InverseHilbertTransform[F[t],t,s]
gives the symbolic inverse Hilbert transform of F[t] in the variable t as f[s] in the variable s.
InverseHilbertTransform[F[t],t,![]() ]
]
gives the numeric inverse Hilbert transform at the numerical value ![]() .
.




InverseHilbertTransform
InverseHilbertTransform[F[t],t,s]
gives the symbolic inverse Hilbert transform of F[t] in the variable t as f[s] in the variable s.
InverseHilbertTransform[F[t],t,![]() ]
]
gives the numeric inverse Hilbert transform at the numerical value ![]() .
.
Details and Options

- Hilbert transforms are used to solve problems in signal processing, communications and other fields.
- The inverse Hilbert transform of a function
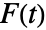 is defined to be principal value integral
is defined to be principal value integral 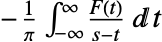 .
. - InverseHilbertTransform shifts every frequency component of a function by a phase of
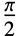 radians.
radians. -
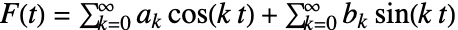
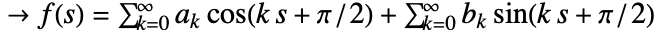
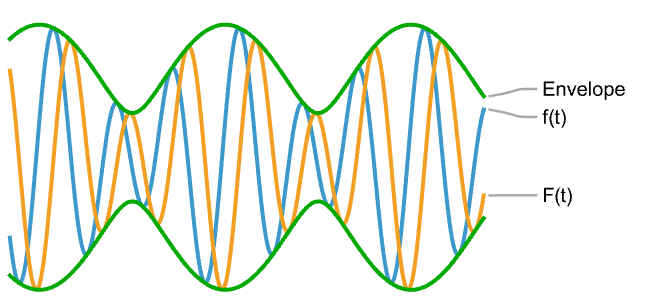
- The conjugate function
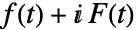 is the analytic representation of
is the analytic representation of 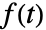 and its magnitude is the Envelope:
and its magnitude is the Envelope: - InverseHilbertTransform is a singular integral transform. Moreover, it is a bounded operator on
![L^p(TemplateBox[{}, Reals]) L^p(TemplateBox[{}, Reals])](Files/InverseHilbertTransform.en/11.png) for
for 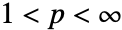 .
. - The integral is computed using numerical methods if the third argument,
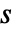 , is given a numerical value.
, is given a numerical value. - The following options can be given:
-
AccuracyGoal Automatic digits of absolute accuracy sought Assumptions $Assumptions assumptions to make about parameters GenerateConditions Automatic whether to generate answers that involve conditions on parameters Method Automatic method to use PrecisionGoal Automatic digits of precision sought WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision used in internal computations
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (30)
Basic Uses (4)
Inverse Hilbert transform of a function for a symbolic parameter ![]() :
:
Inverse Hilbert transforms of simple trigonometric functions:
Evaluate the inverse Hilbert transform for a numerical value of the parameter ![]() :
:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Elementary Functions (5)
Trigonometric Functions (5)
Powers and Algebraic Functions (5)
Generalized Functions (2)
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions (5)
Options (5)
AccuracyGoal (1)
The option AccuracyGoal sets the number of digits of accuracy:
Assumptions (1)
Specify the range of a variable using Assumptions:
GenerateConditions (1)
Use GenerateConditionsTrue to get parameter conditions for when a result is valid:
PrecisionGoal (1)
The option PrecisionGoal sets the relative tolerance in the integration:
WorkingPrecision (1)
If WorkingPrecision is specified, the computation is done at that working precision:
Applications (3)
Basic Applications (1)
Signals and Systems (2)
The inverse Hilbert filter is defined below. It preserves the magnitude of the signal and phase shifts by ![]() for positive frequencies and
for positive frequencies and ![]() for negative frequencies:
for negative frequencies:
The impulse response is the inverse Fourier transform of ![]() :
:
In signal processing, the inverse Hilbert transform provides the real component of the analytic representation of a real-valued signal ![]() .
.
The inverse Hilbert transform of ![]() is:
is:
Properties & Relations (7)
For ![]() , the definite integral for InverseHilbertTransform becomes:
, the definite integral for InverseHilbertTransform becomes:
Compare with InverseHilbertTransform:
Inverse Hilbert transform of an inverse Hilbert transform:
InverseHilbertTransform and HilbertTransform are mutual inverses:
Interactive Examples (2)
InverseHilbertTransform applies a ![]() -degree phase shift:
-degree phase shift:
For a complex signal with negative frequency:
InverseHilbertTransform applies a ![]() -degree phase shift:
-degree phase shift:
Both are parametrizations of the unit circle traversing in the same direction but with a phase shift:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), InverseHilbertTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHilbertTransform.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "InverseHilbertTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHilbertTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). InverseHilbertTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHilbertTransform.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_inversehilberttransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{InverseHilbertTransform}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHilbertTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_inversehilberttransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={InverseHilbertTransform}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/InverseHilbertTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}