InverseErf
InverseErf[s]
gives the inverse error function obtained as the solution for z in ![]() .
.
Details

- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- Explicit numerical values are given only for real values of s between
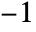 and
and 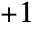 .
. - InverseErf[z0,s] gives the inverse of the generalized error function Erf[z0,z].
- For certain special arguments, InverseErf automatically evaluates to exact values.
- InverseErf can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- InverseErf can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
- InverseErf automatically threads over lists.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (32)
Numerical Evaluation (5)
Evaluate numerically to high precision:
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate InverseErf efficiently at high precision:
Evaluate numerically the inverse of the generalized error function:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix InverseErf function using MatrixFunction:
Visualization (3)
Plot the InverseErf function:
Plot the inverse of the generalized error function for different values of ![]() :
:
Plot the inverse of the generalized error function for different values of ![]() :
:
Function Properties (9)
InverseErf is defined for all real values from the interval (![]() ):
):
InverseErf takes all real values:
InverseErf is an odd function:
InverseErf is an analytic function on its domain:
It is not analytic in general, as it has both singularities and discontinuities:
InverseErf is nondecreasing on its domain:
InverseErf is injective:
InverseErf is surjective:
InverseErf is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
InverseErf is neither convex nor concave on its domain:
Integration (3)
Indefinite integral of InverseErf:
Definite integral of InverseErf over its real domain:
Numerical approximation of the definite integral of InverseErf:
Series Expansions (2)
Taylor expansion for InverseErf:
Plot the first three approximations for InverseErf around ![]() :
:
Series expansion of the inverse of the generalized error function:
Function Identities and Simplifications (2)
Function Representations (4)
Primary definition of the inverse error function:
Relation to the inverse of the generalized error function:
Relation to the inverse complementary error function:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Applications (3)
Generate Gaussian-distributed random numbers:
The number of standard deviations for a 99% confidence interval in the Gaussian distribution:
Plot InverseErf:
Properties & Relations (5)
Solve a transcendental equation:
Numerically find a root of a transcendental equation:
Obtain InverseErf as the solution of a differential equation:
InverseErf is a numeric function:
In TraditionalForm, ![]() is automatically interpreted as an inverse error function:
is automatically interpreted as an inverse error function:
Possible Issues (1)
InverseErf evaluates numerically only for ![]() :
:
Neat Examples (1)
Riemann surface of InverseErf:
Text
Wolfram Research (1996), InverseErf, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseErf.html (updated 2023).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1996. "InverseErf." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2023. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseErf.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1996). InverseErf. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseErf.html