DeconvolutionLayer[n,sz]
represents a trainable deconvolutional net layer having n output channels and using kernels of size sz to compute the deconvolution.
DeconvolutionLayer[n,{s}]
represents a layer performing one-dimensional deconvolutions with kernels of size s.
DeconvolutionLayer[n,{h,w}]
represents a layer performing two-dimensional deconvolutions with kernels of size h×w.
DeconvolutionLayer[n,kernel,opts]
includes options for initial kernels and other parameters.


DeconvolutionLayer
DeconvolutionLayer[n,sz]
represents a trainable deconvolutional net layer having n output channels and using kernels of size sz to compute the deconvolution.
DeconvolutionLayer[n,{s}]
represents a layer performing one-dimensional deconvolutions with kernels of size s.
DeconvolutionLayer[n,{h,w}]
represents a layer performing two-dimensional deconvolutions with kernels of size h×w.
DeconvolutionLayer[n,kernel,opts]
includes options for initial kernels and other parameters.
Details and Options




- DeconvolutionLayer[…][input] explicitly computes the output from applying the layer to input.
- DeconvolutionLayer[…][{input1,input2,…}] explicitly computes outputs for each of the inputi.
- The following optional parameters can be included:
-
"Biases" Automatic initial vector of kernel biases "ChannelGroups" 1 number of channel groups "Dilation" 1 dilation factor Interleaving False the position of the channel dimension LearningRateMultipliers Automatic learning rate multipliers for kernel weights and/or biases PaddingSize 0 amount of padding to remove from the output "Stride" 1 convolution step size to use "Weights" Automatic initial matrix of kernel weights - The setting for PaddingSize can be of the following forms:
-
n crop every dimension by n elements on the beginning and end {n1,n2,…} crop the i 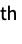 dimension by n elements on the beginning and end
dimension by n elements on the beginning and end{{n1,m1},{n2,m2},…} crop the i 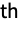 dimension by ni elements at the beginning and mi at the end
dimension by ni elements at the beginning and mi at the end"Same" crop every dimension so that the output size is equal to the input size multiplied by the stride - The settings for "Dilation" and "Stride" can be of the following forms:
-
n use the value n for all dimensions {…,ni,…} use the value ni for the i 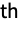 dimension
dimension - By setting "ChannelGroups"g, the m input channels and n output channels are split into g groups of m/g and n/g channels, respectively, where m and n are required to be divisible by g. Separate deconvolutions are performed connecting the i
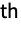 group of input channels with the i
group of input channels with the i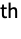 group of output channels, and results are concatenated in the output. Each input/output group pair is connected by n/g×m/g deconvolution, so setting "ChannelGroups"g effectively reduces the number of distinct deconvolutions from n×m to n×m/g.
group of output channels, and results are concatenated in the output. Each input/output group pair is connected by n/g×m/g deconvolution, so setting "ChannelGroups"g effectively reduces the number of distinct deconvolutions from n×m to n×m/g. - With Automatic settings, weights and biases are added automatically when NetInitialize or NetTrain is used.
- The setting "Biases"->None specifies that no biases should be used.
- With the setting InterleavingFalse, the channel dimension is taken to be the first dimension of the input and output arrays.
- With the setting InterleavingTrue, the channel dimension is taken to be the last dimension of the input and output arrays.
- If weights and biases have been added, DeconvolutionLayer[…][input] explicitly computes the output from applying the layer.
- DeconvolutionLayer[…][{input1,input2,…}] explicitly computes outputs for each of the inputi.
- When given a NumericArray as input, the output will be a NumericArray.
- NetExtract can be used to extract weights and biases from a DeconvolutionLayer object.
- DeconvolutionLayer is typically used inside NetChain, NetGraph, etc.
- DeconvolutionLayer exposes the following ports for use in NetGraph etc.:
-
"Input" a rank-3 array "Output" a rank-3 array - When it cannot be inferred from other layers in a larger net, the option "Input"->{d1,d2,d3} can be used to fix the input dimensions of DeconvolutionLayer.
- Given an input array of dimensions d1×d2×d3, the output array will be of dimensions
 ×
× ×
× , where the channel dimension
, where the channel dimension 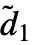 =n and the sizes d2 and d3 are transformed according to
=n and the sizes d2 and d3 are transformed according to 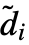 =s(di-1)+df(k-1)+1-pb-pe,where df is the dilation factor,
=s(di-1)+df(k-1)+1-pb-pe,where df is the dilation factor, 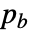 /
/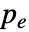 are the padding sizes at the beginning/end of the axis, k is the kernel size, and s is the stride size for each dimension.
are the padding sizes at the beginning/end of the axis, k is the kernel size, and s is the stride size for each dimension. - Options[DeconvolutionLayer] gives the list of default options to construct the layer. Options[DeconvolutionLayer[…]] gives the list of default options to evaluate the layer on some data.
- Information[DeconvolutionLayer[…]] gives a report about the layer.
- Information[DeconvolutionLayer[…],prop] gives the value of the property prop of DeconvolutionLayer[…]. Possible properties are the same as for NetGraph.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Create a DeconvolutionLayer with five output channels and a 2×2 kernel size:
Create a randomly initialized DeconvolutionLayer with the input dimensions specified:
Apply the layer to an input tensor to produce an output tensor:
Create a randomly initialized DeconvolutionLayer that takes in an image and produces an image:
Options (10)
Interleaving (1)
Create a DeconvolutionLayer with InterleavingFalse and one input channel:
Create a DeconvolutionLayer with InterleavingTrue and one input channel:
PaddingSize (4)
By default, no cropping is applied to the output:
Crop by a fixed amount using PaddingSizen:
Crop each dimension by a specific amount:
Use padding to make the output dimensions equivalent to the input dimensions:
This is equivalent to PaddingSize "Same":
In general, PaddingSize "Same" gives an output size equal to the input size multiplied by the stride:
"Dilation" (2)
A dilation factor of size n on a given dimension effectively applies the kernel to elements of the output arrays that are distance n apart.
Create a one-dimensional DeconvolutionLayer with a dilation factor of 2:
Create a random two-dimensional DeconvolutionLayer with a dilation factor of 5:
"Weights" (1)
"Biases" (1)
Create a randomly initialized DeconvolutionLayer without biases:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), DeconvolutionLayer, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DeconvolutionLayer.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "DeconvolutionLayer." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DeconvolutionLayer.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). DeconvolutionLayer. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DeconvolutionLayer.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_deconvolutionlayer, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DeconvolutionLayer}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DeconvolutionLayer.html}", note=[Accessed: 11-December-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_deconvolutionlayer, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DeconvolutionLayer}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DeconvolutionLayer.html}, note=[Accessed: 11-December-2025]}