WOLFRAM SYSTEM MODELER
CytosolCytosolic compartment |
|
Diagram
Wolfram Language
SystemModel["BioChem.Examples.CentralMetabolism.Cytosol"]
Information
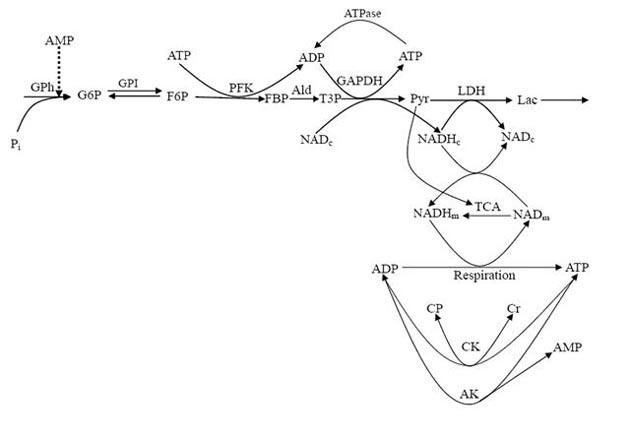
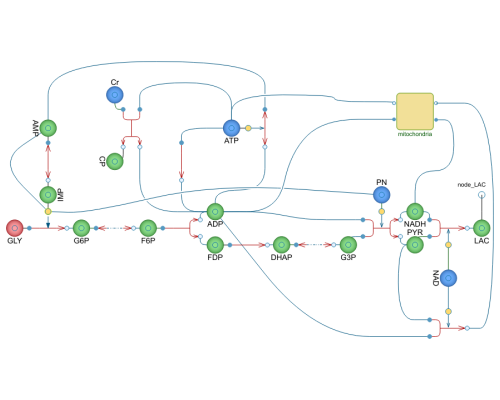
Fig 1. Scheme of glycolysis and coupled processes simulated in the model: consumption and synthesis of ATP and transformation of reducing equivalents of NADH. The relevant equations, which account for stoichiometry of the ATP production, are given in supplementary materials. One molecule of ATP is consumed per molecule of fructose 6-phosphate in the phosphofructokinase reaction; two molecules of ATP per molecule of triose phospate (four molecules per hexose molecule) are then produced on the way to pyruvate; 2.5 molecules of ATP are produced when one molecule of NADH is oxidized. Cytosolic NADH is produced in the reaction of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and consumed when pyruvate is transformed to lactate. In mitochondria one molecule of NADH is produced in the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction and then three NADH molecules and one FADH2 molecule in the tricarboxylate cycle. Abbreviations: AK, adenylate kinase (EC 2.7.4.3); CK, creatine kinase (EC 2.7.3.2); CP, phosphocreatine; Cr, creatine; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.12); GPh, glycogen phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.1); Lac, lactate; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.27); PFK, phosphofructokinase (EC 2.7.1.11); GPI, glucose phosphate isomerase (EC 5.3.1.9.); Pyr, pyruvate. Subscripts: m, mitochondrial; c, cytosolic.
See also
The extra_cellular model for further documentation of the system and simulation results.Parameters (3)
| mainCompartment |
Value: false Type: Boolean Description: Specifies whether the compartment is a main (top-level) compartment. Used in SBML import/export. |
|---|---|
| kh |
Value: Type: Real |
| kt |
Value: Type: Real |
Inputs (6)
| bamp |
Type: Real |
|---|---|
| badp |
Type: Real |
| pn |
Type: Real |
| atp |
Type: Real |
| cr |
Type: Real |
| nad |
Type: Real |
Connectors (1)
| node_LAC |
Type: SubstanceConnector Description: Connector between substances and reactions |
|---|
Components (30)
| NADH |
Type: NADH_ Description: NADH |
|
|---|---|---|
| FDP |
Type: FDP_ Description: Fructose 1,6-diphosphate |
|
| PYR |
Type: PYR_ Description: Pyruvate |
|
| ADP |
Type: ADP_ Description: ADP |
|
| IMP |
Type: IMP_ Description: IMP |
|
| ATP |
Type: ATP_ Description: ATP |
|
| AMP |
Type: AMP_ Description: AMP |
|
| LAC |
Type: LAC_ Description: Lactate |
|
| NAD |
Type: NAD_ Description: NAD |
|
| CP |
Type: CP_ Description: Phosphocreatine |
|
| Cr |
Type: Cr_ Description: Creatine |
|
| GLY |
Type: GLY_ Description: Glycogen |
|
| PN |
Type: PN_ Description: Inorganic phosphate |
|
| G6P |
Type: G6P_ Description: Glucose 6-phosphate |
|
| F6P |
Type: F6P_ Description: Fructose 6-phosphate |
|
| jda |
Type: jda_ Description: jda |
|
| vpfk |
Type: vpfk_ Description: vpfk |
|
| vldh |
Type: vldh_ Description: vldh |
|
| vpdh |
Type: vpdh_ Description: vpdh |
|
| jak |
Type: jak_ Description: jak |
|
| vgph |
Type: vgph_ Description: vgph |
|
| jatpase |
Type: jatpase_ Description: jatpase |
|
| jck |
Type: jck_ Description: jck |
|
| mitochondria |
Type: Mitochondria Description: Mitochondria compartment |
|
| vH6P |
Type: Uuf Description: Fast equilibrium reaction for the compound of G6P and F6P |
|
| vald |
Type: vald_ Description: vald |
|
| DHAP |
Type: DHAP_ |
|
| G3P |
Type: G3P_ |
|
| vgpdh_1 |
Type: vgpdh_ |
|
| vT3P |
Type: Uuf Description: Fast equilibrium reaction for the compound of G6P and F6P |
Used in Examples (1)
|
BioChem.Examples.CentralMetabolism Main model of the example |