations loci.
GeoVectorXYZ[{loc1vec1,loc2vec2,…}]
represents the same collection of vectors.
GeoVectorXYZ[vec]
represents a geo vector whose associated location has been implicitly specified.
Details


- GeoVectorXYZ[…] can represent any vectorial magnitude on the surface of the Earth or any other celestial globe, like wind speed, magnetic field, scalar gradients, etc.
- GeoVectorXYZ describes data using an orthonormal frame of fixed orientation with respect to the ambient 3D space, but origin at the given location.
- GeoVectorXYZ acts both as a vector data container and as a converter from other types of geo vector data, like GeoVector or GeoGridVector.
- In GeoVectorXYZ[locvec], the components of the vector vec can be quantities, but their units must be compatible.
- In GeoVectorXYZ[locvec], the location loc can be given as a {lat,lon} pair in degrees, a geo Entity object or any geo location object with head GeoPosition or similar.
- GeoVectorXYZ[…][prop] gives the specified property of a geo vector.
- Possible properties include:
-
"Count" number of vectors in the GeoVectorXYZ object "Data" first argument of the GeoVectorXYZ object "Depth" vector depth: 0 for a single vector, 1 for a list of them, … "Location" location data of the GeoVectorXYZ object "LocationDimension" number of coordinates for each position "LocationPackingType" Integer or Real if positions are packed; None otherwise "Vector" vector data of the GeoVectorXYZ object "VectorDimension" number of components for each vector "VectorPackingType" Integer or Real if vectors are packed; None otherwise
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Construct two north-pointing vectors at different locations:
Their GeoVectorXYZ forms have different components, due to their different orientations in 3D space:
This is the angle in degrees formed by those two vectors in 3D space:
Take 50 random locations in the world:
Compute the magnetic field at those locations and convert it into GeoVectorXYZ form:
Extract the 3D coordinates of the locations and the 3D components of the vectors, in numeric form:
Scope (7)
Data Specification (4)
Specify the location of a geo vector as a {lat,lon} pair in degrees:
Construct a 3D velocity vector with three identical components at Chicago:
Rewrite the location as a geo position object with any head:
Anything that can be interpreted by GeoPosition can be used as a location:
Geo Vector Arrays (2)
Specify gravitational field data simultaneously for several locations:
Rewrite as a single geo vector array with XYZ components:
Represent the very small horizontal components in a map:
Generate a million random 3D Cartesian vectors at respective random locations:
Use GeoVectorXYZ to transform them back to their 3D Cartesian form:
Properties & Relations (3)
Convert a GeoVectorXYZ expression into other types of geo vectors:
Convert back to GeoVectorXYZ form:
Converting a geo vector into GeoVectorXYZ form does not convert its location into GeoPositionXYZ form:
Use GeoPositionXYZ explicitly to convert the location:
GeoPositionXYZ[{x,y,z}] represents a positional vector from the center of the Earth, in meters:
You can have a tangent vector with the same components at the same location:
Transforming to ENU geo vector form shows that the vector is almost vertical, except for a south component due to the oblateness of the Earth:
Those components can also be computed (modulo sign) using GeoPositionENU:
Related Guides
-
▪
- Geodesy
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2019), GeoVectorXYZ, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoVectorXYZ.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2019. "GeoVectorXYZ." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoVectorXYZ.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2019). GeoVectorXYZ. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoVectorXYZ.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_geovectorxyz, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GeoVectorXYZ}", year="2019", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoVectorXYZ.html}", note=[Accessed: 23-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_geovectorxyz, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GeoVectorXYZ}, year={2019}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoVectorXYZ.html}, note=[Accessed: 23-February-2026]}