yields the core-nilpotent decomposition of a square matrix m.
CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,format]
returns the core-nilpotent decomposition according to the specified format.


CoreNilpotentDecomposition
yields the core-nilpotent decomposition of a square matrix m.
CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,format]
returns the core-nilpotent decomposition according to the specified format.
Details and Options

- CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m] returns a list of matrices {t,c,n} where the core matrix c is nonsingular and the matrix n is nilpotent. »
- The matrix m is related to its core-nilpotent decomposition by
![m=t.(c 0; 0 n).TemplateBox[{t}, Inverse] m=t.(c 0; 0 n).TemplateBox[{t}, Inverse]](Files/CoreNilpotentDecomposition.en/1.png) .
. - For the nilpotent matrix n, there exists a non-negative integer
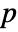 (the index of the matrix m) such that MatrixPower[n,p] is the zero matrix.
(the index of the matrix m) such that MatrixPower[n,p] is the zero matrix. - The core-nilpotent decomposition of a matrix can be used for solving systems of linear differential-algebraic (or difference-algebraic) equations with constant coefficients.
- If either the core or nilpotent parts are trivial, an empty list {} is returned for the trivial part. »
- CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m] is equivalent to CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,"SplitBlocks"].
- CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,"BlockDiagonal"] returns a list of matrices {t,d} where
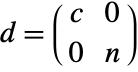 .
. - With the setting TargetStructure->"Dense", CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,"BlockDiagonal"] returns a list of matrices {t,d} where
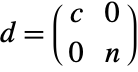 .
. - With the setting TargetStructure->"Structured", the matrix
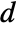 in the list {t,d} is represented as a BlockDiagonalMatrix.
in the list {t,d} is represented as a BlockDiagonalMatrix.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (12)
Basic Uses (7)
Core-nilpotent decomposition of a machine-precision matrix:
Core-nilpotent decomposition of a complex matrix:
Core-nilpotent decomposition of an exact matrix:
Core-nilpotent decomposition of an arbitrary-precision matrix:
Core-nilpotent decomposition of a symbolic matrix:
The decomposition of large machine-precision matrices is efficient:
CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m] is equivalent to CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,"SplitBlocks"], where the core and nilpotent parts are kept separate:
CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,"BlockDiagonal"] brings the core and nilpotent parts together in a block diagonal matrix:
Special Matrices (5)
Options (1)
TargetStructure (1)
With TargetStructure->"Dense", CoreNilpotentDecomposition[m,"BlockDiagonal"] returns a list of two matrices:
The second matrix is a block diagonal matrix consisting of the core and nilpotent parts:
With TargetStructure->"Structured", the second matrix is represented as a BlockDiagonalMatrix:
Applications (2)
Solve the matrix differential equation ![]() ,
, ![]() with singular coefficients:
with singular coefficients:
Both ![]() and
and ![]() are singular, so the equation cannot be put in the standard form
are singular, so the equation cannot be put in the standard form ![]() :
:
Compute the core-nilpotent decomposition of the solution to ![]() :
:
The solution is then ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the solution to
is the solution to ![]() :
:
Compare with the result given by DSolveValue:
Find the general solution of the matrix difference equation ![]() with singular coefficient matrix
with singular coefficient matrix ![]() :
:
Using the core-nilpotent decomposition ![]() , let
, let ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (4)
CoreNilpotentDecomposition returns a triple {t,c,n}:
The original matrix m can be expressed in terms of its core-nilpotent decomposition:
The core part of the decomposition for an invertible matrix is equal to the matrix:
The nilpotent part of the decomposition is an empty list:
The similarity matrix t is taken to be the identity matrix:
The identity expressed using BlockDiagonalMatrix holds nonetheless:
The nilpotent part of the decomposition for a nilpotent matrix is equal to the matrix:
The core part of the decomposition is an empty list:
The similarity matrix t is taken to be the identity matrix:
The identity expressed using BlockDiagonalMatrix holds nonetheless:
DrazinInverse can be computed with CoreNilpotentDecomposition:
Possible Issues (2)
The core-nilpotent decomposition is not unique:
Either ![]() or
or ![]() , but not both, can be equal to {}:
, but not both, can be equal to {}:
Use BlockDiagonalMatrix to reconstruct the original matrix, since it interprets {} as a 0×0 matrix:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), CoreNilpotentDecomposition, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CoreNilpotentDecomposition.html (updated 2023).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "CoreNilpotentDecomposition." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2023. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CoreNilpotentDecomposition.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). CoreNilpotentDecomposition. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CoreNilpotentDecomposition.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_corenilpotentdecomposition, author="Wolfram Research", title="{CoreNilpotentDecomposition}", year="2023", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CoreNilpotentDecomposition.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_corenilpotentdecomposition, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={CoreNilpotentDecomposition}, year={2023}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CoreNilpotentDecomposition.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}