represents a trainable net layer that normalizes its input data across the second and subsequent dimensions and applies an independent scaling and bias to each component of the first dimension.
NormalizationLayer[aggregationlevels]
normalizes data across the specified aggregation levels and applies a learned scaling and bias on the remaining levels.
NormalizationLayer[aggregationlevels,scalinglevels]
applies a learned scaling and bias at the specified scaling levels.


NormalizationLayer
represents a trainable net layer that normalizes its input data across the second and subsequent dimensions and applies an independent scaling and bias to each component of the first dimension.
NormalizationLayer[aggregationlevels]
normalizes data across the specified aggregation levels and applies a learned scaling and bias on the remaining levels.
NormalizationLayer[aggregationlevels,scalinglevels]
applies a learned scaling and bias at the specified scaling levels.
Details and Options




- NormalizationLayer is used to perform data normalization, followed by a learnable affine transformation.
- The aggregationlevels determine which levels of the input are aggregated over to compute the mean and variance statistics, while the scalinglevels determine which levels of the input have componentwise specific scaling values and biases applied to them.
- Possible values of aggregationlevels are:
-
a aggregate level a only a1;;a2 aggregate levels a1 through a2 {a1,…} aggregate levels ai - The default aggregation levels are 2;;All.
- Possible values of scalinglevels are:
-
"Complement" all levels except the aggregation levels (default) "Same" the same levels as the aggregation levels s level s only s1;;s2 levels s1 through s2 {s1,…} levels si - The following optional parameters can be included:
-
"Epsilon" 0.001 stability parameter "GroupNumber" None whether to split the data into groups LearningRateMultipliers Automatic learning rate multipliers for the scaling and/or bias parameters "Unbiased" False whether to normalize the standard deviation by the length minus one (instead of the length) Method "Standardize" the normalization method to use - Possible settings for Method include:
-
"RMS" use the root mean square xi/ 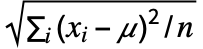
"Standardize" use Standardize (xi-μ)/ 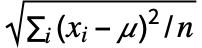
- With aggregation levels {a1,…,an}, by setting "GroupNumber"{g1,…,gn}, the aj level is split into gj groups, which are normalized independently. The dimension of the level aj must be an integer multiple of gj.
- The following learnable parameters can be specified:
-
"Biases" Automatic learnable bias parameters "Scaling" Automatic learnable scaling parameters - With Automatic settings, scaling and bias parameters are initialized automatically when NetInitialize or NetTrain is used. With None settings, scaling and adding biases can be disabled.
- If scaling and bias parameters have been initialized or disabled, NormalizationLayer[…][input] explicitly computes the output from applying the layer.
- NormalizationLayer[…][input] explicitly computes the output from applying the layer to input.
- NormalizationLayer[…][{input1,input2,…}] explicitly computes outputs for each of the inputi.
- When it cannot be inferred from other layers in a larger net, the option "Input"->{d1,d2,…} can be used to fix the input dimensions of NormalizationLayer.
- NetExtract can be used to extract the scaling, biases and epsilon parameters from a NormalizationLayer object.
- NormalizationLayer is typically used inside NetChain, NetGraph, etc.
- NormalizationLayer exposes the following ports for use in NetGraph etc.:
-
"Input" an array of rank greater than 1 "Output" an array of rank greater than 1 - Consider an input array
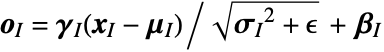 that can be decomposed into da×db×… subarrays xA across the aggregation levels {a,b,…} and into di×dj×… subarrays xI across the scaling levels {i,j,…}. The scaling and biases parameters
that can be decomposed into da×db×… subarrays xA across the aggregation levels {a,b,…} and into di×dj×… subarrays xI across the scaling levels {i,j,…}. The scaling and biases parameters 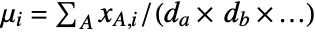 and
and 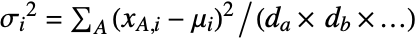 have dimensions (di×dj×…).
have dimensions (di×dj×…). - The output of the "Standardize" method is obtained via
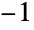 , where the mean array is given by
, where the mean array is given by 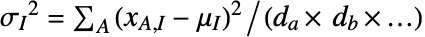 and the variance by
and the variance by 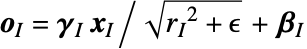 .
