InverseHankelTransform[expr,s,r]
gives the inverse Hankel transform of order 0 for expr.
InverseHankelTransform[expr,s,r,ν]
gives the inverse Hankel transform of order ν for expr.


InverseHankelTransform
InverseHankelTransform[expr,s,r]
gives the inverse Hankel transform of order 0 for expr.
InverseHankelTransform[expr,s,r,ν]
gives the inverse Hankel transform of order ν for expr.
Details and Options
- The inverse Hankel transform of order ν for a function
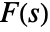 is defined to be
is defined to be ![int_0^inftys F(s) TemplateBox[{v, {s, , r}}, BesselJ]ds int_0^inftys F(s) TemplateBox[{v, {s, , r}}, BesselJ]ds](Files/InverseHankelTransform.en/2.png) .
. - The inverse Hankel transform is defined for
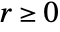 and
and 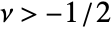 .
. - The following options can be given:
-
Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions on parameters GenerateConditions False whether to generate results that involve conditions on parameters Method Automatic what method to use - In TraditionalForm, InverseHankelTransform is output using
![TemplateBox[{{F, (, s, )}, s, r, nu}, InverseHankelTransform] TemplateBox[{{F, (, s, )}, s, r, nu}, InverseHankelTransform]](Files/InverseHankelTransform.en/5.png) .
.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (16)
Basic Uses (5)
Compute the inverse Hankel transform of order ν for a function:
Use the default value 0 for the parameter ν:
Compute the inverse Hankel transform of a function for a symbolic parameter r:
Obtain the conditions for the convergence:
Display in TraditionalForm:
Elementary Functions (4)
Special Functions (5)
Options (2)
Applications (3)
The inverse Fourier transform of a radially symmetric function in the plane can be expressed as an inverse Hankel transform. Verify this relation for the function defined by:
Compute its inverse Fourier transform:
Obtain the same result using InverseHankelTransform:
Plot the inverse Fourier transform:
Generate a gallery of inverse Fourier transforms for a list of radially symmetric functions:
Compute the inverse Hankel transforms for these functions:
Generate the gallery of inverse Fourier transforms as required:
Obtain a particular solution for an inhomogeneous equation involving the radial Laplacian:
Apply HankelTransform to the equation:
Solve for the Hankel transform:
Apply InverseHankelTransform to obtain a particular solution:
Properties & Relations (7)
Use Asymptotic to compute an asymptotic approximation:
InverseHankelTransform computes the integral ![]() :
:
InverseHankelTransform is the inverse of HankelTransform:
InverseHankelTransform is its own inverse:
InverseHankelTransform is a linear operator:
InverseHankelTransform of derivatives:
Derivative of an inverse Hankel transform with respect to r:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), InverseHankelTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHankelTransform.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "InverseHankelTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHankelTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). InverseHankelTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHankelTransform.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_inversehankeltransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{InverseHankelTransform}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHankelTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_inversehankeltransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={InverseHankelTransform}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHankelTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}