. - The output of the "RMS" method is obtained via
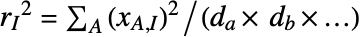 , where the RMS array is given by
, where the RMS array is given by 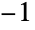 .
. - The output always has the same dimensions as the input.
- The default NormalizationLayer[] corresponds to instance normalization in Ulyanov et al., "Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization", 2016, with the channel dimension at the first level and spatial dimensions at subsequent levels.
- Method"RMS" can be use to recreate the RMSNorm described in Zhang et al., "Root Mean Square Layer Normalization", 2019. »
- NormalizationLayer[2;;All,"Same","Input"{n,Automatic}] corresponds to layer normalization in Ba et al., "Layer Normalization", 2016, with the channel dimension at the last level and the time dimension at the first level.
- NormalizationLayer[All,1,"GroupNumber"{n,1,1,…},"Input"{m*n,…}] corresponds to group normalization Wu et al., "Group Normalization", 2018, with the channel dimension at the first level and spatial dimensions at subsequent levels.
- Options[NormalizationLayer] gives the list of default options to construct the layer. Options[NormalizationLayer[…]] gives the list of default options to evaluate the layer on some data.
- Information[NormalizationLayer[…]] gives a report about the layer.
- Information[NormalizationLayer[…],prop] gives the value of the property prop of NormalizationLayer[…]. Possible properties are the same as for NetGraph.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Create a NormalizationLayer:
Create an initialized NormalizationLayer that takes a rank-3 array:
Scope (3)
Create an instance normalization layer that takes an RGB image and returns an RGB image:
NormalizationLayer automatically threads over batches of inputs:
Create a NormalizationLayer that takes a sequence of two-dimensional vectors and returns the sequence of normalized vectors scaled by a factor of 2 and shifted by ![]() :
:
Apply layer normalization to some sinusoidal input:
Visualize the values before and after normalization:
Create an initialized NormalizationLayer that takes a rank-6 array and normalize across all dimensions:
Options (9)
"Biases" (2)
Create a NormalizationLayer with the biases explicitly specified:
Create a NormalizationLayer without any bias:
"Epsilon" (1)
Create a NormalizationLayer with the "Epsilon" parameter explicitly specified:
"GroupNumber" (2)
NormalizationLayer computes the variance and mean across the entire aggregation level:
Specify that the aggregation level has to be split in two groups:
Each group is normalized independently:
This is equivalent to reshaping the input before the normalization:
In combination with applying the normalization one level deeper:
Create a NormalizationLayer without any scaling:
"Scaling" (2)
Create a NormalizationLayer with the scaling parameter explicitly specified:
Extract the scaling parameters:
Create a NormalizationLayer without any scaling:
"Unbiased" (1)
The default variance estimator is typically biased in neural net applications:
Define a NormalizationLayer with an unbiased variance estimator:
The variance computation is now equivalent to Variance:
Properties & Relations (1)
NormalizationLayer is, in general, not the same as Standardize:
Initialize the layer with unit "Scaling" and zero "Biases":
The stability parameter and the biased variance estimator introduce a difference:
Define a NormalizationLayer without regularization:
The result is closer to Standardize:
Possible Issues (1)
NormalizationLayer cannot be initialized until all its input and output dimensions are known:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2019), NormalizationLayer, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NormalizationLayer.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2019. "NormalizationLayer." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NormalizationLayer.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2019). NormalizationLayer. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NormalizationLayer.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_normalizationlayer, author="Wolfram Research", title="{NormalizationLayer}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NormalizationLayer.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_normalizationlayer, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={NormalizationLayer}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/NormalizationLayer.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}